Retrieval practice in revision involves actively recalling information from memory to enhance learning and retention. For example, students might close their textbooks and write down everything they remember about a historical event before checking their notes. This approach strengthens neural connections related to the studied material and improves long-term recall. Another example of retrieval practice is using flashcards during revision sessions. Learners quiz themselves on key terms, definitions, or concepts without looking at the answers first. Research shows that this method increases memory performance by encouraging repeated retrieval of information, which is critical for mastery in educational settings.
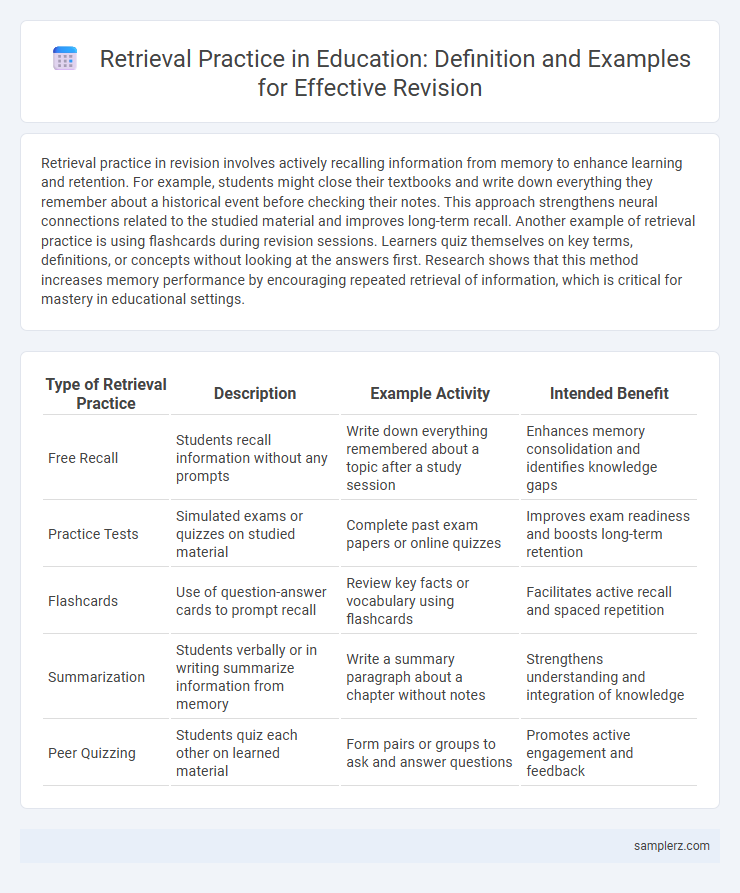
Table of Comparison
| Type of Retrieval Practice | Description | Example Activity | Intended Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Recall | Students recall information without any prompts | Write down everything remembered about a topic after a study session | Enhances memory consolidation and identifies knowledge gaps |
| Practice Tests | Simulated exams or quizzes on studied material | Complete past exam papers or online quizzes | Improves exam readiness and boosts long-term retention |
| Flashcards | Use of question-answer cards to prompt recall | Review key facts or vocabulary using flashcards | Facilitates active recall and spaced repetition |
| Summarization | Students verbally or in writing summarize information from memory | Write a summary paragraph about a chapter without notes | Strengthens understanding and integration of knowledge |
| Peer Quizzing | Students quiz each other on learned material | Form pairs or groups to ask and answer questions | Promotes active engagement and feedback |
Introduction to Retrieval Practice in Revision
Retrieval practice in revision involves actively recalling information from memory instead of passive review, which strengthens long-term retention and understanding. Techniques such as self-quizzing, flashcards, and practice tests encourage learners to reconstruct knowledge, enhancing cognitive connections. Research shows that frequent retrieval practice outperforms rereading by promoting deeper learning and improving exam performance.
Importance of Retrieval Practice for Learning
Retrieval practice enhances long-term retention by actively engaging memory recall during revision, which strengthens neural connections linked to learned material. Frequent self-testing, such as using flashcards or practice quizzes, promotes deeper cognitive processing and reduces forgetting. Research shows students who incorporate retrieval practice into their study routines outperform those relying solely on passive review methods.
Flashcards as a Retrieval Practice Tool
Flashcards serve as an effective retrieval practice tool by prompting active recall of information, which strengthens memory retention and understanding. Utilizing spaced repetition algorithms, digital flashcard apps like Anki optimize learning schedules based on individual performance, enhancing long-term retention. Research shows that consistent use of flashcards during revision significantly improves recall accuracy compared to passive review methods.
Practice Testing Techniques for Revision
Practice testing techniques for revision include self-quizzing, flashcards, and using past exam papers to reinforce memory retrieval. Implementing frequent low-stakes quizzes enhances long-term retention and identifies knowledge gaps effectively. These methods activate active recall, strengthening neural pathways and improving exam performance.
Self-Quizzing Methods for Effective Recall
Self-quizzing methods enhance retrieval practice by encouraging active recall of learned material through flashcards, practice tests, or spaced repetition apps. These techniques strengthen memory consolidation and identify knowledge gaps, leading to improved long-term retention. Incorporating frequent self-assessment sessions during revision boosts cognitive engagement and academic performance.
Using Concept Maps for Retrieval Practice
Using concept maps for retrieval practice enhances long-term memory by enabling learners to visually organize and connect key concepts during revision. This method promotes deeper understanding by requiring active recall and the integration of information rather than passive review. Research shows that students who regularly use concept maps for retrieval practice demonstrate improved retention and higher academic performance in complex subjects.
Spaced Retrieval in Study Schedules
Spaced retrieval in study schedules enhances long-term memory by revisiting material at increasing intervals, such as reviewing vocabulary words after one day, three days, and a week. This technique leverages the psychological spacing effect, reducing forgetting and improving recall efficiency during exams. Implementing spaced retrieval within revision plans optimizes learning retention compared to massed, or crammed, study sessions.
Peer Quizzing and Group Recall Activities
Peer quizzing enhances revision by encouraging students to generate and answer questions collaboratively, reinforcing memory through active engagement. Group recall activities promote collective retrieval of learned material, improving retention by discussing and reconstructing knowledge together. Both methods leverage social interaction to deepen understanding and strengthen long-term memory in educational settings.
Digital Tools for Retrieval Practice
Digital tools like Quizlet and Kahoot enhance retrieval practice by enabling students to actively recall information through interactive quizzes and flashcards. Platforms such as Anki use spaced repetition algorithms to optimize memory retention during revision. These technologies support personalized learning by tracking progress and adapting content based on individual performance data.
Measuring the Impact of Retrieval Practice on Retention
Retrieval practice, such as self-quizzing with flashcards or practice tests, significantly improves long-term retention by reinforcing memory pathways. Research shows students who engage in regular retrieval activities retain up to 50% more information compared to those relying solely on rereading or passive review. Measuring this impact often involves comparing recall accuracy or test scores after intervals ranging from days to weeks, demonstrating the effectiveness of spaced retrieval in strengthening durable learning.
example of retrieval practice in revision Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com