Sanctions in social norms serve as mechanisms to enforce acceptable behavior within a community. An example is the informal sanction of social ostracism, where individuals who violate group norms may be excluded from social activities or interactions. This exclusion reinforces the importance of adhering to shared values and expectations. Formal sanctions also exist within social norms, such as penalties imposed by institutions for rule-breaking behavior. For instance, a workplace may enforce disciplinary actions against employees who breach established codes of conduct. These sanctions help maintain order by deterring misconduct and promoting conformity to societal standards.
Table of Comparison
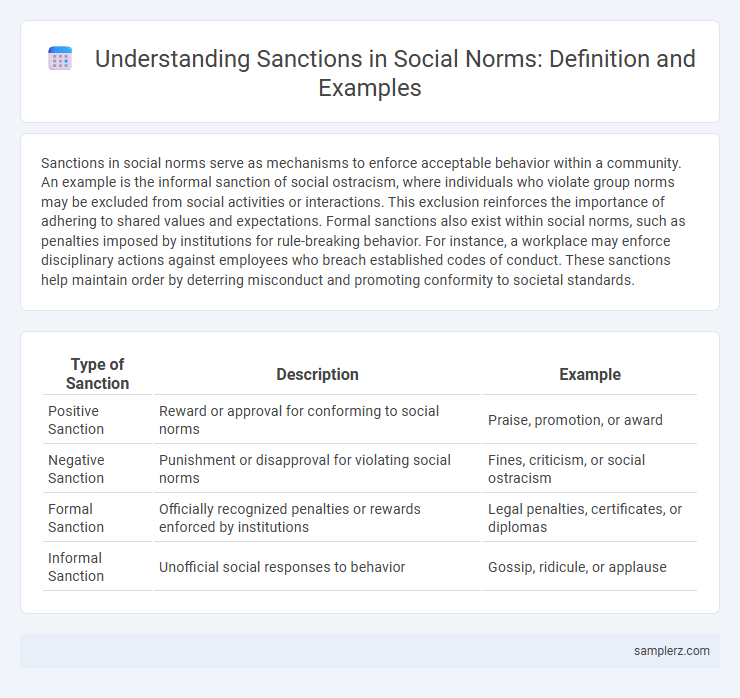
| Type of Sanction | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Sanction | Reward or approval for conforming to social norms | Praise, promotion, or award |
| Negative Sanction | Punishment or disapproval for violating social norms | Fines, criticism, or social ostracism |
| Formal Sanction | Officially recognized penalties or rewards enforced by institutions | Legal penalties, certificates, or diplomas |
| Informal Sanction | Unofficial social responses to behavior | Gossip, ridicule, or applause |
Understanding Social Norms and Sanctions
Social norms regulate behavior through informal sanctions such as social approval, disapproval, or exclusion to maintain group cohesion. For example, a person who consistently interrupts others in conversation may face social sanctions like disapproving looks or exclusion from future discussions. These sanctions reinforce norms by signaling acceptable conduct and discouraging violations within the social setting.
Common Types of Sanctions in Social Contexts
Positive sanctions in social contexts include rewards such as praise, recognition, and social approval that encourage conformity to social norms. Negative sanctions involve punishments like criticism, social ostracism, or fines imposed to deter deviant behavior. Informal sanctions typically arise from peer interactions, while formal sanctions are enforced by institutions such as courts or employers.
Positive vs Negative Sanctions: Key Differences
Positive sanctions include rewards such as praise or promotions that reinforce desired social behaviors, encouraging conformity within a group. Negative sanctions involve punishments like fines, social ostracism, or reprimands aimed at deterring deviant actions and maintaining social order. Understanding these sanctions reveals how societies regulate behavior through incentives and penalties.
The Role of Informal Sanctions in Everyday Life
Informal sanctions play a crucial role in regulating behavior through social disapproval, such as gossip, ridicule, or exclusion within communities, reinforcing norms without legal consequences. These sanctions maintain social order by encouraging conformity and discouraging deviance in daily interactions, often proving more immediate and effective than formal sanctions. Examples include subtle eye-rolling in response to rude behavior or community shaming for violating unwritten social rules.
Peer Pressure as a Form of Social Sanction
Peer pressure acts as a potent social sanction by encouraging individuals to conform to group norms and expectations through subtle or overt influence. Noncompliance often results in social exclusion, ridicule, or diminished status within the peer group. This form of sanction effectively regulates behavior by leveraging the innate human desire for acceptance and belonging.
Ostracism: Exclusion as a Social Norm Sanction
Ostracism serves as a powerful social norm sanction by enforcing exclusion from group activities or interactions, signaling disapproval of behavior that violates community standards. This form of sanction effectively pressures individuals to conform by threatening their social identity and support network within the group. Studies highlight ostracism's psychological impact, demonstrating its role in maintaining social cohesion and regulating norms through indirect yet impactful social exclusion.
Rewards and Praise: Positive Reinforcement in Norms
Rewards and praise serve as powerful positive reinforcement mechanisms within social norms, encouraging compliance and desired behavior by offering recognition and tangible benefits. Public acknowledgment, such as awards or verbal compliments, strengthens group cohesion and motivates individuals to uphold shared values. Consistent positive reinforcement fosters an environment where prosocial actions are repeated and internalized, solidifying normative behaviors.
Shaming: Public Disapproval as Social Control
Shaming acts as a powerful social sanction by publicly expressing disapproval to enforce norms and deter deviant behavior. This form of social control relies on community judgment and reputational consequences to encourage conformity and accountability. Public shaming can reinforce societal values by signaling unacceptable conduct and promoting adherence to group expectations.
Legal Sanctions vs Social Sanctions in Communities
Legal sanctions impose formal penalties such as fines, imprisonment, or community service enforced by government authorities to regulate behavior and maintain social order. Social sanctions, including ostracism, ridicule, and loss of reputation, operate informally within communities to enforce norms and encourage conformity. The effectiveness of legal sanctions depends on codified laws and judicial processes, while social sanctions rely on collective community approval and shared values.
Case Studies: Real-world Examples of Norm-based Sanctions
In social contexts, norm-based sanctions manifest through community enforcement such as ostracism in indigenous tribes, where rule-breakers face exclusion impacting social support networks. Workplace environments often apply informal sanctions like social shaming or reduced collaboration opportunities to uphold professional norms and maintain group cohesion. Online platforms implement norm sanctions through account suspensions or content removal, effectively deterring behavior that violates community guidelines.
example of sanction in norm Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com