Jigsaw in instruction is a cooperative learning strategy where students are divided into small groups, and each member is assigned a different segment of the lesson or topic to learn and teach to their peers. This approach enhances engagement and comprehension by encouraging active participation and accountability within the group. Research shows that jigsaw promotes deeper understanding and retention by leveraging peer teaching and collaborative learning dynamics. In an educational setting, a teacher might use jigsaw by assigning different sections of a textbook chapter on climate change to students. Each student becomes an expert on their assigned section and then shares their knowledge with group members, helping everyone grasp the full scope of the topic. Data from classroom studies indicate improved critical thinking skills and higher test scores when jigsaw is integrated into the curriculum compared to traditional lecture methods.
Table of Comparison
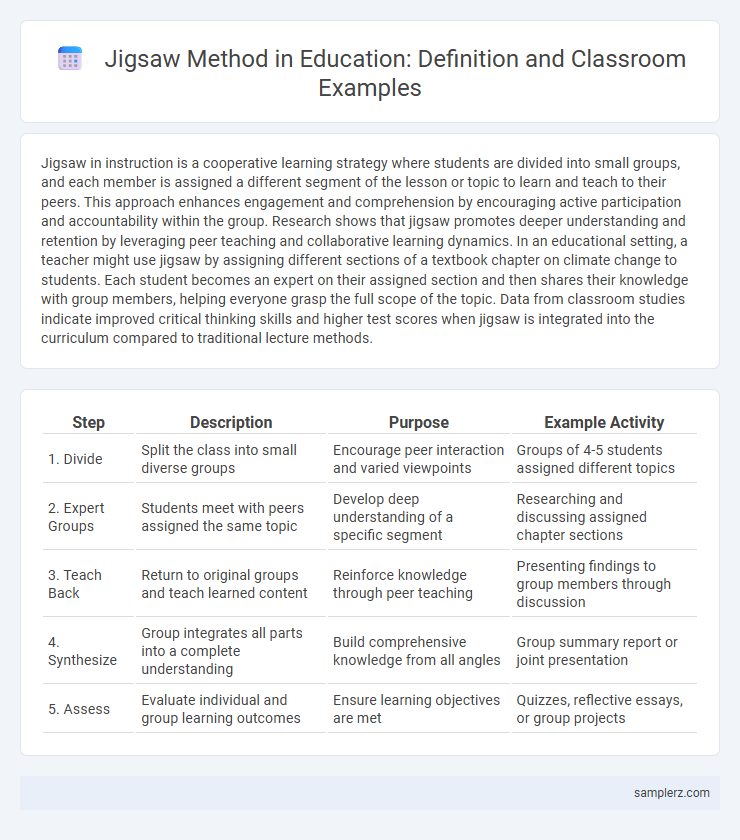
| Step | Description | Purpose | Example Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Divide | Split the class into small diverse groups | Encourage peer interaction and varied viewpoints | Groups of 4-5 students assigned different topics |
| 2. Expert Groups | Students meet with peers assigned the same topic | Develop deep understanding of a specific segment | Researching and discussing assigned chapter sections |
| 3. Teach Back | Return to original groups and teach learned content | Reinforce knowledge through peer teaching | Presenting findings to group members through discussion |
| 4. Synthesize | Group integrates all parts into a complete understanding | Build comprehensive knowledge from all angles | Group summary report or joint presentation |
| 5. Assess | Evaluate individual and group learning outcomes | Ensure learning objectives are met | Quizzes, reflective essays, or group projects |
Understanding the Jigsaw Teaching Method
The Jigsaw teaching method divides students into small groups, each tasked with mastering a specific segment of the lesson before teaching it to peers, promoting active collaboration and deep comprehension. This approach enhances critical thinking and communication skills by requiring students to listen, process, and convey information effectively. Research shows that the Jigsaw method improves retention and engagement, fostering a student-centered learning environment that supports diverse learning styles.
Key Principles of Jigsaw in the Classroom
Jigsaw in instruction emphasizes cooperative learning by dividing students into diverse "home groups," where each member becomes an expert on a specific topic segment before teaching it to peers. Key principles include positive interdependence, individual accountability, and promotive interaction, ensuring all students contribute and learn collaboratively. This method enhances engagement, comprehension, and retention by fostering peer teaching and active participation.
Steps to Implement the Jigsaw Technique
Divide students into diverse home groups where each member is assigned a unique segment of the lesson content to master individually. Form expert groups composed of members from different home groups who study the assigned segment deeply and prepare to teach it. Return to home groups as each expert delivers their segment, facilitating peer teaching and collaborative learning to reinforce understanding and retention.
Jigsaw Activity Example: Science Lesson
In a science lesson on ecosystems, students are divided into expert groups focusing on different components such as producers, consumers, and decomposers. Each group researches their assigned topic and then reassembles into mixed groups to teach their peers, promoting collaborative learning and deepening understanding of ecosystem dynamics. This jigsaw activity encourages active participation and reinforces content mastery through peer instruction.
Jigsaw Example in Social Studies Instruction
In social studies instruction, the jigsaw method involves dividing students into expert groups, each assigned a specific topic such as the causes of the American Revolution or the impact of the Industrial Revolution. Each group researches their topic, then reassembles into mixed groups where members teach their peers, promoting collaborative learning and critical thinking. This approach enhances students' understanding of complex historical events by fostering active engagement and diverse perspectives.
Enhancing Reading Comprehension with Jigsaw
Jigsaw promotes active engagement by dividing reading material into segments assigned to different group members, which they then teach to their peers, fostering deeper understanding of the text. This collaborative approach enhances vocabulary retention and critical thinking as students analyze and discuss key themes and details from their assigned sections. Research shows that jigsaw instruction significantly improves reading comprehension scores by encouraging peer teaching and active processing of information.
Collaborative Problem-Solving Using Jigsaw
Collaborative problem-solving using the jigsaw method involves dividing students into expert groups, where each member masters a specific segment of the content or skill. These experts then reassemble into mixed groups to teach their segment, promoting mutual dependence and active engagement. This instructional strategy enhances critical thinking, communication, and teamwork by requiring students to collectively solve complex problems.
Jigsaw for Language Learning Activities
Jigsaw for language learning involves dividing students into expert groups where each member studies a different language component, such as vocabulary, grammar, or pronunciation. After mastering their segment, students reconvene in mixed groups to teach their peers, promoting collaborative communication and reinforcing language skills. This interactive method enhances comprehension, vocabulary retention, and speaking fluency in target language acquisition.
Assessing Student Outcomes in Jigsaw Lessons
Assessing student outcomes in jigsaw lessons involves evaluating individual accountability and group collaboration through formative assessments such as quizzes, peer evaluations, and reflective journals. Teachers analyze how well students grasp their assigned segments and effectively communicate key points to peers, ensuring mastery of the content. Data from assessment tools guide instructional adjustments and enhance comprehension in cooperative learning settings.
Tips for Effective Jigsaw Group Management
Effective jigsaw group management involves assigning clear roles to each member to ensure accountability and active participation. Facilitators should monitor progress closely and intervene promptly to address misunderstandings or conflicts. Establishing structured time limits for discussion phases helps maintain focus and maximizes collaborative learning outcomes.
example of jigsaw in instruction Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com