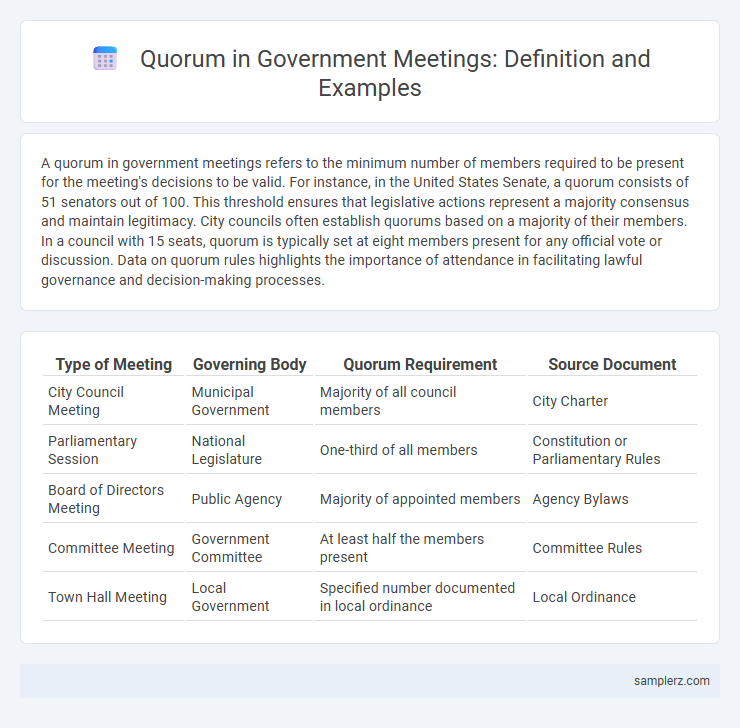
A quorum in government meetings refers to the minimum number of members required to be present for the meeting's decisions to be valid. For instance, in the United States Senate, a quorum consists of 51 senators out of 100. This threshold ensures that legislative actions represent a majority consensus and maintain legitimacy. City councils often establish quorums based on a majority of their members. In a council with 15 seats, quorum is typically set at eight members present for any official vote or discussion. Data on quorum rules highlights the importance of attendance in facilitating lawful governance and decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
| Type of Meeting | Governing Body | Quorum Requirement | Source Document |
|---|---|---|---|
| City Council Meeting | Municipal Government | Majority of all council members | City Charter |
| Parliamentary Session | National Legislature | One-third of all members | Constitution or Parliamentary Rules |
| Board of Directors Meeting | Public Agency | Majority of appointed members | Agency Bylaws |
| Committee Meeting | Government Committee | At least half the members present | Committee Rules |
| Town Hall Meeting | Local Government | Specified number documented in local ordinance | Local Ordinance |
Definition of Quorum in Government Meetings
A quorum in government meetings refers to the minimum number of members required to be present for the meeting to conduct official business and make binding decisions. This threshold, often defined by a specific fraction or percentage of the total membership, ensures that actions taken represent a legitimate and sufficient portion of the governing body. Without a quorum, decisions made may be invalid or subject to challenge, underscoring its critical role in maintaining the integrity of governmental processes.
Importance of Quorum in Legislative Procedures
Quorum requirements ensure that legislative bodies conduct official business with adequate representation, preventing decisions made without sufficient member participation. For example, the U.S. House of Representatives requires a quorum of at least 218 members to pass legislation, safeguarding the legitimacy and fairness of the decision-making process. Maintaining quorum upholds transparency and accountability in government, reinforcing public trust in legislative outcomes.
Quorum Requirements for Parliamentary Sessions
Parliamentary sessions require a quorum, typically defined as a majority of members present, to conduct official business and validate decisions. For example, the U.S. House of Representatives requires at least 218 of its 435 members to be present to meet quorum. Meeting quorum ensures legislative processes uphold constitutional mandates and maintain procedural legitimacy.
Case Study: Quorum in Local Government Councils
In local government councils, quorum requirements ensure effective decision-making by mandating a minimum number of members present, typically more than half of the total council seats, to validate meetings. For example, in the City of Toronto Council, quorum is set at 23 members out of 44 to proceed with official business, safeguarding against decisions made by an unrepresentative minority. This case study highlights the critical role of quorum in maintaining transparency, legitimacy, and accountability in municipal governance.
Quorum Rules in Senate and House of Representatives
The quorum requirement in the U.S. Senate mandates the presence of at least 51 senators to conduct official business, ensuring sufficient representation for legislative decisions. In the House of Representatives, a quorum consists of a majority of members, typically 218 out of 435, to validate proceedings and votes. Both chambers enforce these quorum rules to maintain legislative legitimacy and prevent unauthorized decision-making during sessions.
Consequences of Lacking a Quorum
Lacking a quorum in a government meeting results in the inability to conduct official business, rendering any decisions or votes null and void. This paralysis delays policy implementation, disrupts legislative processes, and can lead to loss of public trust in governance. Persistent quorum issues may necessitate rescheduling meetings or legal interventions to enforce attendance and uphold procedural integrity.
Strategies to Achieve Quorum in Official Meetings
To achieve quorum in official government meetings, strategies often include scheduling meetings at times most convenient for all members, utilizing reminders and digital attendance tools, and instituting proxy voting policies when permitted. Ensuring clear communication of meeting agendas and the significance of members' presence enhances participation rates. Enforcement of attendance requirements through bylaws or regulations also plays a critical role in maintaining quorum for decision-making.
Quorum Examples in Public Hearings
Quorum in public hearings typically requires the presence of a majority of appointed board members, such as five out of nine commissioners, to validate official decisions. For instance, a city council public hearing on zoning changes mandates at least 50% plus one member attendance to proceed with voting. Meeting without quorum invalidates any actions or resolutions passed during the session, ensuring democratic transparency and legal compliance.
Legal Implications of Ignoring Quorum
Ignoring quorum requirements in government meetings can lead to decisions being legally invalidated, resulting in administrative delays and potential court challenges. Failure to maintain quorum undermines the legitimacy of resolutions, exposing the government body to accusations of procedural violations under statutory laws. Ensuring quorum compliance is essential to uphold transparency, legal authority, and public trust in governmental decision-making processes.
Historical Incidents of Quorum Issues in Government
Historical incidents of quorum issues in government highlight the 1856 US Senate where debate over Kansas Territory nearly collapsed due to lack of quorum, stalling legislation. Another notable case is the 1917 Australian Parliament, which faced quorum challenges during contentious wartime legislation debates, prompting reforms in attendance rules. These events underscore the critical role quorum enforcement in maintaining legislative function and preventing procedural deadlock.
example of quorum in meeting Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com