A mind map in education serves as a visual tool that organizes information hierarchically around a central concept. It typically starts with a main topic placed in the center, such as "Photosynthesis," with related subtopics like "Light Absorption," "Chlorophyll," and "Energy Conversion" branching out. Each branch can further divide into smaller nodes containing key facts, definitions, or data to enhance comprehension and retention. This method supports active learning by connecting concepts and facilitating memory through visual representation. In note-taking, mind maps help students capture complex ideas quickly and see relationships between subjects like historical events, scientific processes, or literary themes. Educational software often integrates mind mapping features, allowing users to incorporate multimedia elements such as images, links, and annotations to enrich the data structure.
Table of Comparison
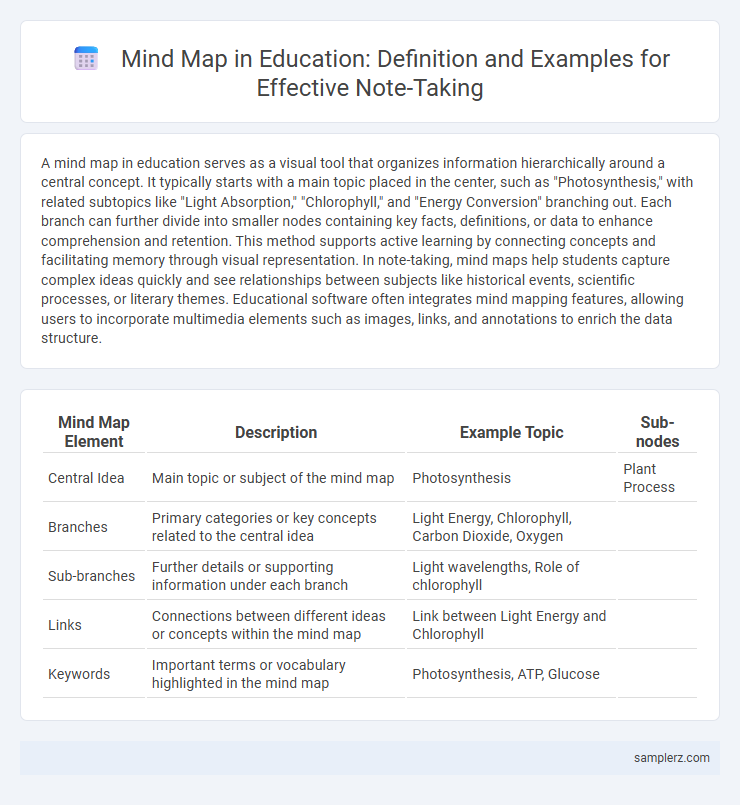
| Mind Map Element | Description | Example Topic | Sub-nodes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Idea | Main topic or subject of the mind map | Photosynthesis | Plant Process |
| Branches | Primary categories or key concepts related to the central idea | Light Energy, Chlorophyll, Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen | |
| Sub-branches | Further details or supporting information under each branch | Light wavelengths, Role of chlorophyll | |
| Links | Connections between different ideas or concepts within the mind map | Link between Light Energy and Chlorophyll | |
| Keywords | Important terms or vocabulary highlighted in the mind map | Photosynthesis, ATP, Glucose |
Introduction to Mind Maps in Note-Taking
Mind maps in note-taking visually organize information by connecting key concepts and ideas around a central topic, enhancing comprehension and retention. For example, in an Introduction to Mind Maps, a central node labeled "Mind Maps" branches into categories like "Definition," "Benefits," and "Techniques," each further subdivided with relevant details. This hierarchical, non-linear structure supports cognitive processes by mimicking natural thought patterns and promoting active learning.
Benefits of Using Mind Maps for Students
Mind maps enhance students' learning by organizing complex information visually, improving memory retention and comprehension. They stimulate creativity and critical thinking by allowing students to structure ideas hierarchically and identify connections between concepts. Using mind maps also promotes active engagement and efficient revision, making study sessions more productive and systematic.
Key Elements of an Effective Mind Map
A well-constructed mind map includes a central topic, branching key concepts, and related subtopics organized hierarchically with clear visual cues such as colors and symbols to enhance memory retention. Effective mind maps use concise keywords, strategic placement, and consistent association patterns to improve comprehension and foster creative thinking. Incorporating images and cross-links between branches further enriches understanding and facilitates efficient note-taking in educational settings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Mind Map
Creating a mind map begins with identifying the central topic and placing it at the center of the page, ensuring it captures the main subject clearly. Branch out from the center with key ideas, each represented by distinct colors and images to enhance memory retention and visual appeal. Develop sub-branches for detailed notes or examples, maintaining a hierarchical structure that promotes organized thinking and easy review.
Example: Mind Map for a History Lesson
A mind map for a history lesson can visually organize key events, dates, and figures related to a specific period, such as the American Revolution, by branching from a central topic. Subtopics might include causes, major battles, influential leaders like George Washington, and outcomes, making complex information easier to remember. Using colors and icons enhances memory retention and aids in connecting related concepts during study sessions.
Example: Mind Map for a Science Topic
A mind map for a science topic like "Photosynthesis" visually organizes key concepts such as light absorption, chlorophyll, and glucose production, connected through branches. Central nodes include processes like the light-dependent reactions and Calvin cycle, illustrating how energy conversion occurs in plants. This structure enhances comprehension by linking vocabulary, chemical equations, and environmental factors coherently for effective study and revision.
Example: Mind Map for Language Learning
A mind map for language learning typically centers on the main topic, such as "Spanish Vocabulary," and branches into categories like "Food," "Travel," "Grammar," and "Common Phrases." Each branch further divides into specific terms or concepts, helping learners visualize connections and improve memory retention. This visual organization enhances active recall and supports efficient study habits in language acquisition.
Example: Mind Map for Exam Preparation
A mind map for exam preparation organizes key subjects and topics visually, with branches representing main concepts such as History, Math, and Science. Each branch further divides into subtopics like dates, formulas, and theories, enabling efficient review and memory retention. This structured approach enhances understanding and helps identify areas needing more focus before exams.
Digital Tools for Mind Mapping in Education
Digital tools like MindMeister, XMind, and Coggle enhance mind mapping in education by enabling dynamic collaboration and real-time updates. These platforms support multimedia integration such as images, links, and videos, which enrich note-taking and conceptual understanding. Utilizing such software increases student engagement and allows educators to track progress efficiently.
Tips for Optimizing Mind Maps in Notes
Effective mind maps in notes enhance memory retention by using clear keywords, vivid colors, and hierarchical structures to organize information visually. Incorporating images and symbols alongside concise phrases boosts comprehension and engagement during review sessions. Regularly updating and simplifying branches prevents clutter, ensuring clarity and efficient knowledge recall.
example of mind map in note Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com