Sgraffito is a decorative technique used in mural art that involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting layer beneath. One notable example of sgraffito in murals can be found in Renaissance frescoes, such as those in the Palazzo Massimo alle Colonne in Rome, where intricate designs emerge from textured plaster layers. This method enhances visual depth and adds a tactile element to the artwork, making it a distinctive feature in historical and contemporary murals. Artists apply layers of colored plaster or paint in succession, then scratch specific patterns or images, exposing the underlying layer's color to create striking contrasts. The sgraffito technique is prominent in various cultural contexts, including Mediterranean and Mexican mural art, showcasing its versatility across different artistic traditions. This approach not only serves aesthetic purposes but also demonstrates the artist's skill in manipulating materials to achieve complex visual effects.
Table of Comparison
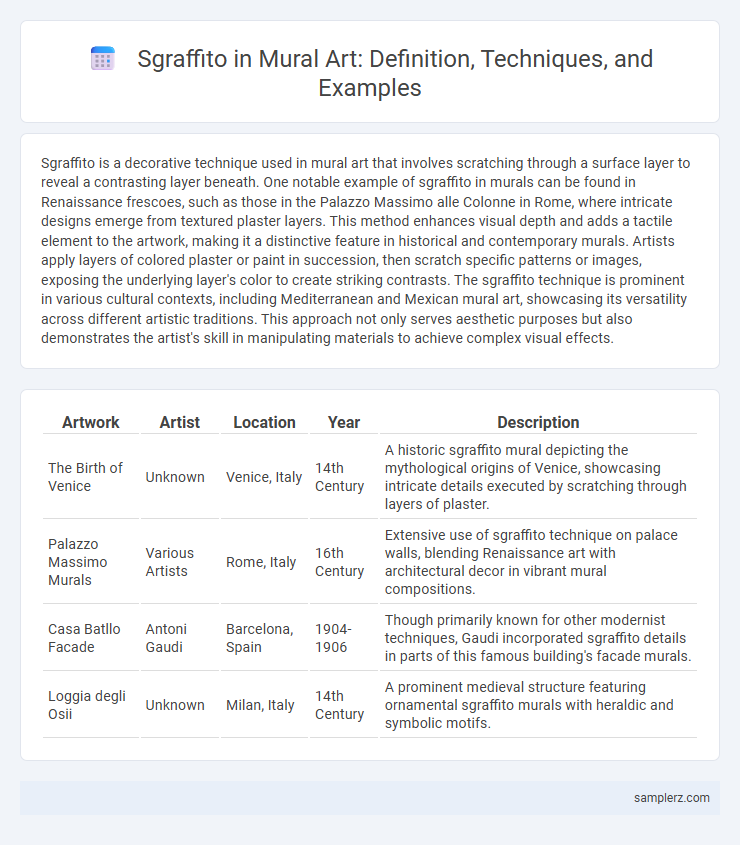
| Artwork | Artist | Location | Year | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Birth of Venice | Unknown | Venice, Italy | 14th Century | A historic sgraffito mural depicting the mythological origins of Venice, showcasing intricate details executed by scratching through layers of plaster. |
| Palazzo Massimo Murals | Various Artists | Rome, Italy | 16th Century | Extensive use of sgraffito technique on palace walls, blending Renaissance art with architectural decor in vibrant mural compositions. |
| Casa Batllo Facade | Antoni Gaudi | Barcelona, Spain | 1904-1906 | Though primarily known for other modernist techniques, Gaudi incorporated sgraffito details in parts of this famous building's facade murals. |
| Loggia degli Osii | Unknown | Milan, Italy | 14th Century | A prominent medieval structure featuring ornamental sgraffito murals with heraldic and symbolic motifs. |
Defining Sgraffito: Technique and Origins in Murals
Sgraffito in murals is a decorative technique involving scratching through a surface layer of plaster or paint to reveal a contrasting color beneath, creating intricate designs and textures. Originating in classical Mediterranean architecture and widely used during the Renaissance, this method combines layering and incising to produce detailed, durable wall art. Famous examples include the 15th-century frescoes in Florence, where artists employed sgraffito to enhance depth and visual interest in public and religious spaces.
Historical Evolution of Sgraffito in Wall Art
Sgraffito in wall art evolved significantly from its origins in Renaissance Italy, where artists scratched through plaster layers to reveal contrasting colors beneath, creating intricate designs and narratives. This technique gained prominence in the Baroque period, integrating dramatic textures and vibrant contrasts on murals, particularly in Central European churches and palaces. Modern applications of sgraffito incorporate contemporary themes and mixed media, preserving its historical essence while adapting to new artistic expressions.
Notable Global Sgraffito Mural Examples
Notable global sgraffito mural examples include the 15th-century Casa delle Armi in Italy, showcasing intricate Renaissance designs carved into plaster surfaces. The facade of the Antonin Dvorak Theatre in the Czech Republic features elaborate sgraffito murals depicting cultural motifs and historical scenes. In Mexico City, Diego Rivera's use of sgraffito techniques in public murals highlights indigenous themes through layered plaster and pigment, emphasizing texture and depth.
Sgraffito in Renaissance and Baroque Murals
Sgraffito in Renaissance and Baroque murals exemplifies the technique's intricate layering and precise incisions, revealing contrasting colors beneath plaster surfaces to create detailed imagery. Prominent examples include the frescoes by Italian artists like Andrea Mantegna and Annibale Carracci, whose works showcase dynamic narratives and texture. This method enhanced visual depth and was integral to decorating palaces and churches, reflecting the era's artistic innovation in mural art.
Contemporary Applications of Sgraffito in Urban Murals
Contemporary applications of sgraffito in urban murals showcase intricate layers of color and texture etched into concrete and plaster surfaces, revitalizing cityscapes with dynamic visual narratives. Artists blend traditional sgraffito techniques with modern themes, creating immersive public artworks that engage diverse communities. Notable examples include large-scale murals in cities like Berlin and Mexico City, where sgraffito enhances cultural expression and urban identity.
Famous Artists Employing Sgraffito in Mural Creation
Famous artists like Diego Rivera and Wassily Kandinsky employed sgraffito in mural creation to add texture and dimension to their works. Rivera's murals often showcased intricate layers of plaster scraped away to reveal contrasting colors beneath, enhancing the visual narrative. Kandinsky integrated sgraffito techniques in his abstract compositions, using the method to create dynamic surface effects that emphasized form and movement.
Sgraffito Techniques: Tools and Materials for Murals
Sgraffito techniques in murals involve layering contrasting plaster colors and then scratching through the top layer to reveal the underlying hue, creating intricate designs. Artists typically use tools such as metal styluses, knives, or trowels to carve precise details into the plaster surface. Common materials include lime-based plasters combined with pigments, ensuring durability and vibrant color retention in large-scale wall art.
Iconic Sgraffito Murals: Case Studies
Sgraffito murals, such as the iconic work on the facade of the Old Town Hall in Prague, showcase intricate layering techniques where contrasting plaster colors are scratched to reveal detailed imagery. Another famous example is the 16th-century sgraffito murals by Italian Renaissance artists, featuring mythological and religious themes that enhance architectural surfaces. These case studies highlight sgraffito's enduring appeal in mural art, blending texture and narrative in public spaces.
Sgraffito’s Cultural Significance in Public Art
Sgraffito murals showcase intricate scratch techniques that reveal contrasting layers of colored plaster, embodying rich cultural narratives intertwined with local heritage. These artworks serve as public symbols of community identity, preserving historical stories and traditions through textured visual language. Their presence in urban spaces fosters cultural continuity and collective memory, enhancing public engagement with art's historical roots.
Preserving and Restoring Sgraffito Murals Today
Preserving and restoring sgraffito murals requires specialized techniques to protect the delicate layers of colored plaster and intricate designs characteristic of this art form. Conservation efforts often include careful cleaning, stabilization of the plaster substrate, and the use of compatible materials to fill losses without compromising the original texture. Modern technologies such as laser cleaning and digital imaging assist restorers in maintaining the visual integrity and historical significance of sgraffito murals in contemporary settings.
example of sgraffito in mural Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com