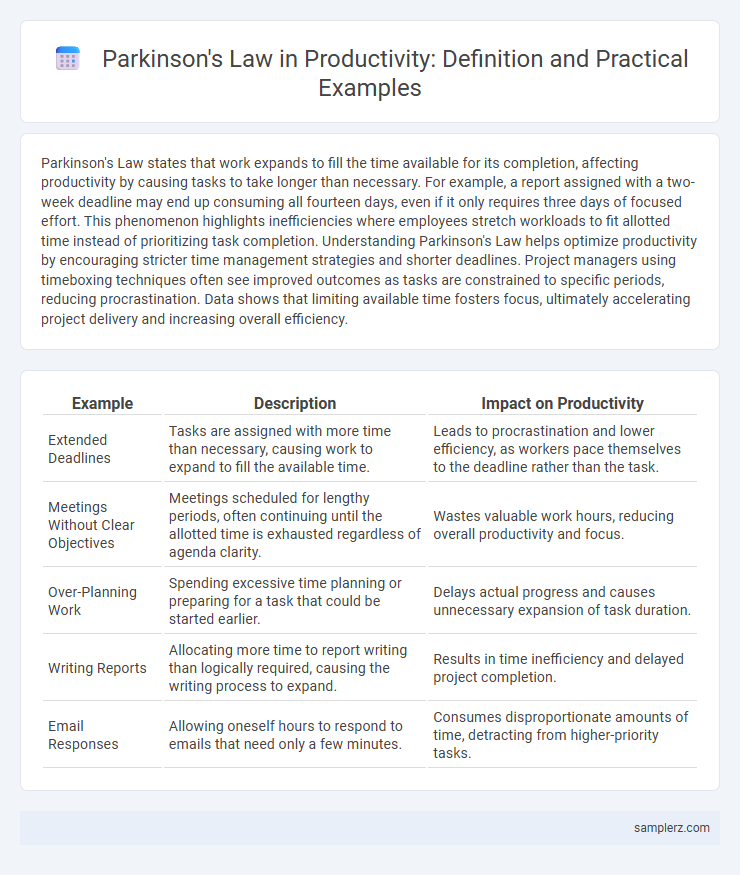
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available for its completion, affecting productivity by causing tasks to take longer than necessary. For example, a report assigned with a two-week deadline may end up consuming all fourteen days, even if it only requires three days of focused effort. This phenomenon highlights inefficiencies where employees stretch workloads to fit allotted time instead of prioritizing task completion. Understanding Parkinson's Law helps optimize productivity by encouraging stricter time management strategies and shorter deadlines. Project managers using timeboxing techniques often see improved outcomes as tasks are constrained to specific periods, reducing procrastination. Data shows that limiting available time fosters focus, ultimately accelerating project delivery and increasing overall efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Example | Description | Impact on Productivity |
|---|---|---|
| Extended Deadlines | Tasks are assigned with more time than necessary, causing work to expand to fill the available time. | Leads to procrastination and lower efficiency, as workers pace themselves to the deadline rather than the task. |
| Meetings Without Clear Objectives | Meetings scheduled for lengthy periods, often continuing until the allotted time is exhausted regardless of agenda clarity. | Wastes valuable work hours, reducing overall productivity and focus. |
| Over-Planning Work | Spending excessive time planning or preparing for a task that could be started earlier. | Delays actual progress and causes unnecessary expansion of task duration. |
| Writing Reports | Allocating more time to report writing than logically required, causing the writing process to expand. | Results in time inefficiency and delayed project completion. |
| Email Responses | Allowing oneself hours to respond to emails that need only a few minutes. | Consumes disproportionate amounts of time, detracting from higher-priority tasks. |
Understanding Parkinson’s Law in Daily Work
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available for its completion, often leading to inefficiency in daily tasks. Understanding this law helps professionals set tighter deadlines, preventing unnecessary time consumption and boosting productivity. Applying Parkinson's Law in time management encourages prioritization and focused effort, resulting in faster task completion and improved work quality.
Classic Workplace Scenarios Illustrating Parkinson’s Law
Parkinson's Law is evident in classic workplace scenarios where tasks expand to fill the time allotted, such as employees spending an entire week to complete a report that could be finished in two days. Meetings often overrun their scheduled time, turning a planned 30-minute session into an hour-long discussion without added value. Project deadlines that are too flexible contribute to procrastination, reducing overall productivity and delaying deliverables.
How Task Deadlines Expand with Parkinson’s Law
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available for its completion, causing task deadlines to stretch unnecessarily and reducing overall productivity. For example, if a task is allotted a week, the effort will often inflate to occupy the full seven days, even if the task could be finished in half the time. This phenomenon highlights the importance of setting tighter, realistic deadlines to enhance efficiency and prevent procrastination.
Meetings as a Case Study of Parkinson’s Law
Meetings often exemplify Parkinson's Law, where the time allocated for a meeting expands to fill the entire schedule regardless of agenda complexity. Research indicates that meetings scheduled for an hour frequently drag on without additional value compared to shorter, focused sessions bounded to 15-30 minutes. Efficient productivity strategies recommend setting strict time limits and clear objectives to counteract this tendency and enhance decision-making efficiency.
Student Projects and the Impact of Parkinson’s Law
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, often causing student projects to drag on longer than necessary. In academic settings, students may procrastinate or overcomplicate assignments when given excessive deadlines, leading to decreased productivity and increased stress. Recognizing this tendency, setting tighter, realistic time constraints can enhance focus, efficiency, and timely project completion.
Email Management: A Modern Example of Parkinson’s Law
Email management exemplifies Parkinson's Law as the time spent organizing and responding to emails often expands to fill the entire allocated period, regardless of the actual workload. Employees who set strict time limits for checking emails typically complete the task more efficiently, reducing distractions and improving overall productivity. Adopting email batching and scheduled review intervals counters unnecessary time inflation and enhances focus on critical work.
The Role of Parkinson’s Law in Remote Work Productivity
Parkinson's Law, stating that work expands to fill the time available, significantly impacts remote work productivity by encouraging employees to set clear deadlines and time blocks to avoid inefficiency. Remote workers often experience blurred boundaries between work and personal time, making task duration management crucial to prevent unnecessary work expansion. Implementing structured schedules and focused time management tools can counteract Parkinson's Law, enhancing productivity in remote environments.
Procrastination Patterns and Parkinson’s Law
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, often causing procrastination patterns where tasks are delayed until deadlines approach. This tendency results in decreased productivity as individuals allocate excessive time for simple tasks, leading to last-minute rushes and stress. Understanding this law helps optimize time management by setting shorter, achievable deadlines to combat procrastination and improve efficiency.
Creative Work and Time Allocation: Parkinson’s Law in Action
Parkinson's Law illustrates that creative work expands to fill the time allocated, often leading to inefficient use of hours when deadlines are flexible. Creative professionals who set strict, shorter time frames for tasks typically produce higher-quality work with increased focus and innovation. Timeboxing techniques leverage this principle by limiting task duration, thereby enhancing productivity and fostering disciplined creative output.
Overcoming Parkinson’s Law to Boost Productivity
Parkinson's Law states that work expands to fill the time available, often leading to inefficiency and procrastination. Overcoming this involves setting strict deadlines and using time-blocking techniques to create urgency and focus. Implementing tools like the Pomodoro Technique can also help in maintaining concentration and preventing tasks from dragging unnecessarily.
example of Parkinson’s law in productivity Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com