A jitney in transportation is a small vehicle that operates on flexible routes and schedules, often serving short-distance trips within urban areas. These shared rides typically accommodate a few passengers and provide an affordable alternative to traditional public transit or taxis. Jitneys play a crucial role in enhancing mobility by filling gaps in transportation networks where demand is inconsistent or low. Data shows that jitneys contribute to reducing congestion by offering last-mile connectivity, especially in densely populated cities. Entities such as local transit authorities and private operators regulate jitney services to ensure safety and efficiency. The integration of jitneys with digital platforms and mobile apps has increased their accessibility, making them a vital component of modern urban transportation systems.
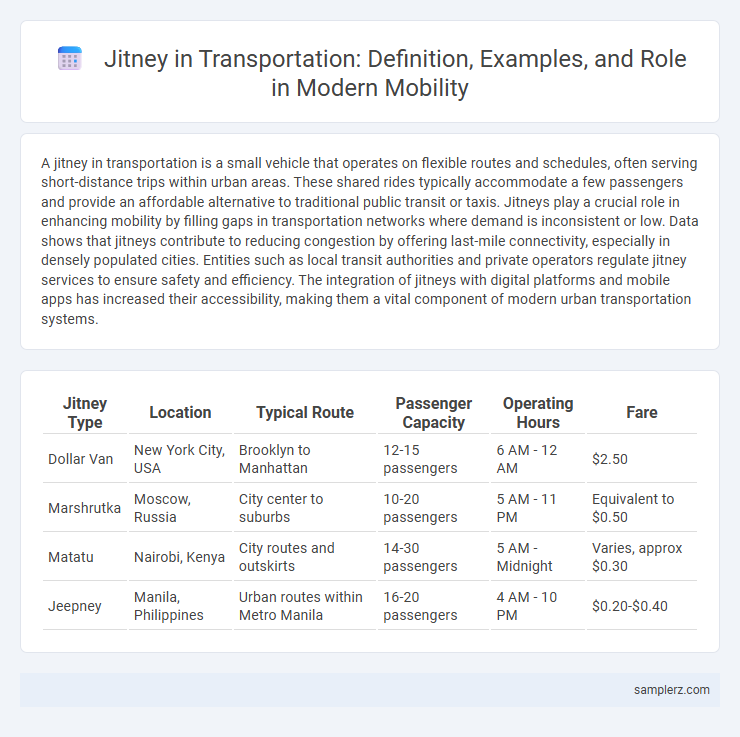
Table of Comparison
| Jitney Type | Location | Typical Route | Passenger Capacity | Operating Hours | Fare |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dollar Van | New York City, USA | Brooklyn to Manhattan | 12-15 passengers | 6 AM - 12 AM | $2.50 |
| Marshrutka | Moscow, Russia | City center to suburbs | 10-20 passengers | 5 AM - 11 PM | Equivalent to $0.50 |
| Matatu | Nairobi, Kenya | City routes and outskirts | 14-30 passengers | 5 AM - Midnight | Varies, approx $0.30 |
| Jeepney | Manila, Philippines | Urban routes within Metro Manila | 16-20 passengers | 4 AM - 10 PM | $0.20-$0.40 |
Definition and Origin of Jitney in Transportation
A jitney is a small, shared vehicle that operates on flexible routes and schedules, typically providing affordable, short-distance transportation in urban areas. The term originated in the early 20th century United States, where drivers charged a nickel, or "jitney," for rides along fixed or semi-fixed routes. Jitneys emerged as an informal transit solution to complement or compete with established public transportation systems.
Characteristics of Jitney Services
Jitney services are characterized by flexible routes and on-demand pickups, typically operating smaller vehicles than standard buses. They provide affordable, short-distance transportation options, often filling gaps in public transit networks. These services prioritize frequent stops and low fares, catering to urban commuters seeking convenience and efficiency.
Historical Evolution of Jitneys Worldwide
Jitneys emerged in the early 20th century as flexible, low-cost public transport options, first appearing in North American cities around 1914. These informal shared taxis quickly spread to urban areas worldwide, adapting to local transportation needs by offering door-to-door service along fixed or semi-fixed routes. Over time, jitneys evolved with regulatory challenges and technological advancements, maintaining their role as essential players in urban mobility ecosystems across diverse regions.
Jitney Operations in Urban Mobility
Jitney operations in urban mobility involve small, flexible shuttle services that bridge gaps in public transportation by offering on-demand, shared rides within city neighborhoods. These services optimize route efficiency and reduce congestion by operating on semi-fixed routes with frequent stops, enhancing accessibility in densely populated areas. Jitneys contribute to sustainable urban transport by decreasing reliance on private vehicles and supporting first- and last-mile connectivity.
Role of Jitneys in Filling Transit Gaps
Jitneys play a crucial role in filling transit gaps by providing flexible, on-demand transportation service in underserved areas where traditional public transit is limited or absent. These small, privately operated vehicles offer last-mile connectivity, enhancing accessibility for commuters and reducing transit deserts. By complementing fixed-route systems, jitneys improve overall urban mobility and support equitable access to transportation.
Regulatory Challenges Facing Jitney Services
Jitney services often face regulatory challenges related to licensing, safety standards, and route approvals, which vary significantly across municipalities and states. These inconsistent regulations can limit jitney operations, leading to conflicts with established public transit authorities and concerns over passenger safety and insurance compliance. Efforts to balance flexible, low-cost transit options with regulatory frameworks remain a critical obstacle for the expansion of jitney services.
Jitney Systems: Case Studies by Region
Jitney systems operate as flexible, demand-responsive shuttle services primarily found in urban and suburban regions across the United States, Caribbean, and parts of Asia. Case studies reveal significant impacts on local mobility patterns in areas like Miami, Florida, where jitneys supplement public transit by providing frequent, low-cost rides along fixed routes with informal stops. In the Philippines, jeepney systems illustrate a similar role by addressing last-mile connectivity challenges and reducing congestion through shared ridership in densely populated cities.
Impact of Jitneys on Commuter Choice
Jitneys influence commuter choice by providing flexible, low-cost alternatives to traditional public transit, often operating on informal routes that better match rider demand. Their ability to reduce wait times and offer door-to-door service increases overall accessibility, especially in underserved urban areas. This adaptability encourages shifts from private vehicle use to shared rides, contributing to decreased traffic congestion and emissions.
Comparing Jitneys with Other Shared Mobility Modes
Jitneys operate on flexible routes with fixed fares, offering more adaptable service than traditional buses and greater cost efficiency compared to ride-hailing services. Unlike fixed-route transit, jitneys can quickly adjust pickups and drop-offs based on passenger demand, enhancing last-mile connectivity. In contrast to carpooling, jitneys maintain consistent schedules and professional drivers, improving reliability and safety for urban commuters.
Future Prospects for Jitney Transportation
Jitney transportation is poised for growth as urban populations increase and demand for flexible, on-demand transit options rises. Integrating electric and autonomous vehicle technologies could enhance jitney efficiency, reduce emissions, and lower operating costs. Data-driven route optimization and app-based booking systems are expected to improve user convenience and expand market reach for jitney services in urban mobility ecosystems.
example of jitney in transportation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com