A summative exam evaluates a student's overall understanding of a course at the end of a learning period, such as a final exam. It typically covers a wide range of topics and skills taught throughout the academic term. Teachers use summative exams to assign grades that reflect students' mastery of the curriculum. Common examples of summative assessments in education include final exams, standardized tests, and comprehensive projects. These exams often consist of multiple-choice questions, essays, or practical tasks designed to measure cumulative knowledge and skills. Summative assessments play a crucial role in determining academic progress and readiness for advancement.
Table of Comparison
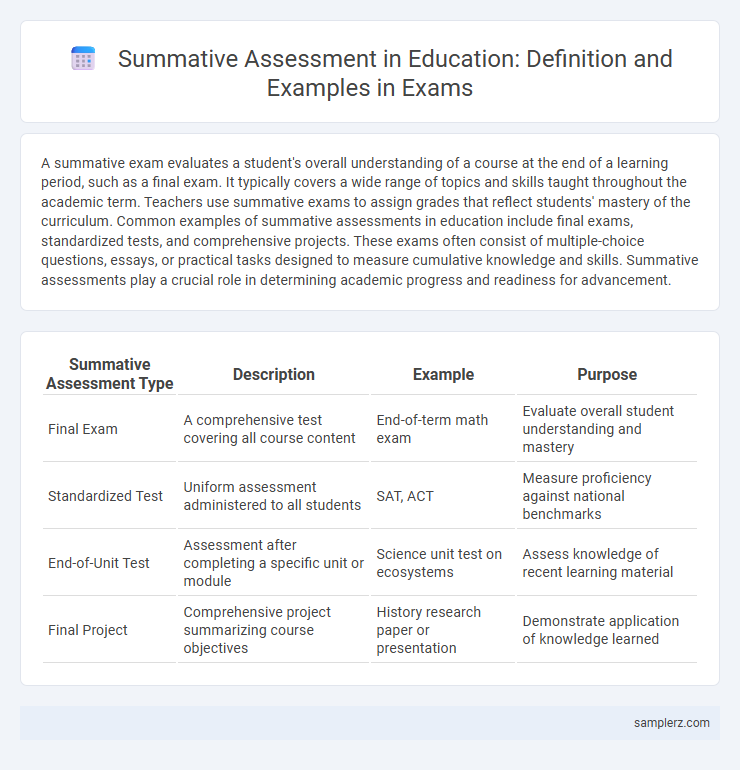
| Summative Assessment Type | Description | Example | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Final Exam | A comprehensive test covering all course content | End-of-term math exam | Evaluate overall student understanding and mastery |
| Standardized Test | Uniform assessment administered to all students | SAT, ACT | Measure proficiency against national benchmarks |
| End-of-Unit Test | Assessment after completing a specific unit or module | Science unit test on ecosystems | Assess knowledge of recent learning material |
| Final Project | Comprehensive project summarizing course objectives | History research paper or presentation | Demonstrate application of knowledge learned |
Understanding Summative Assessments in Education
Summative assessments in education evaluate student learning by measuring mastery of content at the end of an instructional period, such as final exams or standardized tests. These assessments provide quantifiable data on student performance, guiding educators in determining grades and readiness for subsequent courses. Examples include end-of-term exams, statewide assessments, and benchmark tests that assess cumulative knowledge.
Key Features of Summative Exams
Summative exams assess student learning by measuring knowledge retention and understanding at the end of an instructional unit, unit, or course with a focus on cumulative content. These exams often include final projects, standardized tests, or comprehensive written assessments that evaluate overall academic performance. Key features include objective grading criteria, emphasis on content mastery, and results used to inform final grades or academic progression.
Multiple-Choice Exams: A Classic Summative Example
Multiple-choice exams serve as a classic example of summative assessment by evaluating students' knowledge at the end of an instructional period through a structured set of questions with predefined answer choices. This format efficiently measures comprehension, recall, and application of content across diverse subjects, providing quantifiable data for educators to assess overall learning outcomes. High-stakes standardized tests frequently employ multiple-choice items to ensure objective grading and comparability across large student populations.
Final Written Tests as Summative Assessments
Final written tests serve as key summative assessments by evaluating students' comprehensive understanding of course material at the end of an instructional period. These exams typically cover a broad range of topics, measuring knowledge retention, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. Educators use results from final written tests to assign grades and determine overall academic achievement.
Performance-Based Summative Exams
Performance-based summative exams evaluate students through practical demonstrations such as science experiments, presentations, and portfolio assessments, providing a comprehensive measure of their skills and knowledge application. These exams emphasize real-world tasks, requiring learners to apply concepts in authentic contexts, which enhances critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Assessment criteria typically include accuracy, creativity, and process mastery, ensuring a holistic evaluation beyond traditional written tests.
Standardized Testing in Summative Evaluation
Standardized testing is a common example of summative evaluation, designed to measure student learning against established benchmarks at the end of an instructional period. These tests provide quantifiable data to assess overall academic achievement and inform decisions about student progression and curriculum effectiveness. Standardized exams often include multiple-choice, true/false, or essay questions that evaluate knowledge retention and skill mastery across diverse subjects.
Oral Examinations as Summative Tools
Oral examinations serve as effective summative assessment tools by evaluating students' understanding, critical thinking, and verbal communication skills in real time. They provide educators with direct evidence of knowledge retention and conceptual mastery beyond written tests. This method is commonly used in language courses, medical schools, and law programs to assess applied skills and ensure comprehensive learning outcomes.
Project-Based Summative Assessment Examples
Project-based summative assessments in education often include comprehensive final presentations where students design and execute real-world projects, such as creating a business plan or developing a scientific experiment. These assessments measure understanding and application of course concepts through deliverables like detailed reports, prototypes, or multimedia presentations. Effective project-based summative assessments promote critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and synthesis of knowledge, providing a holistic evaluation of student learning outcomes.
End-of-Term Cumulative Exams
End-of-Term Cumulative Exams assess students' comprehensive understanding by covering all material taught throughout the term, providing a thorough evaluation of knowledge retention and mastery. These exams typically include various question formats such as multiple-choice, short answer, and essays to gauge different cognitive skills. Educational institutions rely on these summative assessments to assign final grades and inform curriculum effectiveness.
Portfolio Assessment as a Summative Method
Portfolio assessment as a summative method evaluates a student's comprehensive learning by compiling diverse work samples, projects, and reflections over a period. This approach allows educators to assess critical thinking, creativity, and skill application, providing a multifaceted view of student achievement. Unlike traditional exams, portfolios capture growth and depth, making them a powerful tool for summative evaluation in education.
example of summative in exam Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com