In education, compacting in acceleration refers to the process of streamlining the curriculum to eliminate repetition and focus on advanced content. This method enables gifted students to progress through material at a faster pace by mastering essential concepts quickly. Data shows that compacting can significantly reduce time spent on redundant lessons, allowing more opportunity for enrichment and deeper learning. Educators use assessments and pre-tests to identify which topics students have already mastered before accelerating their instruction. Compacting reallocates instructional time toward developing higher-order thinking skills and complex problem-solving abilities. Research indicates that this approach improves student engagement and academic performance by tailoring education to individual readiness levels.
Table of Comparison
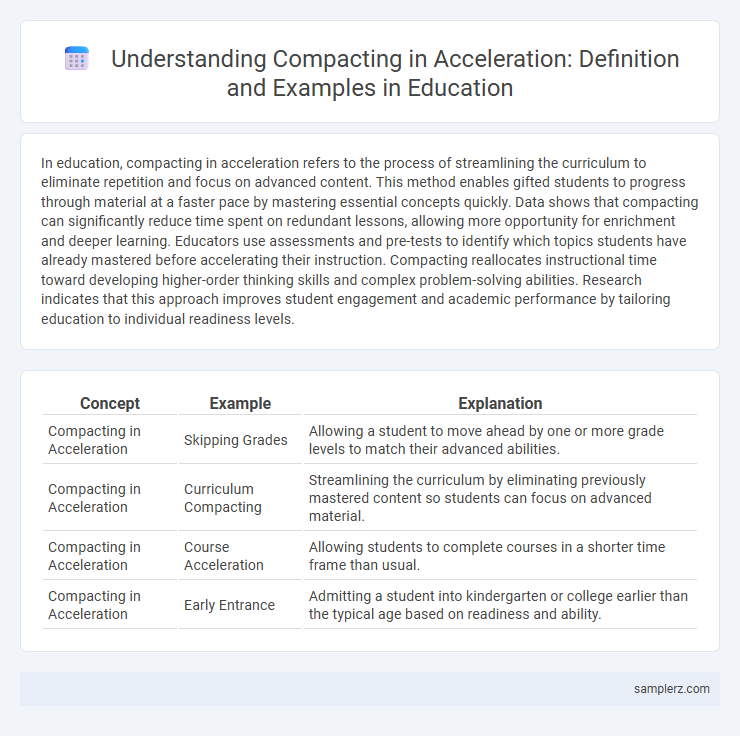
| Concept | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Compacting in Acceleration | Skipping Grades | Allowing a student to move ahead by one or more grade levels to match their advanced abilities. |
| Compacting in Acceleration | Curriculum Compacting | Streamlining the curriculum by eliminating previously mastered content so students can focus on advanced material. |
| Compacting in Acceleration | Course Acceleration | Allowing students to complete courses in a shorter time frame than usual. |
| Compacting in Acceleration | Early Entrance | Admitting a student into kindergarten or college earlier than the typical age based on readiness and ability. |
Understanding Compacting in Academic Acceleration
Compacting in academic acceleration involves streamlining the curriculum by eliminating content that students have already mastered, allowing them to progress faster through subjects. This strategy increases instructional efficiency and enhances student engagement by focusing on new and challenging material. Research shows that compacting can improve academic achievement and motivation, particularly for gifted learners in K-12 settings.
Key Principles of Compacting for Gifted Learners
Compacting in acceleration involves assessing a gifted learner's current knowledge and skills to eliminate redundant instruction, allowing them to progress at an advanced pace. Key principles include pre-assessment to identify mastery, differentiating curriculum to challenge strengths, and providing enriched activities that promote higher-order thinking. This approach maximizes learning efficiency while maintaining engagement and motivation for gifted students.
Steps to Implement Curriculum Compacting in the Classroom
Curriculum compacting involves assessing students' current knowledge through pretests to identify mastery of key concepts, allowing educators to eliminate redundant instruction and provide enriched learning opportunities. Implementing this strategy requires developing tailored compacting plans that outline specific content to be omitted and replacement activities to deepen understanding. Monitoring student progress with formative assessments ensures the accelerated curriculum meets individual educational needs effectively.
Real-Life Examples of Compacting in Elementary Education
Compacting in elementary education accelerates learning by assessing students' prior knowledge and streamlining curriculum to focus on new, challenging content. For example, a third grader who masters basic multiplication may bypass repetitive exercises and engage directly in problem-solving activities involving multi-step word problems. This approach saves time, maintains student motivation, and allows educators to introduce enrichment opportunities aligned with advanced math concepts.
Compacting Strategies for Middle School Accelerated Programs
Compacting strategies in middle school accelerated programs involve pre-assessing students' mastery of curriculum standards to eliminate content they have already learned, allowing more time for advanced or enrichment activities. Examples include curriculum pre-testing, curriculum mapping, and individualized learning plans to ensure efficient pacing and deeper engagement. These methods optimize academic acceleration by tailoring instruction to students' existing knowledge and promoting challenge without redundancy.
Compacting Case Study: High School Math Advancement
In a compacting case study on high school math advancement, students demonstrated mastery by completing standard coursework in half the usual time, allowing them to accelerate to advanced topics like calculus earlier. Teachers utilized pre-assessments and individualized learning plans to identify and support students' strengths, resulting in improved engagement and higher test scores. This model reduced instructional time without sacrificing content quality, effectively promoting accelerated learning in mathematics.
Customizing Compacting for Diverse Student Needs
Customizing compacting in acceleration involves tailoring curriculum adjustments based on individual student abilities, ensuring advanced learners are neither bored nor constrained. Techniques include pre-assessment to identify mastered skills and flexible pacing to allow students to progress at their own rate. This student-centered approach enhances engagement and maximizes academic growth across diverse learning profiles.
Benefits of Compacting in Accelerated Learning
Compacting in accelerated learning streamlines the curriculum by eliminating content students have already mastered, allowing focus on new, challenging material. This method enhances student engagement and motivation by providing personalized learning paths that match their readiness. Improved efficiency leads to higher academic achievement and better preparation for advanced studies.
Challenges and Solutions in Curriculum Compacting
Curriculum compacting accelerates learning by streamlining content to match advanced student readiness, but challenges include accurately identifying essential knowledge and ensuring engagement without gaps. Solutions involve comprehensive pre-assessment tools and differentiated instruction strategies to maintain rigor while eliminating redundancy. Teacher training in curriculum adaptation and ongoing progress monitoring enhances effectiveness and addresses diverse learner needs.
Measuring Success: Outcomes of Compacting in Education
Compacting in education accelerates learning by allowing students to master content at their own pace, focusing on pre-assessment to identify prior knowledge and skill gaps. Measuring success involves analyzing improved student achievement scores, increased engagement levels, and reduced time spent on redundant instruction. Data from standardized tests and formative assessments provide quantifiable evidence of the effectiveness of curriculum compacting strategies.
example of compacting in acceleration Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com