Steganography in images involves embedding hidden data within an image file without altering its visible appearance. A common example uses the least significant bit (LSB) technique, where binary data is inserted into the LSBs of pixel values. This method allows secret messages, such as text or encryption keys, to be concealed within digital images seamlessly. The application of image steganography extends to secure communication and digital watermarking. Software tools like OpenPuff and SilentEye enable users to encode data into image formats like PNG or BMP. Researchers also explore robust algorithms to improve data capacity and resist detection through statistical analysis or image manipulation.
Table of Comparison
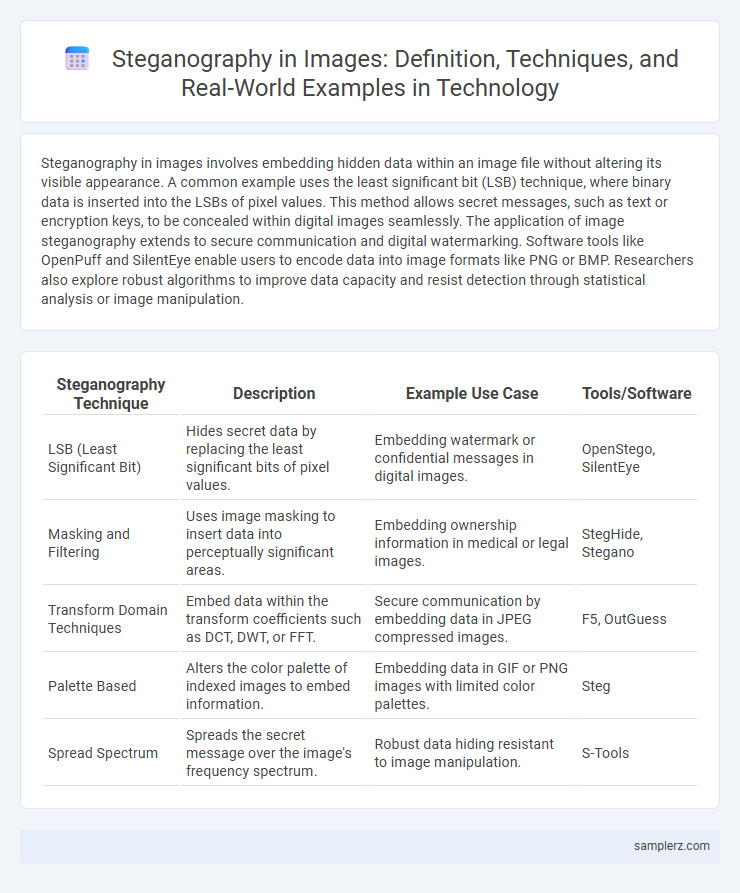
| Steganography Technique | Description | Example Use Case | Tools/Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSB (Least Significant Bit) | Hides secret data by replacing the least significant bits of pixel values. | Embedding watermark or confidential messages in digital images. | OpenStego, SilentEye |
| Masking and Filtering | Uses image masking to insert data into perceptually significant areas. | Embedding ownership information in medical or legal images. | StegHide, Stegano |
| Transform Domain Techniques | Embed data within the transform coefficients such as DCT, DWT, or FFT. | Secure communication by embedding data in JPEG compressed images. | F5, OutGuess |
| Palette Based | Alters the color palette of indexed images to embed information. | Embedding data in GIF or PNG images with limited color palettes. | Steg |
| Spread Spectrum | Spreads the secret message over the image's frequency spectrum. | Robust data hiding resistant to image manipulation. | S-Tools |
Introduction to Image Steganography
Image steganography involves embedding hidden data within digital images to ensure covert communication and protect sensitive information. Techniques such as least significant bit (LSB) modification alter pixel values imperceptibly to encode secret messages without affecting image quality. This method is widely used in cybersecurity for watermarking, copyright protection, and secure data transmission.
Historical Background of Image Steganography
Image steganography dates back to ancient times when hidden messages were concealed within artwork and illuminated manuscripts. In modern history, during World War II, invisible ink and microdots embedded in photographs served as critical tools for covert communication. Advances in digital technology have since transformed these techniques into complex algorithms embedding data within pixel values, enabling secure transmission of information without detection.
Basic Principles of Hiding Data in Images
Steganography in images utilizes the manipulation of pixel values to conceal data within the color information, often by altering the least significant bits (LSBs) without perceptible changes to the human eye. The basic principle involves embedding secret messages into digital images by modifying individual pixels' binary representation, leveraging the image's redundancy to hide information securely. This method ensures covert communication by maintaining the image's appearance while encoding hidden data in a way that is resistant to casual inspection.
Common Algorithms for Image Steganography
Common algorithms for image steganography include Least Significant Bit (LSB) insertion, which modifies the least significant bits of pixel values to embed secret data without perceptible changes. Another widely used method is Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) embedding, where data is hidden in the frequency domain by altering DCT coefficients typically applied in JPEG compression. Wavelet Transform techniques are also popular, using discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to embed information in multi-resolution wavelet coefficients, enhancing robustness against compression and noise.
Example: Hiding Text in JPEG Images
Hiding text in JPEG images involves embedding secret messages within the image's discrete cosine transform (DCT) coefficients to maintain visual quality and avoid detection. This steganographic technique carefully modifies the least significant bits of compressed image data, ensuring that the hidden information remains imperceptible to human eyes and standard image analysis tools. Advanced algorithms optimize data embedding capacity while preserving JPEG compression characteristics, making it a practical method for secure communication in digital media.
Example: Embedding Secret Messages in PNG Files
Embedding secret messages in PNG files utilizes the least significant bit (LSB) steganography technique, which modifies the pixel values without significantly altering the image quality. This method hides text or binary data within the image's color channels, ensuring that the encoded message remains imperceptible to the human eye and standard image viewers. PNG's lossless compression maintains the integrity of the hidden information, making it an ideal format for secure and covert communication.
Real-World Applications of Image Steganography
Image steganography is extensively used in secure communication by embedding confidential information within digital images, making data transmission covert and resistant to interception. In digital watermarking, companies embed copyright information directly into images to protect intellectual property and combat unauthorized distribution. Moreover, law enforcement agencies utilize image steganography to discreetly exchange sensitive information during undercover operations without detection.
Steganography Tools and Software for Images
Steganography tools like OpenPuff and SilentEye enable users to embed hidden messages within digital images by altering pixel values without noticeable distortion. These software applications support various image formats such as BMP, PNG, and JPEG, leveraging techniques like least significant bit (LSB) modification to conceal data imperceptibly. Advanced steganography software also provides encryption features to enhance the security of the embedded information against unauthorized extraction.
Detecting Hidden Data in Digital Images
Detecting hidden data in digital images involves analyzing pixel patterns and color variations to uncover steganographic content embedded within an image file. Techniques such as statistical analysis, histogram analysis, and machine learning algorithms can reveal anomalies indicative of concealed messages by identifying irregularities in least significant bits or pixel noise distributions. Advanced tools like StegDetect and StegSpy automate this process, improving accuracy in extracting and verifying hidden information without compromising image integrity.
Future Trends of Image Steganography in Technology
Emerging trends in image steganography leverage deep learning algorithms to enhance hidden data capacity and improve detection resistance. Quantum computing advancements are expected to revolutionize encryption methods, enabling more secure and imperceptible embedding of secret information within digital images. Integration of blockchain technology promises to authenticate and verify steganographic content integrity, ensuring tamper-proof communication in future technological applications.
example of steganography in image Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com