Proctoring in examination refers to the supervised monitoring of students during tests to ensure academic integrity and prevent cheating. This process can involve in-person proctors or online proctoring software that uses webcam surveillance, AI algorithms, and screen monitoring to detect suspicious behavior. Institutions rely on proctoring data to verify the authenticity of exam results and uphold standardized testing protocols. Digital proctoring systems analyze video feeds and keystroke patterns to identify potential violations such as unauthorized materials or impersonation. Data collected during examinations includes timestamps, facial recognition outputs, and environmental scans, which are stored for audit purposes. Educational organizations use this entity-driven data to maintain fairness in assessments and improve security measures in both remote and on-site testing environments.
Table of Comparison
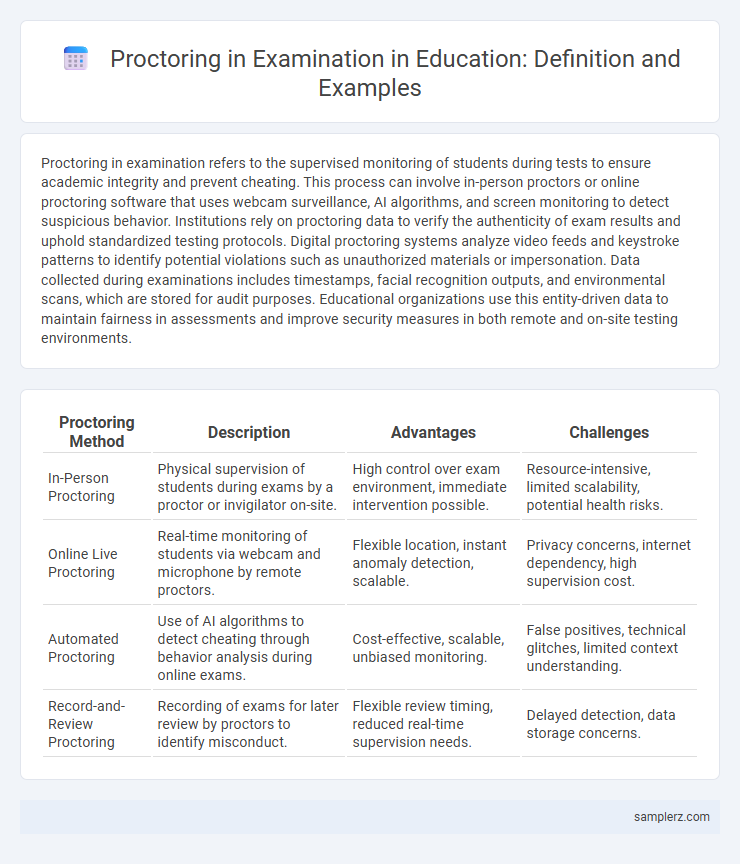
| Proctoring Method | Description | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-Person Proctoring | Physical supervision of students during exams by a proctor or invigilator on-site. | High control over exam environment, immediate intervention possible. | Resource-intensive, limited scalability, potential health risks. |
| Online Live Proctoring | Real-time monitoring of students via webcam and microphone by remote proctors. | Flexible location, instant anomaly detection, scalable. | Privacy concerns, internet dependency, high supervision cost. |
| Automated Proctoring | Use of AI algorithms to detect cheating through behavior analysis during online exams. | Cost-effective, scalable, unbiased monitoring. | False positives, technical glitches, limited context understanding. |
| Record-and-Review Proctoring | Recording of exams for later review by proctors to identify misconduct. | Flexible review timing, reduced real-time supervision needs. | Delayed detection, data storage concerns. |
Introduction to Proctoring in Examinations
Proctoring in examinations involves monitoring students during tests to ensure academic integrity and prevent cheating. This process can include live observation, automated software using AI to detect suspicious behavior, and identity verification methods. Advanced proctoring solutions often combine video surveillance, screen recording, and biometric authentication to maintain a secure testing environment.
Importance of Proctoring for Academic Integrity
Proctoring in examinations ensures strict monitoring to prevent cheating and maintain fairness, directly supporting academic integrity. Advanced proctoring technologies, such as AI-driven remote invigilation and biometric verification, enhance the reliability of assessments by detecting suspicious behaviors in real-time. Maintaining rigorous proctoring standards protects the value of certifications and upholds institutional reputation by guaranteeing genuine student performance.
Types of Proctoring Methods Used in Education
Proctoring methods in education encompass in-person, online, and automated proctoring systems, each designed to ensure exam integrity by monitoring student behavior and environment. In-person proctoring involves a physical supervisor observing test participants, while online proctoring uses webcams and screen-sharing technology to detect suspicious activity remotely. Automated proctoring leverages artificial intelligence to analyze video and audio feeds, flagging potential cheating incidents without human intervention.
Traditional In-Person Proctoring: Procedures and Examples
Traditional in-person proctoring involves a designated invigilator physically monitoring students during examinations to prevent cheating by enforcing strict seating arrangements and observing behaviors. Common procedures include verifying student identities, distributing and collecting exam materials, and maintaining a quiet, controlled environment to ensure fairness. Examples include classroom-based exams supervised by teachers or external proctors at testing centers where candidates are closely watched throughout the duration of the test.
Online Proctoring: Technologies and Case Studies
Online proctoring leverages AI-powered video monitoring, biometric authentication, and browser lockdown technologies to ensure exam integrity in remote settings. Case studies from universities like Harvard and Stanford demonstrate significant reductions in cheating incidents through real-time behavior analysis and automated suspicious activity alerts. These technologies enable scalable, secure, and efficient monitoring, critical for maintaining academic standards in digital assessments.
Automated Proctoring: AI-Based Examination Monitoring
Automated proctoring uses AI-based examination monitoring systems to prevent cheating by analyzing real-time video, audio, and screen activity during online tests. Advanced algorithms detect suspicious behaviors such as gaze deviation, unauthorized device usage, or background noise, ensuring exam integrity without human intervention. This technology enhances scalability and reduces costs while maintaining strict adherence to academic honesty standards.
Hybrid Proctoring: Blending In-Person and Online Techniques
Hybrid proctoring in education combines in-person supervision with advanced online monitoring tools such as AI-driven video analysis and identity verification to ensure exam integrity. This approach enables institutions to maintain high security standards while offering flexibility for remote and on-site students. Blending these techniques reduces cheating risks and enhances accuracy in detecting irregularities during examinations.
Real-World Examples of Proctoring in Universities
Universities such as Harvard and Stanford utilize AI-powered proctoring systems like ProctorU and ExamSoft to monitor students during online exams, using keystroke analysis and video surveillance to ensure academic integrity. These platforms detect suspicious behaviors such as unauthorized device usage or face deviation, instantly alerting exam administrators. The real-time analytics and reporting capabilities of such proctoring solutions help institutions maintain strict examination standards while enabling remote learning environments.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Proctoring
Proctoring in examinations faces challenges such as ensuring academic integrity while respecting student privacy and preventing technical issues that may disrupt the testing environment. Ethical considerations include balancing surveillance measures to deter cheating without creating an atmosphere of distrust or disproportionately impacting marginalized students. Effective proctoring solutions require transparent policies and robust technologies designed to minimize bias and protect personal data.
Future Trends in Examination Proctoring
Future trends in examination proctoring emphasize AI-driven technologies, such as facial recognition and behavior analysis, to enhance security and authenticity in remote assessments. Blockchain integration ensures immutable audit trails and prevents exam tampering, while adaptive proctoring systems use real-time data analytics to customize monitoring based on individual risk factors. These innovations collectively aim to create more reliable, scalable, and user-friendly online examination environments.
example of Proctoring in examination Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com