Deschooling in education reform involves removing traditional structures and rigid schedules from the learning process. This approach encourages learners to explore knowledge outside formal classrooms, fostering self-directed learning and critical thinking. Entities such as homeschooling networks and democratic schools exemplify deschooling by prioritizing student autonomy and personalized education paths. Data from recent studies show that deschooling methods improve engagement and creativity among students. These reforms challenge conventional metrics by emphasizing experiential learning and social development. Schools implementing deschooling strategies report increased student satisfaction and adaptability, highlighting the shift towards more flexible and inclusive educational ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
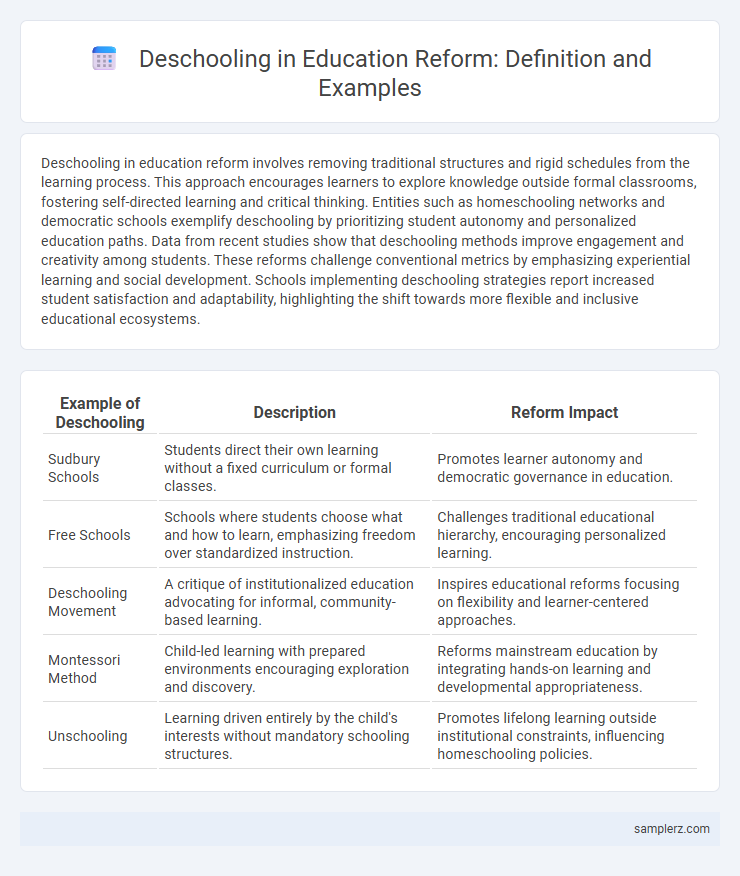
| Example of Deschooling | Description | Reform Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sudbury Schools | Students direct their own learning without a fixed curriculum or formal classes. | Promotes learner autonomy and democratic governance in education. |
| Free Schools | Schools where students choose what and how to learn, emphasizing freedom over standardized instruction. | Challenges traditional educational hierarchy, encouraging personalized learning. |
| Deschooling Movement | A critique of institutionalized education advocating for informal, community-based learning. | Inspires educational reforms focusing on flexibility and learner-centered approaches. |
| Montessori Method | Child-led learning with prepared environments encouraging exploration and discovery. | Reforms mainstream education by integrating hands-on learning and developmental appropriateness. |
| Unschooling | Learning driven entirely by the child's interests without mandatory schooling structures. | Promotes lifelong learning outside institutional constraints, influencing homeschooling policies. |
Understanding Deschooling: Key Concepts in Educational Reform
Deschooling involves dismantling traditional school structures to promote learner autonomy and personalized education paths. It emphasizes informal learning environments, community engagement, and experiential education as essential components in reform efforts. Key concepts include reducing reliance on standardized curricula and fostering critical thinking through self-directed learning models.
Historical Movements: Early Examples of Deschooling Efforts
The Summerhill School, founded by A.S. Neill in 1921, exemplifies early deschooling efforts by prioritizing student autonomy and voluntary learning over formal curricula. Similarly, Ivan Illich's 1971 book "Deschooling Society" critiqued institutionalized education and advocated for learning webs that empower learners outside traditional schools. These historical movements laid the groundwork for progressive education reforms that challenge conventional schooling structures.
Community-Led Learning: Case Studies in Deschooling Practice
Community-led learning initiatives such as the Big Picture Learning network exemplify deschooling in reform by prioritizing personalized, student-driven education guided by community mentors. These programs dismantle traditional classroom structures, fostering experiential learning through real-world projects aligned with local needs. Research indicates that students engaged in community-led models demonstrate higher motivation and improved critical thinking skills compared to conventional schooling systems.
Montessori and Unschooling: Alternative Pathways in Reform
Montessori education emphasizes self-directed learning through hands-on materials, fostering autonomy and critical thinking in students. Unschooling promotes child-led learning without a fixed curriculum, encouraging exploration based on individual interests and intrinsic motivation. Both approaches exemplify deschooling by challenging traditional educational structures and prioritizing personalized, experiential learning pathways.
Deschooling in Finland: Success Stories and Outcomes
Deschooling in Finland revolutionized education by replacing traditional classroom settings with personalized learning plans and less formal, student-centered environments. Finnish reforms emphasize trust in educators, minimal standardized testing, and equal access to high-quality education, resulting in consistently high PISA scores and global recognition. This approach fosters creativity, critical thinking, and lifelong learning skills, contributing to Finland's status as a leader in educational outcomes.
Homeschooling Networks: Modern Approaches to Deschooling
Homeschooling networks exemplify modern approaches to deschooling by creating collaborative communities that prioritize personalized learning without traditional classroom constraints. These networks use digital platforms and peer support to foster autonomy, critical thinking, and experiential education, challenging standard curricula and promoting flexible knowledge acquisition. The deschooling process within these networks facilitates a transition from institutionalized education to learner-driven exploration, emphasizing real-world skills and intrinsic motivation.
Technology-Driven Deschooling: Digital Platforms and Open Education
Technology-driven deschooling leverages digital platforms such as Khan Academy, Coursera, and edX to provide accessible, self-paced learning outside traditional classrooms. Open education initiatives promote free access to high-quality resources, enabling learners worldwide to customize education according to individual needs. This reform model reduces reliance on standardized curricula by empowering students with flexible, technology-enhanced educational pathways.
Social Justice and Equity in Deschooling Reforms
Deschooling reforms emphasize dismantling traditional educational hierarchies to promote social justice by valuing diverse learning styles and community knowledge. Programs like Sudbury schools and democratic education models prioritize equity by empowering students from marginalized backgrounds to co-create curricula that reflect their cultural identities. This approach addresses systemic inequalities, ensuring inclusive access and fostering critical consciousness among all learners.
Policy Shifts: Government Strategies Embracing Deschooling
Government strategies embracing deschooling prioritize increased funding for community-based learning centers and the integration of experiential, student-led curricula within public education systems. Policy shifts include dismantling standardized testing mandates and promoting digital platforms that facilitate personalized, interest-driven learning outside traditional classroom settings. These reforms reflect a commitment to decentralized education models that foster autonomy, critical thinking, and lifelong learning skills.
Future Directions: Emerging Trends in Deschooling and Educational Change
Emerging trends in deschooling emphasize personalized learning environments that leverage technology to foster self-directed education outside traditional classrooms. Innovative models incorporate project-based and experiential learning, promoting student autonomy and critical thinking skills aligned with 21st-century competencies. Future directions also explore decentralized education networks, where community engagement and digital platforms enable continuous, adaptive learning pathways.
example of deschooling in reform Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com