Inquiry in educational methodology refers to a systematic process where students actively explore questions through investigation and critical thinking. This approach encourages learners to gather data, analyze evidence, and formulate conclusions based on their findings. It shifts the focus from passive reception of information to active engagement, promoting deeper understanding and cognitive development. Teachers implement inquiry by designing activities that require observation, experimentation, and reflection, often utilizing tools like surveys, experiments, and case studies. Data collected during inquiry helps students develop skills in research, data interpretation, and problem-solving, essential for academic and real-world applications. This methodology supports personalized learning by allowing learners to pursue topics of interest, fostering motivation and curiosity.
Table of Comparison
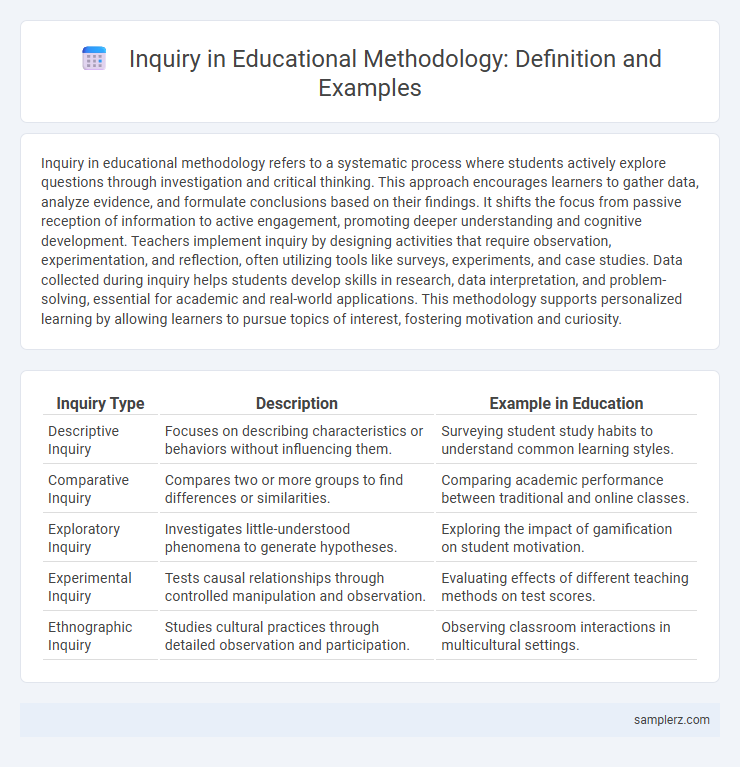
| Inquiry Type | Description | Example in Education |
|---|---|---|
| Descriptive Inquiry | Focuses on describing characteristics or behaviors without influencing them. | Surveying student study habits to understand common learning styles. |
| Comparative Inquiry | Compares two or more groups to find differences or similarities. | Comparing academic performance between traditional and online classes. |
| Exploratory Inquiry | Investigates little-understood phenomena to generate hypotheses. | Exploring the impact of gamification on student motivation. |
| Experimental Inquiry | Tests causal relationships through controlled manipulation and observation. | Evaluating effects of different teaching methods on test scores. |
| Ethnographic Inquiry | Studies cultural practices through detailed observation and participation. | Observing classroom interactions in multicultural settings. |
Defining Inquiry-Based Methodology in Education
Inquiry-based methodology in education centers on students actively exploring questions, problems, or scenarios to construct knowledge rather than passively receiving information. This approach emphasizes critical thinking, problem-solving, and research skills by engaging learners in formulating hypotheses, investigating, and reflecting on findings. Effective implementation involves structuring curriculum around open-ended questions that promote curiosity and deeper understanding across various subjects.
Key Principles of Inquiry-Driven Learning
Inquiry-driven learning emphasizes student-centered exploration where learners formulate questions, investigate answers, and construct new knowledge. Key principles include fostering curiosity, encouraging critical thinking, and promoting active engagement through hands-on activities and reflection. This methodology enhances problem-solving skills and deepens understanding by connecting theoretical concepts to real-world contexts.
Types of Inquiry Approaches in the Classroom
Inquiry approaches in the classroom include structured, guided, and open-ended inquiry, each promoting varying levels of student autonomy and critical thinking. Structured inquiry provides students with specific questions and procedures, while guided inquiry allows students to explore with teacher support. Open-ended inquiry encourages independent investigation, fostering creativity and deeper understanding of subject matter.
Case Study: Guided Inquiry in Science Lessons
Guided Inquiry in science lessons involves students actively exploring scientific concepts through structured questioning and investigation, promoting critical thinking and deeper understanding. Case studies highlight how this methodology encourages learners to formulate hypotheses, conduct experiments, and analyze data collaboratively under teacher guidance. This approach enhances student engagement and retention by linking theoretical knowledge to real-world scientific phenomena.
Examples of Open Inquiry Projects in Schools
Open inquiry projects in schools, such as student-led science experiments on local environmental issues, promote critical thinking and self-guided research. Examples include designing sustainable gardens to study plant growth or investigating water quality in nearby streams through hypothesis formulation and data collection. These projects encourage autonomy and real-world problem-solving, enhancing engagement and deeper understanding in subjects like biology and environmental science.
Role of Questioning in the Inquiry Process
Questioning serves as a foundation of the inquiry process, driving critical thinking and deep exploration in educational settings. Effective inquiry methodology utilizes open-ended questions to encourage learners to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information actively. This dynamic role of questioning transforms passive reception of knowledge into active discovery and understanding.
Integrating Inquiry Methods into Curriculum Design
Integrating inquiry methods into curriculum design enhances critical thinking and student engagement by encouraging exploration and questioning. For example, a science curriculum might incorporate project-based learning where students design experiments to test hypotheses, fostering hands-on investigation and problem-solving skills. This approach promotes active learning and helps students develop a deeper understanding of subject matter through guided inquiry.
Assessing Student Learning Through Inquiry
Assessing student learning through inquiry involves evaluating students' ability to formulate questions, investigate problems, and synthesize information independently. This approach emphasizes critical thinking skills and the application of knowledge in real-world contexts, utilizing formative assessments such as reflective journals, project presentations, and peer reviews. Inquiry-based assessment provides educators with insights into students' depth of understanding and their capacity to engage in self-directed learning processes.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Inquiry-Based Methods
Implementing inquiry-based methods often faces challenges such as limited teacher training, insufficient classroom resources, and time constraints within standardized curricula. Solutions include professional development programs focused on inquiry pedagogy, integrating flexible lesson plans that prioritize student-driven questions, and utilizing technology to facilitate interactive exploration. These strategies enhance student engagement and support a deeper understanding of subject matter through active participation.
Benefits of Inquiry Methodology for Student Engagement
Inquiry methodology encourages active student participation by promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills through hands-on exploration. This approach enhances engagement by allowing students to formulate questions, investigate evidence, and construct knowledge collaboratively. Research shows inquiry-based learning increases motivation and deepens understanding, leading to improved academic performance and long-term retention.
example of Inquiry in methodology Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com