Craquelure is a fine network of cracks that often appears on the surface of paintings, especially on canvas. A well-known example of craquelure is found in Leonardo da Vinci's "Mona Lisa," where the aging varnish and paint layers have developed intricate crack patterns. These cracks provide valuable information about the painting's age, materials, and environmental conditions. In art conservation, craquelure serves as a diagnostic tool to authenticate and analyze historical artworks. The patterns vary depending on the type of paint, drying time, and the canvas substrate used by the artist. Studying craquelure helps experts understand the painting's provenance and guides restoration efforts to preserve the artwork's integrity.
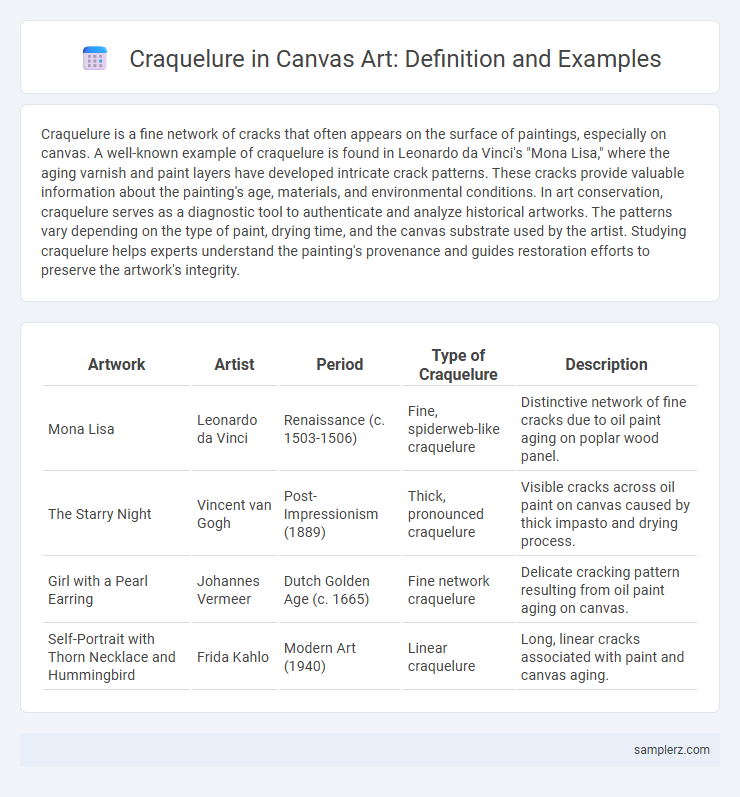
Table of Comparison
| Artwork | Artist | Period | Type of Craquelure | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mona Lisa | Leonardo da Vinci | Renaissance (c. 1503-1506) | Fine, spiderweb-like craquelure | Distinctive network of fine cracks due to oil paint aging on poplar wood panel. |
| The Starry Night | Vincent van Gogh | Post-Impressionism (1889) | Thick, pronounced craquelure | Visible cracks across oil paint on canvas caused by thick impasto and drying process. |
| Girl with a Pearl Earring | Johannes Vermeer | Dutch Golden Age (c. 1665) | Fine network craquelure | Delicate cracking pattern resulting from oil paint aging on canvas. |
| Self-Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird | Frida Kahlo | Modern Art (1940) | Linear craquelure | Long, linear cracks associated with paint and canvas aging. |
Understanding Craquelure: Definition and Origins
Craquelure refers to the fine network of cracks that naturally develops on the surface of painted canvases due to aging, drying, and environmental factors affecting the paint and varnish layers. This phenomenon provides valuable insights into the artwork's age, authenticity, and the materials used by artists, often observed in masterpieces from the Renaissance or Baroque periods. Understanding craquelure helps art conservators determine appropriate restoration techniques and preserve the painting's historical integrity.
Famous Artworks Exhibiting Craquelure
The Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci exhibits delicate craquelure patterns that have developed over centuries, contributing to its aged and iconic appearance. Rembrandt's Night Watch also showcases pronounced craquelure, revealing the natural aging of its oil paint layers on canvas. Van Gogh's Starry Night features distinct craquelure that enhances the texture and vibrancy of the swirling brushstrokes.
Key Causes of Craquelure in Canvas Paintings
Craquelure in canvas paintings primarily results from natural aging processes, where the drying and shrinking of oil paint layers create fine cracks on the surface. Environmental factors such as fluctuations in temperature and humidity accelerate the formation of craquelure by causing expansion and contraction of both the paint and the underlying canvas. Mechanical stress from handling or improper stretching of the canvas further contributes to the development of these distinctive crack patterns.
Craquelure Patterns in Renaissance Masterpieces
Craquelure patterns in Renaissance masterpieces, such as Leonardo da Vinci's "Mona Lisa" and Raphael's "The School of Athens," reveal intricate networks of fine cracks caused by the natural aging of oil paint on canvas. These patterns serve as important indicators of authenticity and provenance, reflecting the unique drying and curing processes of pigments used during the 15th and 16th centuries. Conservation experts analyze variations in crack density and direction to understand the environmental history and preservation state of these iconic artworks.
How Craquelure Reveals a Painting’s Age
Craquelure, the network of fine cracks that naturally develops on a canvas, serves as a key indicator of a painting's age and authenticity. The pattern, size, and distribution of craquelure vary depending on factors like the artist's technique, the medium used, and environmental conditions over centuries. Analyzing craquelure allows art historians and conservators to accurately date artworks and distinguish genuine pieces from forgeries.
Scientific Analysis of Craquelure on Canvas
Scientific analysis of craquelure on canvas involves microscopic examination and infrared imaging to identify the patterns and causes of the fine cracks in paint layers. Techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) reveal the chemical composition of pigments and binders, helping to determine the age and authenticity of the artwork. These methods contribute to understanding environmental effects, degradation processes, and guide conservation strategies in preserving historical paintings.
Craquelure as an Authentication Tool in Art
Craquelure patterns, which form naturally over time due to the aging and drying of paint layers on canvas, serve as a vital authentication tool in art. Experts analyze the unique network of fine cracks to determine the age, origin, and authenticity of paintings, differentiating genuine works from forgeries. The study of craquelure involves examining factors such as crack width, depth, and pattern consistency relative to known periods and artists' techniques.
Restoration Techniques for Craquelure-Damaged Canvases
Craquelure in canvas paintings, characterized by a network of fine cracks, often results from aging and environmental fluctuations. Restoration techniques for craquelure-damaged canvases include consolidation using synthetic resins like Paraloid B-72 to stabilize the paint layers and prevent further flaking. Additionally, careful humidity control and the application of reversible adhesives help preserve the artwork's structural integrity without compromising its aesthetic value.
Notable Case Studies: Craquelure in Iconic Paintings
The Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci exhibits fine craquelure patterns resulting from centuries of aging and varnish layer changes, providing insights into its preservation state. Vincent van Gogh's Starry Night displays a distinctive network of craquelure linked to the rapid drying and brittle oil paint application typical of his technique. Rembrandt's portraits often reveal deep, pronounced craquelure, reflecting the artist's thick paint layers and natural canvas tension over time.
Preserving Craquelure: Conservation Best Practices
Craquelure, the network of fine cracks in oil paintings on canvas, serves as an important indicator of a painting's age and authenticity, requiring precise preservation methods. Conservation best practices include maintaining stable environmental conditions, controlling humidity and temperature, and avoiding direct light exposure to prevent further deterioration of the fragile surface. Employing non-invasive cleaning techniques and using reversible consolidants ensures the craquelure remains intact without compromising the artwork's integrity.
example of craquelure in canvas Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com