Sgraffito in ceramic art is a decorative technique where layers of colored slip or glaze are scratched away to reveal a contrasting surface beneath. This method creates intricate designs and textures on pottery, showcasing the artist's precision and creativity. It is widely used in various cultural ceramic traditions, such as Italian Renaissance maiolica and Mexican talavera. One prominent example of sgraffito in ceramic art is the work of Pablo Picasso during his experimentation with ceramics at the Madoura Pottery in Vallauris, France. Picasso utilized sgraffito to etch bold, expressive lines onto glazed vessels, merging traditional methods with modern artistic forms. These pieces highlight the versatility of sgraffito as a medium for fine art and functional ceramics.
Table of Comparison
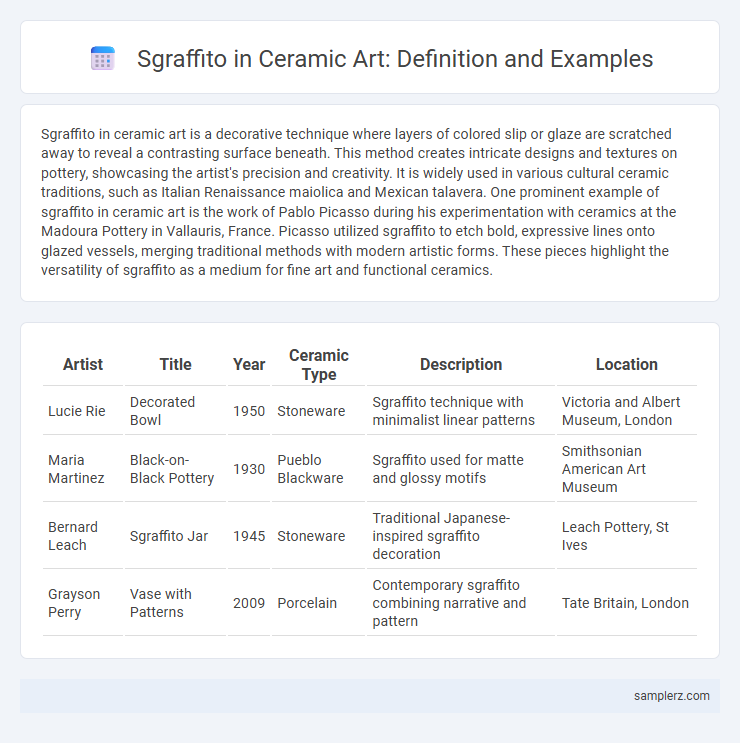
| Artist | Title | Year | Ceramic Type | Description | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lucie Rie | Decorated Bowl | 1950 | Stoneware | Sgraffito technique with minimalist linear patterns | Victoria and Albert Museum, London |
| Maria Martinez | Black-on-Black Pottery | 1930 | Pueblo Blackware | Sgraffito used for matte and glossy motifs | Smithsonian American Art Museum |
| Bernard Leach | Sgraffito Jar | 1945 | Stoneware | Traditional Japanese-inspired sgraffito decoration | Leach Pottery, St Ives |
| Grayson Perry | Vase with Patterns | 2009 | Porcelain | Contemporary sgraffito combining narrative and pattern | Tate Britain, London |
Introduction to Sgraffito in Ceramic Art
Sgraffito in ceramic art involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, creating intricate designs and textures. This technique dates back to ancient civilizations and remains popular for its ability to add depth and detail to pottery. Contemporary artists often combine sgraffito with glazing methods to enhance the visual complexity of ceramic pieces.
Historical Origins of Sgraffito Technique
The sgraffito technique in ceramics originated during the Renaissance period in Italy, where artisans scratched through a layer of colored slip to reveal a contrasting clay body beneath. This method was widely used in 15th-century Italian maiolica pottery, exemplified by Urbino ware, known for its intricate designs and vibrant colors. Historical sgraffito pieces often reflect cultural and artistic influences from both Islamic pottery traditions and European medieval art.
Notable Ancient Sgraffito Ceramics
Notable ancient sgraffito ceramics include the Byzantine bowls from the 10th century, featuring intricate scratched designs revealing contrasting clay layers. Early Islamic pottery, such as the 9th-century Abbasid ceramics, displays sgraffito techniques with floral and geometric patterns carved through slip layers. These ancient examples highlight the cultural significance and technical mastery of sgraffito decoration in historic ceramic art.
Renaissance Sgraffito Ceramics Examples
Renaissance sgraffito ceramics showcase intricate designs achieved by scratching through a surface layer of slip to reveal contrasting clay beneath, exemplified by Italian maiolica from the 15th and 16th centuries. Notable examples include Deruta and Urbino pottery, where artisans created detailed narrative scenes and floral motifs using this technique. These ceramics reflect the period's emphasis on classical themes and innovations in glazing, cementing sgraffito as a hallmark of Renaissance ceramic art.
Sgraffito in Contemporary Ceramic Art
Sgraffito in contemporary ceramic art involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, creating intricate, textured designs. Artists like Betty Woodman and Magdalene Odundo utilize sgraffito to explore themes of identity and nature, blending traditional techniques with modern aesthetics. This method enriches ceramic surfaces with depth and narrative, making it a pivotal technique in innovative ceramic expressions.
Regional Variations in Sgraffito Ceramics
Sgraffito ceramics exhibit notable regional variations, with Italian potters in Deruta emphasizing intricate floral motifs and geometric patterns, while Mexican Talavera artisans integrate vibrant colors and bold designs reflecting indigenous culture. In Moroccan sgraffito, artisans employ earthy tones and repetitive linear carvings, showcasing traditional Berber influences unique to the region. These regional styles highlight the cultural significance and localized techniques that define the sgraffito ceramic art form worldwide.
Influential Ceramic Artists Using Sgraffito
Pablo Picasso revolutionized ceramic art by integrating sgraffito techniques, using intricate scratched patterns to enhance form and texture. Maria Martinez, renowned for black-on-black pottery, employed sgraffito to create contrasting designs that highlight cultural symbolism. Ruthandro Heinz's contemporary ceramics showcase sgraffito's versatility in layering distinct textures and colors for dynamic visual effects.
Museum-Displayed Sgraffito Ceramic Works
Museum-displayed sgraffito ceramic works showcase intricate designs achieved by scratching through surface layers to reveal contrasting colors beneath, exemplified by the renowned pieces at the Victoria and Albert Museum. These artifacts highlight traditional techniques from regions like Italy's Deruta and modern adaptations found in contemporary art galleries such as the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. The combination of texture and color in sgraffito ceramics emphasizes both historical craftsmanship and artistic innovation.
Step-by-Step Examples of Creating Sgraffito
Creating sgraffito in ceramics begins by applying a contrasting layer of colored slip or underglaze over a leather-hard clay surface. Artists carefully scratch intricate designs into the top layer using a sharp tool, revealing the clay body underneath to create detailed patterns. After drying, the piece is bisque fired and often glazed, preserving the sgraffito design while adding a glossy finish.
Sgraffito Ceramics in Modern Design and Decor
Sgraffito ceramics in modern design leverage the ancient technique of scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, creating intricate patterns and textures that add depth to contemporary decor. Artists apply sgraffito on porcelain and stoneware, blending traditional craftsmanship with sleek, minimalist aesthetics to enhance visual interest in functional pieces. This fusion of heritage and innovation positions sgraffito ceramics as a popular choice in boutique interiors and artisanal homeware collections.
example of sgraffito in ceramic Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com