A phoneme in literacy is the smallest unit of sound that distinguishes one word from another in a specific language. For example, the word "cat" contains three phonemes: /k/, /ae/, and /t/. Recognizing phonemes is crucial for phonemic awareness, which supports reading and spelling development in early education. Phoneme identification helps children decode words by blending sounds, which forms the foundation of effective reading instruction. Teachers often use activities such as segmenting and manipulating phonemes to strengthen students' auditory discrimination skills. Mastery of phoneme concepts leads to improved literacy rates and better comprehension of written language.
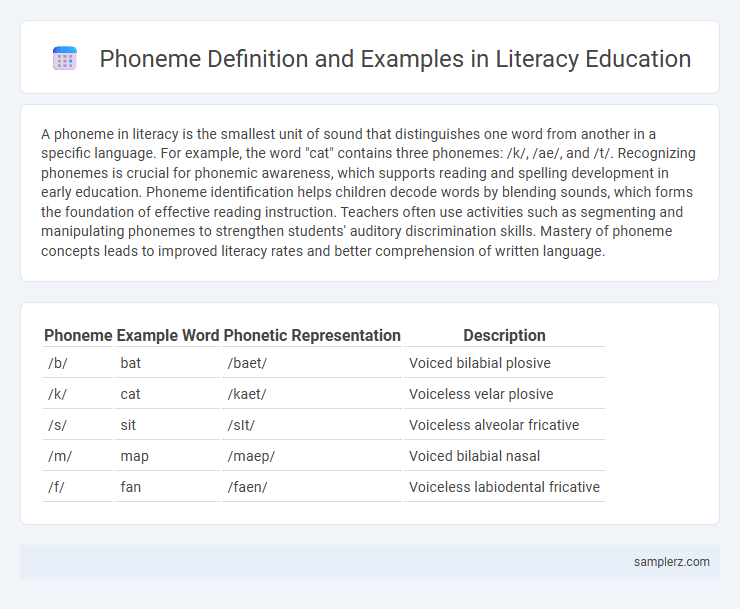
Table of Comparison
| Phoneme | Example Word | Phonetic Representation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| /b/ | bat | /baet/ | Voiced bilabial plosive |
| /k/ | cat | /kaet/ | Voiceless velar plosive |
| /s/ | sit | /sIt/ | Voiceless alveolar fricative |
| /m/ | map | /maep/ | Voiced bilabial nasal |
| /f/ | fan | /faen/ | Voiceless labiodental fricative |
Understanding Phonemes: The Building Blocks of Literacy
Phonemes are the smallest units of sound in a language, such as the /b/ in "bat" or the /sh/ in "ship," which are crucial for decoding words in reading. Mastery of phoneme recognition enables learners to connect sounds to letters, facilitating spelling and pronunciation skills. Developing phonemic awareness lays the foundation for proficient reading and literacy development in early education.
Common Examples of Phonemes in Early Reading
Common examples of phonemes in early reading include /b/ as in "bat," /m/ as in "mat," and /s/ as in "sat." Recognizing these distinct sounds helps children decode words and develop foundational literacy skills. Phonemic awareness of sounds like /f/, /t/, and /k/ supports accurate pronunciation and spelling during early literacy instruction.
How Phonemes Influence Word Recognition
Phonemes, the smallest units of sound in a language such as /b/, /a/, and /t/ in the word "bat," play a critical role in literacy by enabling efficient word recognition. The ability to isolate and manipulate phonemes supports decoding skills, allowing readers to connect sounds with corresponding letters or letter patterns. Mastery of phonemic awareness accelerates reading fluency and comprehension by facilitating rapid and accurate identification of words during reading.
Differentiating Phonemes in English Language
Differentiating phonemes in English literacy is crucial for developing reading and spelling skills, with examples such as distinguishing between /b/ in "bat" and /p/ in "pat." Recognizing these subtle sound differences helps learners decode words accurately and improves phonemic awareness. Effective instruction often involves auditory discrimination exercises targeting minimal pairs to reinforce phoneme differentiation.
Role of Phoneme Awareness in Literacy Development
Phoneme awareness plays a crucial role in literacy development by enabling learners to recognize and manipulate individual sounds within words, such as /k/ in "cat" or /b/ in "bat." This skill forms the foundation for decoding and encoding words, which are essential for proficient reading and spelling. Research indicates that early phoneme awareness intervention significantly improves reading fluency and comprehension outcomes in young children.
Teaching Phoneme Segmentation in the Classroom
Teaching phoneme segmentation in the classroom involves helping students break down words like "cat" into individual sounds: /k/, /ae/, and /t/. Effective phoneme segmentation activities include clapping or tapping for each sound, guiding learners to recognize and manipulate phonemes to improve decoding skills. Mastery of phoneme segmentation directly enhances reading fluency and spelling accuracy in early literacy development.
Activities to Identify and Practice Phonemes
Activities to identify and practice phonemes in literacy include phoneme segmentation, where students break words into individual sounds, and phoneme blending, where they combine sounds to form words. Using tools like Elkonin boxes helps learners visually separate and manipulate phonemes to enhance decoding skills. Interactive games and rhyming exercises further reinforce phonemic awareness by engaging students in recognizing and producing targeted speech sounds.
The Connection Between Phonemes and Spelling
Phonemes, the smallest units of sound in language, play a crucial role in literacy by linking spoken language to written text through spelling patterns. For example, the phoneme /k/ can be represented by different graphemes such as "c," "k," and "ck" in words like "cat," "kite," and "duck," demonstrating how sound-to-letter correspondence is essential for decoding and encoding words. Mastery of phoneme-spelling relationships supports phonics instruction and improves reading fluency and spelling accuracy in early literacy development.
Challenges Learners Face with Phoneme Identification
Learners often struggle with phoneme identification due to the subtle differences in sounds, especially with phonemes that are phonetically similar, such as /b/ and /p/. Difficulty distinguishing these sounds can impede decoding skills and hinder reading fluency. Effective phonemic awareness instruction targets these challenges by using explicit practice in segmenting and blending phonemes.
Phoneme Manipulation: Advanced Literacy Strategies
Phoneme manipulation strategies in advanced literacy involve identifying, segmenting, and blending individual sounds to enhance reading proficiency. Techniques such as phoneme substitution, deletion, and reversal enable students to decode unfamiliar words and improve spelling skills. Mastery of these phonemic awareness tasks supports fluent reading and accurate comprehension in complex texts.
example of phoneme in literacy Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com