Peer tutoring in education serves as an effective intervention strategy where students assist their classmates in understanding academic concepts. This method involves pairing a tutor student, who has a stronger grasp of the subject, with a tutee student needing additional support. Research data indicates that peer tutoring not only improves academic performance but also enhances social skills and motivation among students. Implementing peer tutoring interventions requires structured training sessions for tutors to ensure quality guidance. Data from multiple studies shows significant improvement in subjects like math and reading when peer tutoring is employed consistently. Schools often report increased student engagement and a positive classroom environment as measurable outcomes of this intervention.
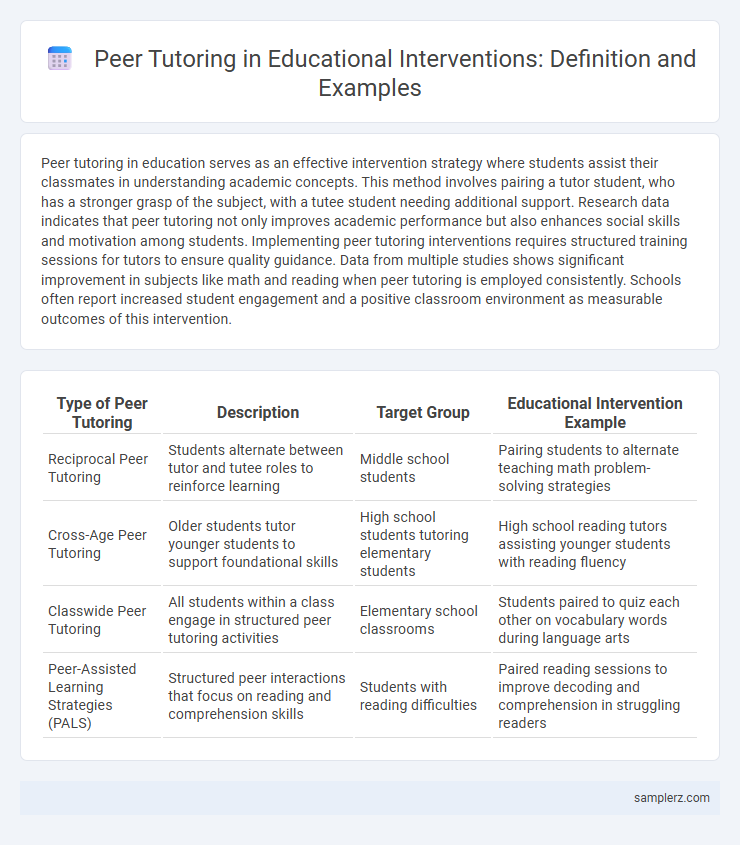
Table of Comparison
| Type of Peer Tutoring | Description | Target Group | Educational Intervention Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reciprocal Peer Tutoring | Students alternate between tutor and tutee roles to reinforce learning | Middle school students | Pairing students to alternate teaching math problem-solving strategies |
| Cross-Age Peer Tutoring | Older students tutor younger students to support foundational skills | High school students tutoring elementary students | High school reading tutors assisting younger students with reading fluency |
| Classwide Peer Tutoring | All students within a class engage in structured peer tutoring activities | Elementary school classrooms | Students paired to quiz each other on vocabulary words during language arts |
| Peer-Assisted Learning Strategies (PALS) | Structured peer interactions that focus on reading and comprehension skills | Students with reading difficulties | Paired reading sessions to improve decoding and comprehension in struggling readers |
Understanding Peer Tutoring in Educational Interventions
Peer tutoring in educational interventions involves students teaching and supporting their classmates to enhance academic understanding and skills retention. Research shows that structured peer tutoring programs, such as cross-age tutoring or reciprocal peer tutoring, significantly improve reading comprehension and mathematical problem-solving abilities. Implementing peer tutoring fosters collaborative learning environments and promotes social interaction, which are critical for effective educational outcomes.
Key Benefits of Peer Tutoring for Struggling Students
Peer tutoring provides struggling students with personalized academic support, improving comprehension and retention through collaborative learning. Engaging with peers in a supportive environment boosts confidence and motivation, leading to increased participation and reduced anxiety in classroom settings. Research shows peer tutoring enhances critical thinking skills and fosters social connections, contributing to overall academic success.
Successful Peer Tutoring Models in Schools
Successful peer tutoring models in schools include the Cross-Age Tutoring and Reciprocal Peer Tutoring programs, which enhance student achievement through structured interaction and collaboration. These models leverage the benefits of cognitive and social congruence by pairing students of different or similar academic levels to support individualized learning and skill development. Research indicates that schools implementing these evidence-based peer tutoring interventions experience significant improvements in literacy, mathematics, and overall academic performance.
Case Study: Peer Tutoring in Reading Intervention
Peer tutoring in reading intervention demonstrated significant improvements in literacy skills among elementary students struggling with comprehension and fluency. In a case study conducted at Lincoln Elementary School, trained peer tutors worked alongside third graders to practice decoding and vocabulary exercises, increasing reading proficiency scores by 25% over a 12-week period. This intervention leveraged peer interactions to enhance engagement and personalized support, proving effective in closing achievement gaps.
Implementing Peer Tutoring for Math Support
Implementing peer tutoring for math support involves pairing students with strong math skills with peers who need help mastering concepts like fractions and algebraic expressions. Structured sessions promote not only problem-solving abilities but also collaborative learning and confidence in math. Research shows peer tutoring can improve students' math performance by 20% on average and increase engagement in STEM subjects.
Training Student Tutors for Effective Interventions
Training student tutors through structured workshops enhances their understanding of subject content and effective communication strategies, resulting in improved peer tutoring outcomes. Incorporating role-playing exercises and feedback sessions equips tutors with practical skills to address diverse learning needs and foster student engagement. Such targeted training programs lead to more impactful interventions, promoting academic achievement and confidence among tutees.
Peer Tutoring for Special Education Needs
Peer tutoring in special education needs often involves pairing students with learning disabilities with typically developing peers to enhance academic and social skills. Research shows that structured peer tutoring programs improve reading comprehension, communication, and self-confidence in students with autism spectrum disorder and dyslexia. Schools implementing evidence-based peer tutoring models report increased engagement and individualized support promoting inclusive learning environments.
Monitoring and Evaluating Peer Tutoring Outcomes
Effective monitoring and evaluating peer tutoring outcomes involves tracking student progress through pre- and post-assessment scores, observation checklists, and regular feedback sessions. Data collected helps identify strengths and areas for improvement in peer tutors' instructional strategies and learners' academic growth. Consistent evaluation supports evidence-based adjustments to interventions, enhancing the overall impact of peer tutoring programs in educational settings.
Challenges and Solutions in Peer Tutoring Programs
Peer tutoring programs often face challenges such as mismatched skill levels and limited student engagement, which can hinder learning outcomes. Solutions include providing structured training for tutors and implementing consistent monitoring to ensure alignment between tutor and tutee abilities. Schools that adopt adaptive pairing and ongoing support report increased academic performance and enhanced social skills among participants.
Best Practices for Sustainable Peer Tutoring Interventions
Implementing clear role definitions for tutors and tutees enhances accountability and learning outcomes in peer tutoring interventions. Consistent training sessions focusing on communication, empathy, and subject mastery ensure tutors effectively support their peers. Regular progress monitoring and feedback loops sustain engagement and adapt strategies for continuous improvement in educational settings.
example of peer tutoring in intervention Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com