A shadow cabinet is a group of senior members from the main opposition party in a parliamentary system who scrutinize and challenge the policies and actions of the government. Each shadow minister is tasked with overseeing a specific governmental department, such as finance, health, or education, mirroring the official cabinet members. This arrangement ensures that the opposition is prepared to assume power and provides an alternative policy framework for voters. One prominent example of a shadow cabinet is found in the United Kingdom, where the Labour Party, when serving as the opposition, appoints shadow ministers to correspond to each government department led by the ruling party. These shadow ministers hold the government accountable through debates, parliamentary questions, and committee work. Their role is crucial in maintaining a healthy democratic process by offering policy alternatives and scrutinizing legislative proposals.
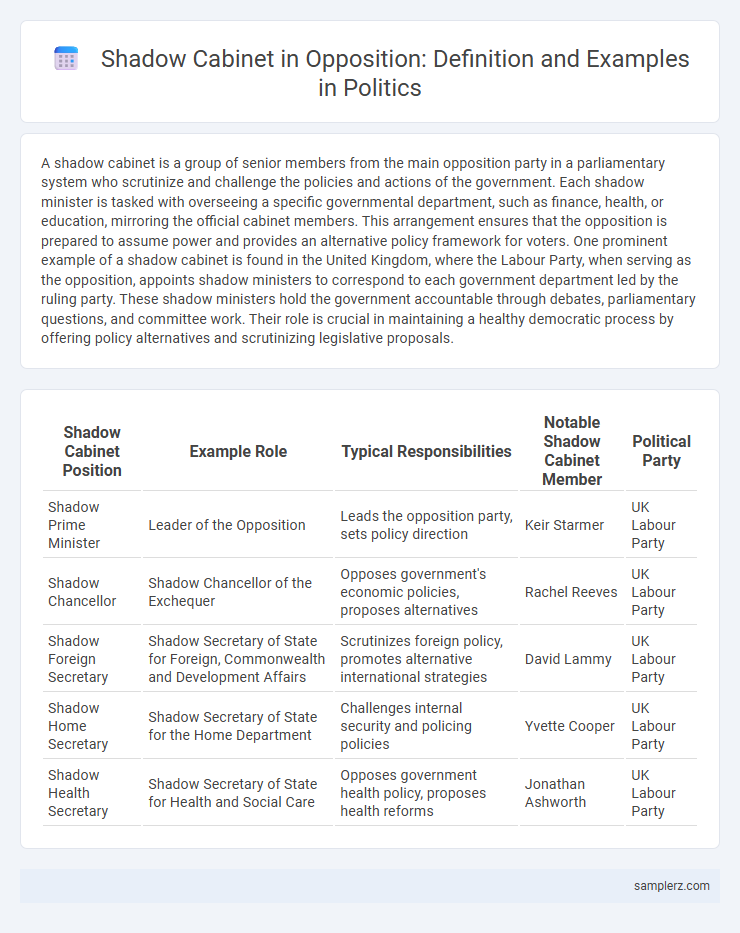
Table of Comparison
| Shadow Cabinet Position | Example Role | Typical Responsibilities | Notable Shadow Cabinet Member | Political Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shadow Prime Minister | Leader of the Opposition | Leads the opposition party, sets policy direction | Keir Starmer | UK Labour Party |
| Shadow Chancellor | Shadow Chancellor of the Exchequer | Opposes government's economic policies, proposes alternatives | Rachel Reeves | UK Labour Party |
| Shadow Foreign Secretary | Shadow Secretary of State for Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Affairs | Scrutinizes foreign policy, promotes alternative international strategies | David Lammy | UK Labour Party |
| Shadow Home Secretary | Shadow Secretary of State for the Home Department | Challenges internal security and policing policies | Yvette Cooper | UK Labour Party |
| Shadow Health Secretary | Shadow Secretary of State for Health and Social Care | Opposes government health policy, proposes health reforms | Jonathan Ashworth | UK Labour Party |
Understanding the Role of a Shadow Cabinet in Opposition
A shadow cabinet mirrors the official government cabinet, with each member scrutinizing and challenging the policies of their corresponding minister to ensure accountability. This structure enables the opposition to present alternative policies and maintain readiness to govern, strengthening democratic processes. Effective shadow cabinets enhance transparency, improve policy debates, and hold the ruling party accountable.
Historical Origins of the Shadow Cabinet System
The shadow cabinet system originated in the United Kingdom during the 19th century as a formalized opposition structure to hold the government accountable. It evolved from the practice of assigning specific opposition members to monitor and critique corresponding government ministers, enhancing parliamentary scrutiny and policy debate. This framework provides organized alternative policies and prepares the opposition for potential governance.
Structure and Composition of a Shadow Cabinet
A shadow cabinet in opposition mirrors the official government cabinet, with appointed members assigned to scrutinize and challenge specific ministerial portfolios. Each shadow minister focuses on policy areas such as health, education, or finance, ensuring accountability and presenting alternative solutions. The structure emphasizes a coherent team aligned with the party leader's strategic priorities, enhancing readiness for potential governance.
Key Functions of Shadow Ministers
Shadow ministers play a crucial role in holding the government accountable by scrutinizing policies, proposing alternative strategies, and representing the opposition's stance. They closely monitor the actions of their corresponding government ministers, ensuring transparency and fostering political debate. By developing expertise in specific portfolios, shadow ministers help shape effective policy critiques and contribute to the democratic process.
Examples of Shadow Cabinets in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom's Labour Party frequently forms a Shadow Cabinet to mirror the official government, with prominent figures like Keir Starmer serving as Leader of the Opposition and Rachel Reeves as Shadow Chancellor. The Shadow Cabinet members hold portfolios corresponding to government ministers, enabling effective scrutiny and policy development on issues such as the economy, health, and foreign affairs. This structure allows the opposition to present itself as a government-in-waiting, ready to assume office following elections.
Shadow Cabinet’s Influence on Policy Debates
The Shadow Cabinet plays a critical role in shaping policy debates by scrutinizing government actions and presenting alternative proposals, thereby influencing public discourse and legislative priorities. For example, the UK's Labour Party Shadow Cabinet actively challenges Conservative government policies on healthcare, education, and climate change, driving media coverage and parliamentary discussions. This opposition structure ensures accountability and encourages policy innovation by maintaining pressure on incumbents to justify their decisions.
Comparing Shadow Cabinets Across Different Democracies
Shadow cabinets in parliamentary democracies such as the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia serve as critical instruments for the opposition to hold the government accountable and present alternative policies. The UK's shadow cabinet is highly institutionalized, with designated spokespersons mirroring each government minister, while Canada's shadow cabinet is smaller but strategically focused on key portfolios. Australia's opposition shadow cabinet emphasizes regional representation and often includes senior party members tasked with scrutinizing government actions across various policy areas, highlighting distinct national political cultures influencing shadow cabinet structures.
High-Profile Leaders Who Served in Shadow Cabinets
High-profile leaders who served in shadow cabinets have significantly shaped political opposition strategies by scrutinizing government policies and presenting alternative agendas. Notable figures include Jeremy Corbyn, who led the UK Labour shadow cabinet before becoming party leader, and Michael Howard, a former shadow chancellor who later became Conservative party leader. These leaders utilized their roles to gain visibility, influence public debate, and prepare for governance.
Challenges Faced by Shadow Cabinets in Opposition
Shadow cabinets in opposition often struggle with limited access to confidential government information, hindering their ability to develop fully informed alternative policies. They face difficulties in gaining media exposure and public recognition compared to the official cabinet, reducing their influence on public discourse. Resource constraints and internal party disagreements further challenge their effectiveness in holding the government accountable.
The Shadow Cabinet’s Impact on General Elections
The Shadow Cabinet plays a critical role in shaping public perception during general elections by presenting a ready alternative government that challenges the incumbent's policies. Effective shadow ministers highlight governmental shortcomings and propose clear, policy-driven alternatives, influencing voter decisions and party credibility. Data shows that opposition parties with well-organized shadow cabinets often experience improved electoral performance by demonstrating preparedness and policy expertise.
example of shadowcabinet in opposition Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com