Remedial education in curriculum typically includes targeted reading and math programs designed to help students meet grade-level standards. These programs use diagnostic assessments to identify specific learning gaps and provide personalized instruction. Schools often integrate remedial classes during or after regular school hours to support struggling learners. Data shows that remedial courses can improve students' foundational skills, leading to better academic performance and increased graduation rates. Entities like the Department of Education recommend incorporating evidence-based interventions such as phonics instruction and conceptual math drills. Tracking student progress through formative assessments ensures that remedial efforts align with individual learning needs.
Table of Comparison
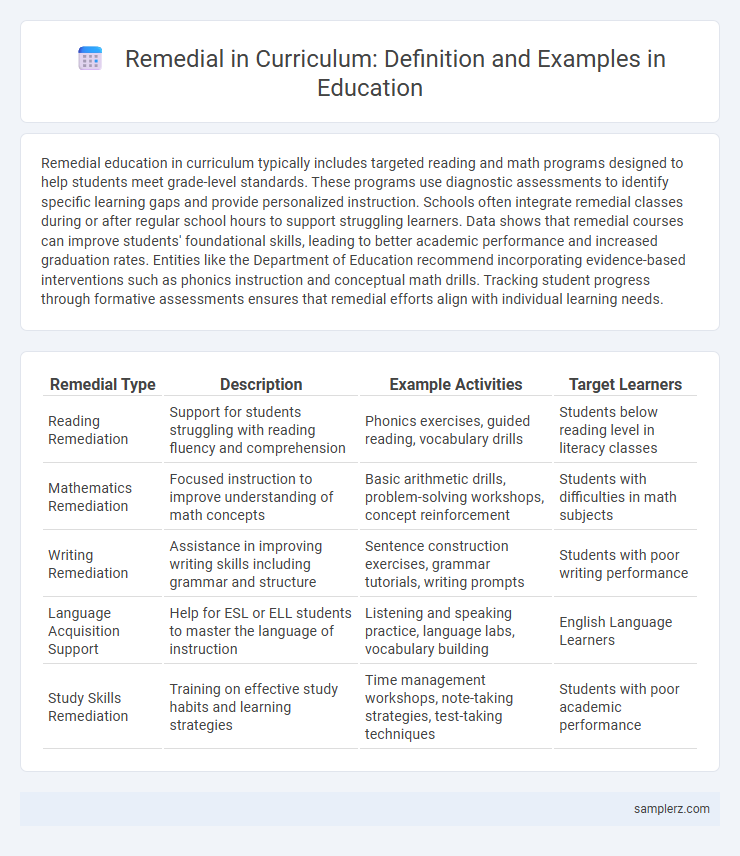
| Remedial Type | Description | Example Activities | Target Learners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reading Remediation | Support for students struggling with reading fluency and comprehension | Phonics exercises, guided reading, vocabulary drills | Students below reading level in literacy classes |
| Mathematics Remediation | Focused instruction to improve understanding of math concepts | Basic arithmetic drills, problem-solving workshops, concept reinforcement | Students with difficulties in math subjects |
| Writing Remediation | Assistance in improving writing skills including grammar and structure | Sentence construction exercises, grammar tutorials, writing prompts | Students with poor writing performance |
| Language Acquisition Support | Help for ESL or ELL students to master the language of instruction | Listening and speaking practice, language labs, vocabulary building | English Language Learners |
| Study Skills Remediation | Training on effective study habits and learning strategies | Time management workshops, note-taking strategies, test-taking techniques | Students with poor academic performance |
Understanding Remedial Education in Modern Curricula
Remedial education in modern curricula often involves targeted interventions such as supplemental tutoring, foundational skill workshops, and personalized learning plans designed to address gaps in student understanding. These programs emphasize mastery of core subjects like mathematics and literacy, aiming to bring students up to grade-level proficiency. Data from recent studies show that tailored remedial instruction significantly improves academic outcomes and reduces dropout rates.
Key Principles Behind Remedial Programs
Remedial programs in education focus on diagnosing learning gaps through targeted assessments and providing personalized instruction to address those deficiencies. These programs emphasize scaffolding, continuous progress monitoring, and adaptive teaching methods to ensure mastery of foundational skills. Incorporating evidence-based interventions such as phonics for reading or math drills for numeracy aligns with the principle of meeting students at their current level to build competence and confidence.
Identifying Students in Need of Remedial Support
Teachers use formative assessments such as quizzes, class assignments, and observational checklists to identify students who struggle with key concepts. Data from standardized tests and diagnostic evaluations highlight gaps in foundational skills requiring targeted intervention. Early identification through these measures enables schools to implement tailored remedial programs that improve student outcomes and prevent academic failure.
Types of Remedial Interventions in Schools
Types of remedial interventions in schools include targeted tutoring, skill-specific workshops, and peer-assisted learning sessions designed to address students' individual academic weaknesses. These interventions focus on core subjects such as mathematics, reading, and writing, using diagnostic assessments to tailor instruction. Implementation often involves small group settings, personalized learning plans, and continuous progress monitoring to ensure effective remediation and improve student outcomes.
Examples of Remedial Activities in the Classroom
Remedial activities in the classroom include targeted reading interventions, math skill drills, and individualized tutoring sessions designed to address specific learning gaps. Techniques such as phonics practice, guided reading groups, and basic arithmetic exercises help reinforce foundational skills. Interactive tools like educational software and peer-assisted learning also support student progress in remedial education.
Integrating Remedial Strategies into the Curriculum
Integrating remedial strategies into the curriculum involves targeted support such as differentiated instruction, scaffolded lessons, and formative assessments to identify learning gaps early. Structured interventions like small group tutoring and personalized learning plans are embedded within core subjects to reinforce foundational skills in literacy and numeracy. This approach ensures students receive continuous support tailored to their specific needs, promoting academic achievement and reducing failure rates.
Measuring Success in Remedial Education
Measuring success in remedial education involves tracking student progress through formative assessments and performance benchmarks aligned with core curriculum standards. Data-driven tools such as diagnostic tests, progress monitoring, and outcome evaluations provide quantifiable insights into skills acquisition and academic improvement. Student retention rates, course completion statistics, and post-remedial achievement levels serve as critical indicators of the effectiveness of remedial interventions.
The Role of Technology in Remedial Instruction
Technology in remedial instruction enhances personalized learning by using adaptive software that targets individual student weaknesses in subjects like math and reading. Digital tools such as interactive apps and online assessments provide real-time feedback, allowing educators to monitor progress and adjust strategies effectively. Incorporating technology fosters student engagement and supports differentiated instruction critical for successful remediation in diverse classroom settings.
Teacher Training for Effective Remedial Teaching
Teacher training programs emphasize developing skills in diagnosing learning gaps and implementing targeted interventions to improve student outcomes in remedial education. Effective remedial teaching strategies include differentiated instruction, formative assessments, and personalized feedback tailored to individual student needs. Continuous professional development equips educators with evidence-based methods to enhance literacy, numeracy, and critical thinking skills within remedial curricula.
Case Studies: Successful Remedial Programs
Case studies of successful remedial programs highlight targeted interventions such as one-on-one tutoring, adaptive learning technologies, and foundational skills workshops that significantly improve student outcomes. Programs like the AVID (Advancement Via Individual Determination) initiative demonstrate measurable gains in college readiness and academic performance through structured support and mentoring. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics shows schools implementing these remedial approaches experience increased graduation rates and narrowed achievement gaps.
example of remedial in curriculum Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com