Cangiante is a Renaissance painting technique characterized by the use of different hues to depict light and shadow on drapery, creating a vivid and dynamic effect. This method often employs contrasting colors, such as shifting from green to yellow or red to orange, to enhance the volume and texture of fabric folds. Giotto's frescoes and Michelangelo's Sistine Chapel ceiling showcase prominent examples where cangiante brings lifelike vibrancy to draped garments. Artists utilized cangiante to overcome the limitations of available pigments, enriching the visual depth of textiles in their compositions. Tintoretto, a master of Venetian Renaissance art, frequently applied this approach to render luxurious silks and velvets with dramatic color transitions. The technique emphasizes color contrast over tonal gradation, making the fabric appear illuminated and three-dimensional within the artwork.
Table of Comparison
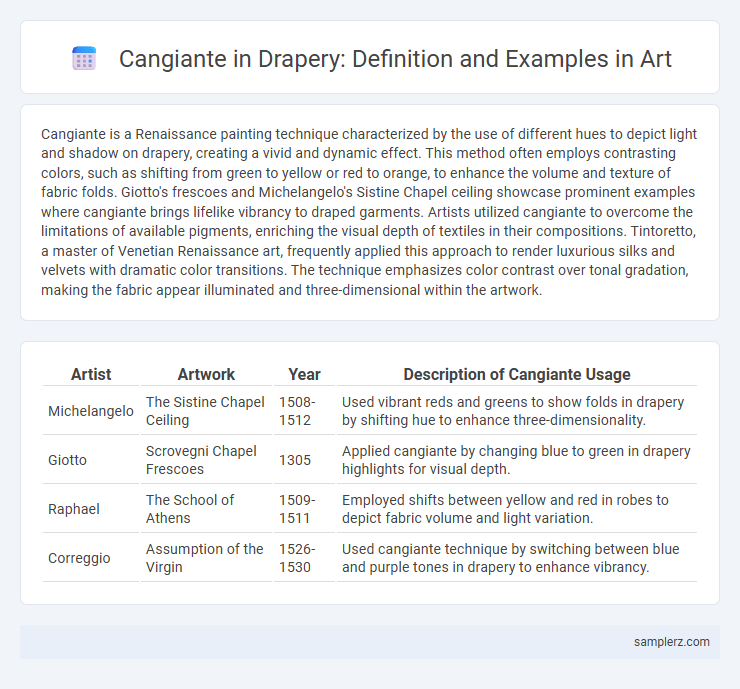
| Artist | Artwork | Year | Description of Cangiante Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Michelangelo | The Sistine Chapel Ceiling | 1508-1512 | Used vibrant reds and greens to show folds in drapery by shifting hue to enhance three-dimensionality. |
| Giotto | Scrovegni Chapel Frescoes | 1305 | Applied cangiante by changing blue to green in drapery highlights for visual depth. |
| Raphael | The School of Athens | 1509-1511 | Employed shifts between yellow and red in robes to depict fabric volume and light variation. |
| Correggio | Assumption of the Virgin | 1526-1530 | Used cangiante technique by switching between blue and purple tones in drapery to enhance vibrancy. |
Understanding Cangiante: A Renaissance Coloring Technique
Cangiante is a Renaissance coloring technique characterized by the use of contrasting hues to depict shadows and highlights in drapery, creating a vivid and dynamic effect. Artists like Michelangelo employed cangiante to enhance the texture and volume of fabric by shifting from one color to another, such as from green to yellow or red to orange, rather than relying solely on light and dark shades of a single hue. This technique brought Renaissance paintings to life, emphasizing the sculptural quality of clothing and contributing to the emotional expression within compositions.
Historical Origins of Cangiante in Drapery Art
Cangiante, a vibrant color technique characterized by dramatic shifts in hue to depict light and shadow, originated during the Italian Renaissance, prominently featured in works by Michelangelo and Raphael. This method enhanced the three-dimensionality of drapery by shifting colors to represent folds and volume without relying solely on tonal variations. Historical frescoes in the Sistine Chapel exemplify cangiante's role in creating dynamic, expressive fabric textures that challenge traditional shading methods.
Characteristics of Cangiante in Fabric Depiction
Cangiante in fabric depiction is characterized by dramatic color shifts that enhance the perception of volume and light on drapery folds, often contrasting with the natural hues of the fabric. This technique uses bold, unexpected pigments such as transitioning from green to yellow or red to orange, creating a vibrant interplay of shadows and highlights. The intentional departure from realistic color replication emphasizes texture and depth, making the fabric appear dynamic and richly dimensional.
Notable Artists Who Used Cangiante in Drapery
Michelangelo employed cangiante in drapery to create dynamic shifts in color that enhanced the volumetric form of his figures in the Sistine Chapel ceiling. Raphael also utilized this technique, blending hues to depict the intricate folds and light interactions in his Madonna series. Titian's use of cangiante in drapery emphasized vibrant contrasts, enriching the texture and depth within his Renaissance portraits.
Iconic Renaissance Paintings Featuring Cangiante Draperies
Iconic Renaissance paintings such as Michelangelo's "The Last Judgment" showcase cangiante draperies through bold shifts from red to green or blue, emphasizing volume and light with vibrant color contrasts. Raphael's "The School of Athens" also features this technique, using dramatic color changes in fabric to define folds and depth, enhancing the three-dimensionality of the scene. These masterpieces illustrate cangiante's role in Renaissance art as a dynamic method to depict fabric texture and form beyond traditional shading.
Step-by-Step Analysis of Cangiante in Michelangelo’s Works
Michelangelo's use of cangiante in drapery is evident in the Sistine Chapel ceiling, where he applies contrasting hues to depict light and shadow on fabric folds. Instead of traditional shading, he shifts colors from dark blues to vibrant greens and reds, enhancing depth and volume dynamically. This technique highlights the sculptural quality of the drapery, emphasizing form through bold color transitions that define physical structure and movement.
Comparing Cangiante with Other Color Techniques in Drapery
Cangiante, a Renaissance painting technique, uses vibrant color shifts to depict drapery folds by transitioning to a different hue rather than relying solely on light and dark shades, unlike chiaroscuro which focuses on tonal contrast. This method creates dynamic, eye-catching fabric textures, contrasting with sfumato's soft, blended edges that evoke subtle volume and atmosphere. Cangiante's bold color contrasts enhance the visual impact of drapery, making it distinct in works by artists like Michelangelo compared to the more tonal or gradient approaches of Leonardo da Vinci and Raphael.
Visual Impact of Cangiante on Textiles and Garments
Cangiante dramatically enhances the visual impact of textiles and garments by shifting hues to create vibrant, luminous effects that simulate volume and movement in drapery. This technique leverages contrasting colors to highlight folds and contours, resulting in a dynamic interplay of light and shadow that brings fabric to life. Masters like Michelangelo employed cangiante to transform flat surfaces into rich, three-dimensional textures, elevating the realism and emotional intensity of painted garments.
Practical Tips for Painting Drapery Using Cangiante
Using cangiante in painting drapery involves shifting hues to convey light and shadow without relying solely on value changes, typically transitioning from a base color to a brighter or warmer tone on highlighted folds. Practical tips include selecting complementary or analogous colors to maintain harmony and enhance depth, such as moving from deep blue shadows to vibrant purples or warm reds on illuminated areas. Applying cangiante encourages bold color contrasts that emphasize the fabric's texture and form, creating dynamic and visually rich drapery effects.
The Legacy of Cangiante in Contemporary Drapery Art
Cangiante is evident in contemporary drapery art through the vibrant shifts in color tones that enhance fabric texture and depth, echoing Renaissance masters like Michelangelo. Artists employ contrasting hues such as bold reds and greens or blues and yellows to simulate light reflections and shadows, creating dynamic visual movement. This technique enriches the tactile illusion of drapery, sustaining cangiante's legacy by transforming static fabric into expressive, almost sculptural forms in modern artworks.
example of cangiante in drapery Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com