A boutique's retail footprint refers to its physical presence and layout within a specific location, which directly influences customer engagement and sales performance. Key data points include store size, shelf space allocation, and display arrangement, all designed to maximize product visibility and enhance the shopping experience. Entities involved in establishing this footprint typically comprise retail managers, visual merchandisers, and supply chain coordinators. Footprint optimization in a boutique often involves analyzing customer traffic patterns and sales data to strategically position high-demand products. Retailers use heat maps and sales reports to determine effective product placements that drive impulse purchases and increase conversion rates. The boutique's footprint also extends to branding elements, floor design, and lighting, which collectively support customer retention and brand recognition.
Table of Comparison
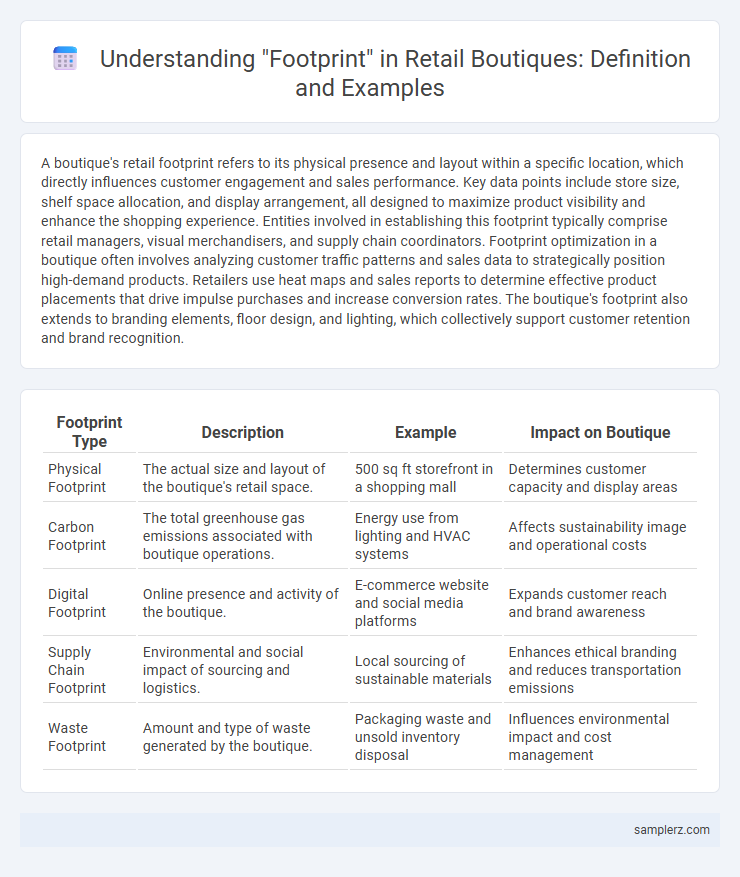
| Footprint Type | Description | Example | Impact on Boutique |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Footprint | The actual size and layout of the boutique's retail space. | 500 sq ft storefront in a shopping mall | Determines customer capacity and display areas |
| Carbon Footprint | The total greenhouse gas emissions associated with boutique operations. | Energy use from lighting and HVAC systems | Affects sustainability image and operational costs |
| Digital Footprint | Online presence and activity of the boutique. | E-commerce website and social media platforms | Expands customer reach and brand awareness |
| Supply Chain Footprint | Environmental and social impact of sourcing and logistics. | Local sourcing of sustainable materials | Enhances ethical branding and reduces transportation emissions |
| Waste Footprint | Amount and type of waste generated by the boutique. | Packaging waste and unsold inventory disposal | Influences environmental impact and cost management |
Understanding Footprint in Boutique Retail
Footprint in boutique retail refers to the physical space occupied by the store, including the layout, display areas, and customer flow zones, which directly impact sales performance and customer experience. An optimized boutique footprint balances product assortment with aesthetic appeal to maximize engagement within limited square footage, often ranging between 500 to 2,000 square feet for boutique stores. Efficient use of footprint enhances inventory management, visibility, and brand differentiation, crucial for specialty retail success.
Key Elements of Boutique Store Footprint
Boutique store footprint design prioritizes maximizing customer flow and product visibility within a limited space, incorporating strategic layout planning such as focal entry points and clear, navigable pathways. Key elements include tailored merchandising displays, optimized lighting to highlight premium products, and the integration of interactive zones to enhance the sensory shopping experience. Efficient use of square footage balances aesthetic appeal with functional zones like cashier areas and fitting rooms, driving both engagement and sales conversion rates.
Maximizing Space: Boutique Footprint Strategies
Maximizing space in boutique retail involves strategic footprint planning such as utilizing multi-functional furniture and modular displays that adapt to changing inventory. Implementing vertical storage solutions and optimizing layout flow enhances customer experience while increasing merchandise visibility. Efficient use of square footage drives higher sales per square foot and improves operational agility in boutique settings.
Small Boutique Footprint Examples
Small boutique footprints typically range from 500 to 1,500 square feet, strategically maximizing product display and customer experience within limited space. Custom shelving, modular fixtures, and digital signage enhance the visual appeal while optimizing floor layout for high traffic flow. Locations in urban neighborhoods or trendy shopping districts benefit from compact designs that emphasize unique branding and personalized service.
Sustainable Footprint Practices in Boutiques
Boutiques increasingly adopt sustainable footprint practices by utilizing energy-efficient LED lighting, sourcing eco-friendly materials for decor and packaging, and implementing waste reduction programs such as recycling and composting. Many stores also integrate locally sourced products to minimize carbon emissions associated with transportation. These efforts contribute to a reduced environmental impact while promoting responsible consumerism in the retail sector.
Visual Merchandising and Footprint Optimization
Visual merchandising in boutique retail strategically utilizes footprint optimization to enhance product visibility and customer flow, maximizing sales per square meter. Effective display layouts, such as modular shelving and focal point arrangements, create an immersive shopping experience while reducing clutter. Data-driven analysis of shopper behavior informs placement decisions, ensuring high-demand items occupy prime locations within the limited boutique footprint.
Customer Flow and Boutique Footprint Design
Optimizing customer flow in boutique footprint design enhances shopper experience by strategically positioning entry points, product displays, and checkout counters to encourage natural movement and reduce congestion. Effective layout planning maximizes floor space utilization, increases product visibility, and guides customers through high-margin merchandise zones. Incorporating clear pathways and intuitive signage supports seamless navigation, boosting engagement and sales conversion rates in retail boutiques.
Digital Integration in Boutique Retail Footprint
Digital integration in boutique retail footprint enhances customer engagement through interactive displays and mobile payment solutions. In-store digital kiosks provide personalized product recommendations based on real-time inventory data and customer preferences. Seamless omnichannel experiences connect online browsing with in-store purchases, increasing conversion rates and brand loyalty.
Common Footprint Mistakes in Boutiques
Common footprint mistakes in boutiques include overcrowded displays that hinder customer movement, poor lighting that diminishes product appeal, and inconsistent signage that confuses shoppers. Inefficient use of floor space often leads to cluttered aisles, reducing overall shopping comfort and limiting product visibility. Neglecting to create intuitive pathways can result in lower engagement and decreased sales opportunities.
Future Trends in Boutique Retail Footprint
Boutique retail footprints are evolving with the integration of augmented reality (AR) and personalized data analytics to offer immersive and customized shopping experiences that increase customer engagement. Future trends indicate a shift towards smaller, modular store designs that emphasize local sourcing and sustainable materials, reflecting growing consumer demand for eco-friendly practices. Retailers are also leveraging smart inventory systems and AI-driven insights to optimize product placement and enhance operational efficiency within compact boutique spaces.
example of footprint in boutique Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com