Summative evaluation in education assesses student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against a standard or benchmark. Common examples include final exams, end-of-term projects, and standardized tests, which provide measurable data on student comprehension and mastery of the material. These assessments help educators determine overall achievement and inform decisions about grades and curriculum effectiveness. Data collected from summative evaluations are critical for analyzing the performance of both students and educational programs. Entities such as schools, districts, and educational researchers use this information to identify trends, allocate resources, and develop strategies for improvement. The results serve as a definitive measure of learning outcomes, guiding policy and instructional adjustments to enhance future educational experiences.
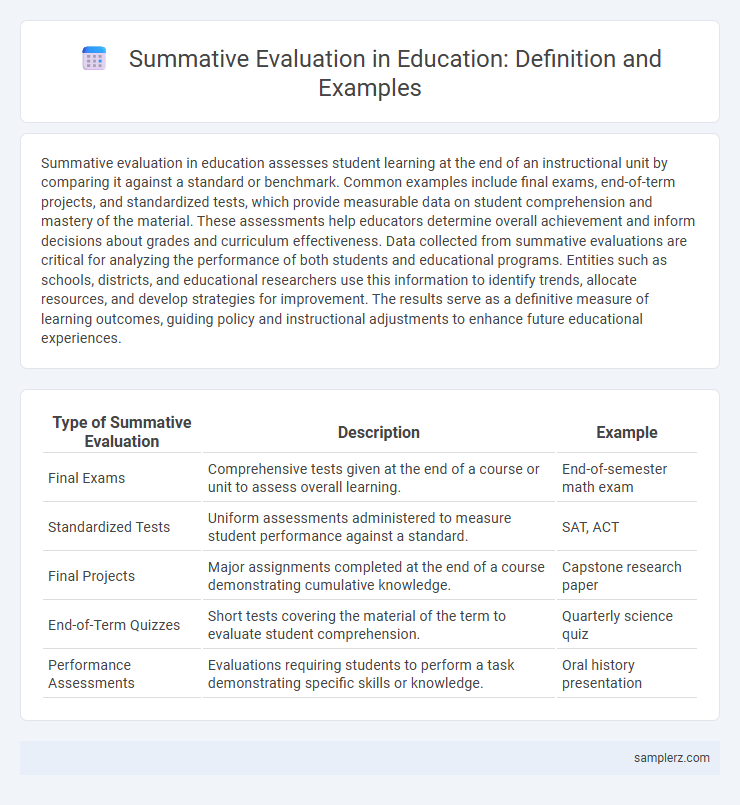
Table of Comparison
| Type of Summative Evaluation | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Final Exams | Comprehensive tests given at the end of a course or unit to assess overall learning. | End-of-semester math exam |
| Standardized Tests | Uniform assessments administered to measure student performance against a standard. | SAT, ACT |
| Final Projects | Major assignments completed at the end of a course demonstrating cumulative knowledge. | Capstone research paper |
| End-of-Term Quizzes | Short tests covering the material of the term to evaluate student comprehension. | Quarterly science quiz |
| Performance Assessments | Evaluations requiring students to perform a task demonstrating specific skills or knowledge. | Oral history presentation |
Understanding Summative Evaluation in Education
Summative evaluation in education measures student learning at the end of an instructional period through final exams, standardized tests, or end-of-term projects. These assessments provide comprehensive data on overall achievement and mastery of curriculum objectives. By analyzing summative evaluation results, educators identify areas needing improvement and adjust teaching strategies for future courses.
Key Characteristics of Summative Assessments
Summative assessments are designed to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, typically through exams, final projects, or standardized tests. Key characteristics include comprehensive coverage of content, grading that reflects overall achievement, and a focus on measuring cumulative knowledge and skills. These assessments are essential for determining if educational goals have been met and informing future instructional decisions.
Common Examples of Summative Evaluation Methods
Common examples of summative evaluation methods in education include final exams, standardized tests, and end-of-term projects. These assessments measure student learning by providing comprehensive data on knowledge retention and skill mastery after instruction. The results help educators determine overall effectiveness and inform grade assignments or curriculum adjustments.
Traditional Examinations as Summative Tools
Traditional examinations serve as primary summative evaluation tools by assessing student knowledge and skills at the end of instructional units. These exams typically include multiple-choice, short-answer, and essay questions designed to measure comprehensive understanding and retention of subject matter. Results from traditional examinations provide quantifiable data that inform grading decisions and curriculum effectiveness.
Standardized Testing in Educational Evaluation
Standardized testing serves as a prevalent example of summative evaluation in education, providing consistent measures of student achievement across various schools and districts. These tests assess cumulative knowledge and skills at the end of instructional periods, informing decisions on student advancement and curriculum effectiveness. The use of nationwide exams like the SAT, ACT, and state-mandated assessments exemplifies standardized testing's role in quantifying educational outcomes through summative evaluation.
Final Projects and Capstone Assignments
Final projects and capstone assignments serve as quintessential examples of summative evaluation by assessing students' comprehensive understanding and application of course material. These assessments require critical thinking, integration of knowledge, and problem-solving skills applied in real-world or simulated scenarios, reflecting students' mastery of learning objectives. The evaluative focus on outcomes, originality, and practical implementation makes these culminating activities essential for measuring educational achievement and readiness for professional challenges.
End-of-Term Report Cards and Grades
End-of-term report cards provide a comprehensive summary of a student's academic performance across all subjects, reflecting cumulative learning outcomes and mastery of curriculum standards. These grades serve as summative evaluations by measuring student achievement at the conclusion of an instructional period, often influencing promotion decisions and academic records. Schools rely on these assessments to communicate progress to parents and guide future educational planning.
Summative Evaluation Through Portfolios
Summative evaluation through portfolios involves assessing a student's cumulative work over a course or program to measure learning achievements and skill development. Portfolios provide a comprehensive collection of assignments, projects, and reflections that showcase growth and mastery of specific educational standards. This method enables educators to evaluate both the product and the process of learning, offering a holistic view of student performance at the end of an instructional period.
Performance-Based Summative Assessments
Performance-based summative assessments evaluate student learning through real-world tasks such as presentations, projects, and portfolios that demonstrate mastery of skills and knowledge. These assessments provide comprehensive insights into students' capabilities by requiring application, analysis, and synthesis rather than rote memorization. Examples include science experiments, art exhibitions, and business simulations, which measure critical thinking and problem-solving effectively at the end of an instructional period.
The Role of Summative Evaluation in Student Achievement
Summative evaluation plays a crucial role in measuring student achievement by providing comprehensive assessments that reflect cumulative learning at the end of instructional units or courses. Tools such as final exams, standardized tests, and end-of-term projects offer quantitative data that inform educators about overall student performance and mastery of curriculum objectives. This evaluative approach helps identify learning gaps, guide curriculum adjustments, and support accountability in educational settings.
example of summative in evaluation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com