Flunking a course occurs when a student fails to achieve the minimum required grade or standards set by an educational institution. For example, if a university mandates a passing grade of 60% in a mathematics course and a student scores 45%, the student flunks the course. This failure often results in the need to retake the course to meet academic progress requirements. Data from academic institutions indicate that students who flunk courses in core subjects like mathematics and science face delays in graduation timelines. Entity-specific records show that high failure rates in introductory courses contribute to an increase in overall dropout rates. Schools implement targeted interventions, such as tutoring and remedial classes, to reduce the incidence of course failures.
Table of Comparison
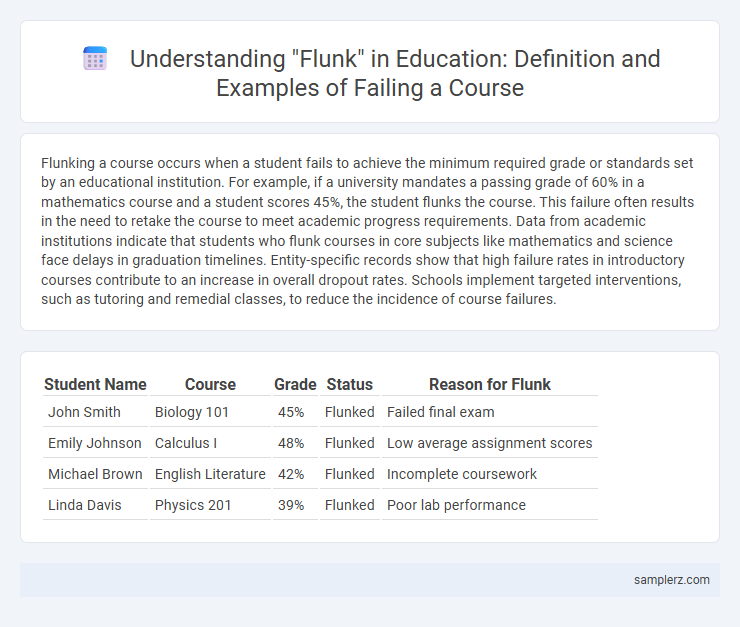
| Student Name | Course | Grade | Status | Reason for Flunk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| John Smith | Biology 101 | 45% | Flunked | Failed final exam |
| Emily Johnson | Calculus I | 48% | Flunked | Low average assignment scores |
| Michael Brown | English Literature | 42% | Flunked | Incomplete coursework |
| Linda Davis | Physics 201 | 39% | Flunked | Poor lab performance |
Common Reasons Students Flunk Courses
Poor time management, lack of preparation, and insufficient understanding of course material are common reasons students flunk courses. Frequent absences and failure to seek help when struggling with complex topics further contribute to academic failure. Additionally, low motivation and external distractions often hinder students' ability to succeed.
Warning Signs You’re At Risk of Failing
Consistently missing assignments and low quiz scores are clear warning signs you're at risk of failing a course. Difficulty understanding key concepts during lectures or falling behind in note-taking can lead to poor exam performance. Frequent absences and lack of participation also strongly correlate with increased chances of flunking a class.
Real-Life Stories: Students Who Flunked
A student who flunked Calculus struggled with time management and underestimated the course's difficulty, leading to a failing grade despite strong performance in other subjects. Another case involved a freshman in Chemistry who missed numerous lab sessions, resulting in an inability to pass the practical exam and ultimately failing the course. These real-life stories highlight common pitfalls such as lack of preparation and attendance that often cause students to flunk critical courses.
How Flunking a Course Impacts Your GPA
Flunking a course significantly lowers your GPA because the failing grade is calculated into your cumulative average, dragging down overall academic performance. Since GPA is often weighted by credit hours, a failed course with more credits has a more severe impact than one with fewer credits. Repeating the course may provide an opportunity to improve your GPA, but policies vary by institution on how grades are averaged.
The Emotional Effects of Failing a Class
Failing a course often triggers intense feelings of disappointment, shame, and frustration, which can undermine a student's self-esteem and motivation. Emotional distress from academic failure may lead to increased anxiety and depressive symptoms, negatively impacting overall mental health. Persistent negative emotions can create a cycle of disengagement, making recovery and academic improvement more challenging.
Steps to Take After Flunking a Course
After flunking a course, immediately review the course syllabus and identify areas where performance was lacking, such as missed assignments or failed exams. Schedule a meeting with the instructor or academic advisor to discuss options for retaking the course or enrolling in supplemental tutoring programs. Develop a study plan incorporating time management techniques and utilize campus resources like study groups or academic workshops to improve understanding and avoid repeating the failure.
Academic Probation: What It Means
Academic probation occurs when a student's GPA falls below the institution's minimum requirement, often set at 2.0 on a 4.0 scale, signaling unsatisfactory academic performance. For example, a student who fails multiple courses in a semester and ends with a cumulative GPA of 1.8 may be placed on academic probation, requiring immediate improvement to avoid suspension. This status serves as a formal warning and provides resources or restrictions to help students regain good standing.
Tips to Avoid Failing in School
Consistently attending classes and actively participating in discussions helps reinforce understanding and retention of course material. Developing a structured study schedule and utilizing resources such as tutoring centers or study groups strengthens academic performance. Staying organized with assignments and seeking clarification from instructors promptly can prevent misunderstandings that often lead to failing grades.
Can You Retake a Failed Course?
Failing a course often raises concerns about academic progress, but many educational institutions offer the opportunity to retake the failed course. Students can typically enroll again in the same class to improve their grades and meet graduation requirements, although policies on grade replacement vary by school. Retaking a course not only enhances understanding of the material but also positively impacts GPA and transcript records when the institution allows the new grade to replace the failing one.
Moving Forward After Academic Failure
Failing a course in college, such as a core math or writing class, often signals the need for reassessment of study habits and time management strategies. Students can move forward after academic failure by seeking support from academic advisors, utilizing tutoring centers, and developing a structured study schedule. Emphasizing resilience and proactive planning helps improve future academic performance and regain confidence.
example of flunk in course Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com