Endogamy is a social practice where individuals marry within a specific community, caste, or ethnic group. An example of endogamy can be observed among the Amish communities in the United States, where members typically marry within their own religious and cultural group. This practice helps maintain cultural continuity and reinforces social bonds within the community. In many Indian caste groups, endogamy remains a prevalent tradition, with marriages arranged within the same caste to preserve social hierarchy and cultural identity. Data from sociological studies indicate that endogamous practices contribute to stronger community cohesion and shared values. These patterns highlight the role of endogamy in shaping social structures and maintaining group identity over generations.
Table of Comparison
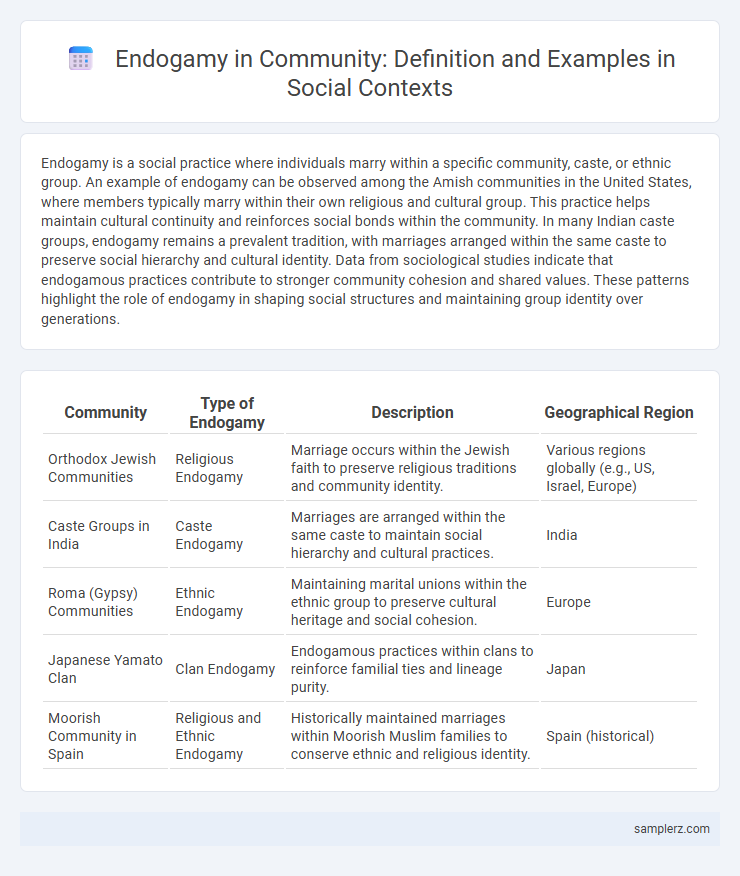
| Community | Type of Endogamy | Description | Geographical Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orthodox Jewish Communities | Religious Endogamy | Marriage occurs within the Jewish faith to preserve religious traditions and community identity. | Various regions globally (e.g., US, Israel, Europe) |
| Caste Groups in India | Caste Endogamy | Marriages are arranged within the same caste to maintain social hierarchy and cultural practices. | India |
| Roma (Gypsy) Communities | Ethnic Endogamy | Maintaining marital unions within the ethnic group to preserve cultural heritage and social cohesion. | Europe |
| Japanese Yamato Clan | Clan Endogamy | Endogamous practices within clans to reinforce familial ties and lineage purity. | Japan |
| Moorish Community in Spain | Religious and Ethnic Endogamy | Historically maintained marriages within Moorish Muslim families to conserve ethnic and religious identity. | Spain (historical) |
Understanding Endogamy in Social Communities
Endogamy in social communities is exemplified by the caste system in India, where marriage occurs within specific social groups to preserve cultural identity and social structure. This practice reinforces group cohesion and restricts genetic variation within the community, often linking social status to marital choices. Understanding endogamy highlights its role in maintaining traditional boundaries and social stratification in various cultures worldwide.
Historical Instances of Endogamy
Historical instances of endogamy are evident in the caste system of India, where marriage within specific social groups was strictly enforced to preserve cultural identity and social hierarchy. European royal families, such as the Habsburgs, practiced endogamy to maintain political alliances and consolidate power, often resulting in genetic issues due to limited gene pools. In Jewish communities, endogamous marriages helped maintain religious traditions and communal cohesion through centuries of diaspora.
Religious Endogamy: Faith-Based Practices
Religious endogamy occurs when individuals marry within their own faith community to preserve religious identity and cultural traditions. For example, Orthodox Jewish communities often encourage marriage exclusively within the faith to maintain religious observance and communal cohesion. This practice reinforces shared beliefs and ensures continuity of religious values across generations.
Endogamy Among Ethnic Groups
Endogamy among ethnic groups is prominently observed in communities such as the Amish in the United States, where marriage within the group preserves cultural and religious identity. Similarly, the Druze community in the Middle East practices strict endogamy to maintain social cohesion and lineage purity. These practices help reinforce group solidarity and continuity of shared traditions over generations.
Caste Systems and Endogamous Traditions
Endogamy in caste systems manifests through rigid social structures that mandate marriage within the same caste, preserving cultural and economic boundaries. This practice reinforces community identity and maintains social hierarchy by limiting interactions between distinct groups. Examples include traditional Indian caste communities where endogamous traditions sustain lineage purity and social cohesion.
Endogamy in Royal and Noble Lineages
Endogamy in royal and noble lineages is a practice where marriages occur exclusively within the same social or familial group to preserve bloodlines and consolidate power. Historical examples include European royal families marrying within their own aristocracy, such as the Habsburgs, who maintained political alliances and wealth through intermarriage. This practice often results in limited genetic diversity but reinforces social stratification and the continuity of elite status.
Rural Communities and Marital Boundaries
Endogamy in rural communities often reinforces marital boundaries by encouraging marriages within the same village or social group, preserving cultural traditions and kinship ties. This practice strengthens social cohesion and maintains property within extended families, limiting external influences on the community's social structure. Rural endogamy supports a network of mutual obligations and shared identity, which is critical for sustaining local customs and social stability.
Social Impacts of Endogamous Marriages
Endogamous marriages, such as those prevalent in the Amish community, reinforce social cohesion and cultural preservation by limiting marriages within the group. This practice strengthens intra-group identity and continuity but often results in reduced genetic diversity, impacting public health through increased hereditary conditions. Socially, endogamy can limit social mobility and maintain existing social hierarchies within the community.
Educational Backgrounds and Endogamous Choices
Endogamy often occurs within communities where individuals select marriage partners based on similar educational backgrounds, reinforcing social cohesion and shared values. Studies show that people with comparable levels of education are more likely to marry each other, promoting homogeneous social networks and sustaining class structures. This pattern is particularly evident in professional and academic circles, where educational attainment serves as a key criterion for endogamous unions.
Endogamy in Modern Urban Societies
Endogamy in modern urban societies often manifests within specific ethnic, religious, or socio-economic groups that seek to preserve cultural identity and social cohesion. For example, South Asian communities in cities like London or New York frequently practice endogamy to maintain linguistic and traditional values across generations. This social pattern reinforces group solidarity while navigating the complexities of multicultural urban environments.
example of endogamy in community Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com