Rubrication in a syllabus involves the clear categorization and labeling of learning outcomes, assessment criteria, and grading standards. For example, a syllabus might use rubrication to outline specific performance levels for an essay assignment, with categories such as "Content Understanding," "Organization," and "Language Use." Each category is further detailed with descriptors that define what constitutes excellent, good, average, and poor work, providing measurable benchmarks for student evaluation. This structured approach enhances transparency and consistency in grading, helping both instructors and students understand expectations. It supports data-driven assessment by linking student performance to defined criteria, facilitating targeted feedback and improvement. Entities such as learning objectives, assessment tasks, and performance indicators are systematically organized within the rubricated syllabus to optimize educational outcomes.
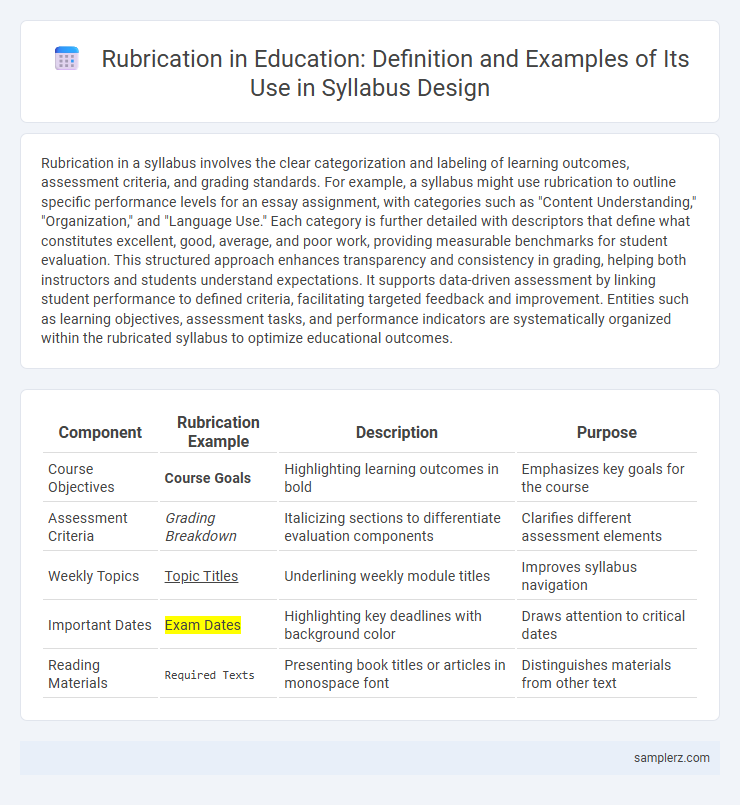
Table of Comparison
| Component | Rubrication Example | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Course Objectives | Course Goals | Highlighting learning outcomes in bold | Emphasizes key goals for the course |
| Assessment Criteria | Grading Breakdown | Italicizing sections to differentiate evaluation components | Clarifies different assessment elements |
| Weekly Topics | Topic Titles | Underlining weekly module titles | Improves syllabus navigation |
| Important Dates | Exam Dates | Highlighting key deadlines with background color | Draws attention to critical dates |
| Reading Materials | Required Texts |
Presenting book titles or articles in monospace font | Distinguishes materials from other text |
Understanding Rubrication in Syllabus Development
Rubrication in syllabus development involves clearly defining assessment criteria to enhance student understanding and guide performance expectations. A well-structured rubric categorizes learning outcomes, assigns weightage, and provides descriptive levels of achievement, facilitating transparent grading and feedback. This approach promotes consistency in evaluation and helps students identify key competencies for mastery throughout the course.
Key Elements of a Rubric in Educational Syllabi
Key elements of a rubric in educational syllabi include clear criteria outlining specific learning objectives, performance levels that describe varying degrees of achievement, and detailed descriptors that provide measurable expectations for student work. Effective rubrics enhance assessment transparency by aligning course goals with grading standards, enabling objective evaluation of student performance. Incorporating well-defined criteria and performance indicators fosters consistency and clarity in the assessment process within educational frameworks.
Benefits of Incorporating Rubrics in Course Outlines
Incorporating rubrics in course outlines enhances clarity by providing explicit criteria for assessment, which helps students understand expectations and learning objectives. This transparency supports consistent and objective grading, reducing ambiguity and bias in evaluation. Rubrication also fosters self-regulation in learners by guiding their focus on key competencies, ultimately improving academic performance and motivation.
Sample Rubric Structures for Assessment Criteria
Sample rubric structures for assessment criteria in syllabi often include clear categories such as understanding of content, application of concepts, critical thinking, and communication skills. Each category is typically rated on a scale (e.g., 1-4 or 1-5) with detailed descriptors outlining performance levels from novice to exemplary. Incorporating precise, measurable criteria within rubrics enhances transparency and guides students in meeting academic expectations effectively.
Integrating Learning Outcomes with Rubrication
Integrating learning outcomes with rubrication enhances syllabus clarity by explicitly aligning assessment criteria with desired competencies such as critical thinking, collaboration, and content mastery. This approach facilitates transparent evaluation through detailed performance levels, guiding students in understanding expectations and promoting targeted skill development. Rubricated syllabi also support instructors in consistently measuring progress and providing actionable feedback tied directly to defined educational goals.
Rubric Examples for Grading Classroom Participation
Rubric examples for grading classroom participation typically include criteria such as frequency of contributions, quality of comments, and engagement with peers, each rated on a scale from poor to excellent. For instance, "Rarely contributes or engages" may score 1 point, while "Consistently offers insightful comments and encourages discussion" scores 5 points. These rubrics provide clear standards for assessing participation, promoting fairness and transparency in evaluation.
Designing Rubrics for Project-Based Learning
Designing rubrics for project-based learning involves clearly defining criteria that assess critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity, ensuring alignment with learning objectives. Each performance level should describe specific evidence of student mastery, facilitating transparent evaluation and consistent feedback. Incorporating dimensions such as problem-solving skills, presentation quality, and application of knowledge enhances the effectiveness of the syllabus rubric.
Case Study: Rubric Application in a Syllabus
Case Study: Rubric Application in a Syllabus demonstrates how clear assessment criteria enhance student understanding and performance expectations. Rubrics provide detailed descriptors for grading, facilitating consistent evaluation and targeted feedback across diverse assignments. Integrating rubrics within syllabi supports transparent communication of learning outcomes and performance standards in educational settings.
Tips for Creating Effective Rubrics in Syllabi
Effective rubrication in syllabi involves clearly defining assessment criteria aligned with learning objectives, ensuring transparency in grading standards for students. Incorporate descriptive performance levels that distinguish various degrees of achievement, facilitating objective and consistent evaluation across assignments. Use concise and specific language in rubrics to enhance student understanding and guide improvement effectively throughout the course.
Evaluating Student Performance Using Rubrics
Evaluating student performance using rubrics involves clearly defining criteria and performance levels for each assignment or activity within the syllabus, such as specifying categories like comprehension, analysis, and creativity. Rubrics provide consistent, objective measures that help educators assess varying degrees of student achievement and offer transparent feedback tailored to learning outcomes. Integrating detailed rubrication in syllabi enhances fairness and clarity in grading, guiding students on expectations and areas for improvement.
example of rubrication in syllabus Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com