A time audit is a systematic analysis of how individuals allocate their working hours across various tasks and activities. By recording and categorizing time spent on specific duties, a time audit reveals inefficiencies and identifies opportunities for better time management. Data from digital tools, such as time-tracking software, and manual logs contribute to an accurate overview of productivity patterns. In productivity analysis, a time audit provides quantifiable insights into task prioritization and workflow effectiveness. For example, an audit might show that 40% of a workday is consumed by meetings, signaling a need to streamline or reduce these sessions. This entity-focused data enables managers to implement targeted strategies that enhance overall efficiency and optimize resource allocation.
Table of Comparison
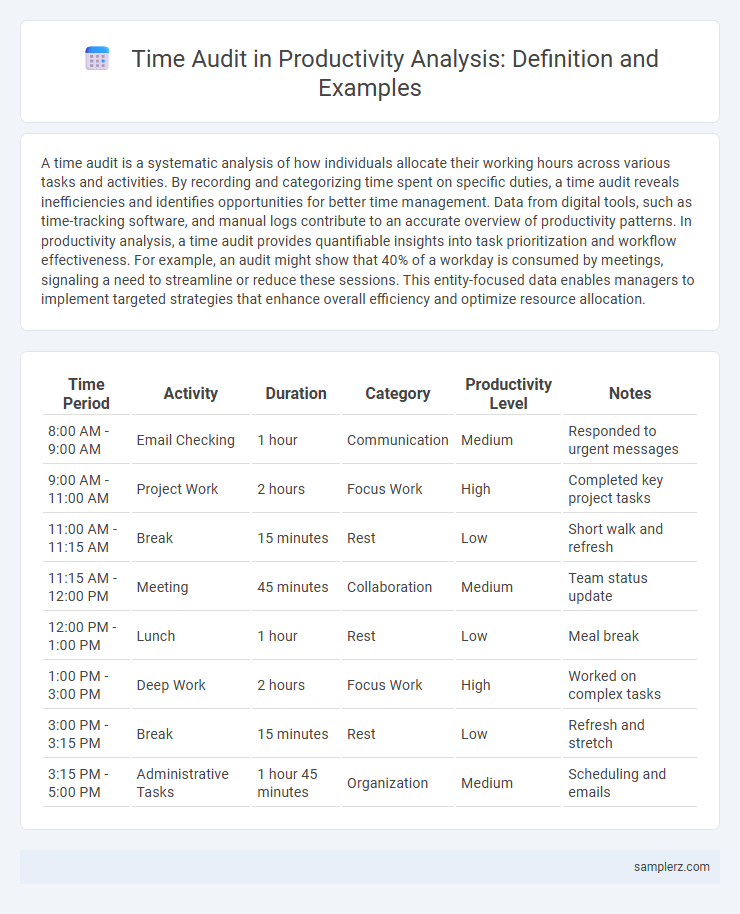
| Time Period | Activity | Duration | Category | Productivity Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:00 AM - 9:00 AM | Email Checking | 1 hour | Communication | Medium | Responded to urgent messages |
| 9:00 AM - 11:00 AM | Project Work | 2 hours | Focus Work | High | Completed key project tasks |
| 11:00 AM - 11:15 AM | Break | 15 minutes | Rest | Low | Short walk and refresh |
| 11:15 AM - 12:00 PM | Meeting | 45 minutes | Collaboration | Medium | Team status update |
| 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM | Lunch | 1 hour | Rest | Low | Meal break |
| 1:00 PM - 3:00 PM | Deep Work | 2 hours | Focus Work | High | Worked on complex tasks |
| 3:00 PM - 3:15 PM | Break | 15 minutes | Rest | Low | Refresh and stretch |
| 3:15 PM - 5:00 PM | Administrative Tasks | 1 hour 45 minutes | Organization | Medium | Scheduling and emails |
Understanding Time Audits: A Productivity Game-Changer
Time audits involve tracking every activity within a set period to identify productivity patterns and time-wasting habits, using tools like time-tracking apps or detailed logs. Analyzing this data reveals crucial insights into how time is allocated across tasks, enabling targeted adjustments to optimize efficiency. Understanding time audits empowers individuals and teams to make informed decisions that enhance focus, reduce distractions, and maximize productive output.
Why Perform a Time Audit? Key Benefits for Efficiency
Performing a time audit reveals hidden patterns of inefficiency by tracking how every minute is spent, enabling more accurate prioritization of high-impact tasks. Key benefits include identifying time-wasting activities, increasing focus on goal-oriented work, and optimizing daily schedules for maximum productivity. This data-driven approach empowers professionals to eliminate distractions, streamline workflows, and significantly enhance overall efficiency.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Your First Time Audit
Begin your time audit by tracking daily activities in 15-minute intervals for one week, ensuring accurate data collection. Analyze the recorded data to identify time-wasting habits, productive periods, and task durations. Use insights from the audit to restructure your schedule, prioritize high-impact activities, and eliminate non-essential tasks.
Real-Life Example: Daily Time Audit Analysis
A daily time audit reveals that more than 40% of a typical 8-hour workday is consumed by unplanned interruptions and task switching, significantly reducing deep work efficiency. By tracking activities in 15-minute intervals, individuals identify patterns such as excessive social media use or prolonged email checking that fragment focus. Implementing targeted adjustments based on audit data, like scheduling specific email times, can increase productive work periods by up to 30%.
Identifying Time Wasters Through Audit Data
Analyzing audit data reveals patterns of unproductive activities such as excessive social media use, frequent unnecessary meetings, and prolonged email checking. Identifying these time wasters enables employees to restructure their schedules, allocate focused work periods, and implement targeted strategies to enhance overall efficiency. Using precise time audit insights drives more effective time management and productivity improvements.
Categorizing Activities: Productive vs. Non-Productive Tasks
A time audit involves identifying and categorizing daily activities into productive and non-productive tasks to enhance time management. Productive tasks, such as project work and goal-oriented meetings, directly contribute to achieving objectives, while non-productive tasks include excessive social media use and unnecessary emails. This categorization helps prioritize efforts, reduce time wastage, and improve overall productivity efficiency.
Interpreting Your Time Audit Results: Actionable Insights
Interpreting your time audit results reveals patterns of unproductive time blocks and identifies high-efficiency periods ideal for focused work. Analyzing these insights allows for strategic scheduling adjustments, such as reallocating low-energy tasks to off-peak hours. Implementing targeted changes based on audit data enhances overall productivity by maximizing peak performance intervals.
Optimizing Workflows Based on Time Audit Findings
Analyzing time audit data reveals specific tasks and processes that consume excessive hours, enabling targeted workflow optimization. Streamlining repetitive activities and reallocating resources based on audit insights enhances efficiency and reduces bottlenecks. Time audit findings directly inform adjustments to task prioritization, meeting schedules, and tool usage for maximizing productivity.
Tools and Templates for Effective Time Auditing
Time audit tools such as Toggl and RescueTime provide detailed tracking of daily activities, enabling precise identification of time sinks and productivity patterns. Templates like Excel time logs or Google Sheets audit sheets standardize data entry, facilitating clear visualization and analysis of time allocation across tasks. Integrating these tools and templates empowers users to conduct thorough time audits that drive actionable productivity improvements.
Maintaining Productivity: Regular Time Audit Best Practices
A regular time audit involves tracking daily activities in 15-30 minute intervals to identify productivity patterns and time-wasting habits. Using tools like Toggl or RescueTime helps quantify work hours and optimize task prioritization based on data-driven insights. Maintaining productivity relies on consistent reviews and adjustments to workflows informed by detailed time audit analyses.
example of time audit in analysis Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com