A caucus in parliament refers to a group of legislators who come together to promote common legislative objectives and coordinate strategies within a political party or faction. One notable example is the Congressional Progressive Caucus in the United States House of Representatives, which consists of members advocating for progressive policies including economic equality and social justice. This caucus influences lawmaking by shaping party platforms and mobilizing support for key bills. In Canada, the Liberal Party caucus in the House of Commons serves as a platform for members to discuss policy proposals and align on party discipline. The caucus meetings provide an opportunity for parliamentarians to exchange information, strategize on legislative priorities, and prepare for parliamentary debates. These caucus groups play a critical role in organizing the parliamentary agenda and maintaining party cohesion during voting processes.
Table of Comparison
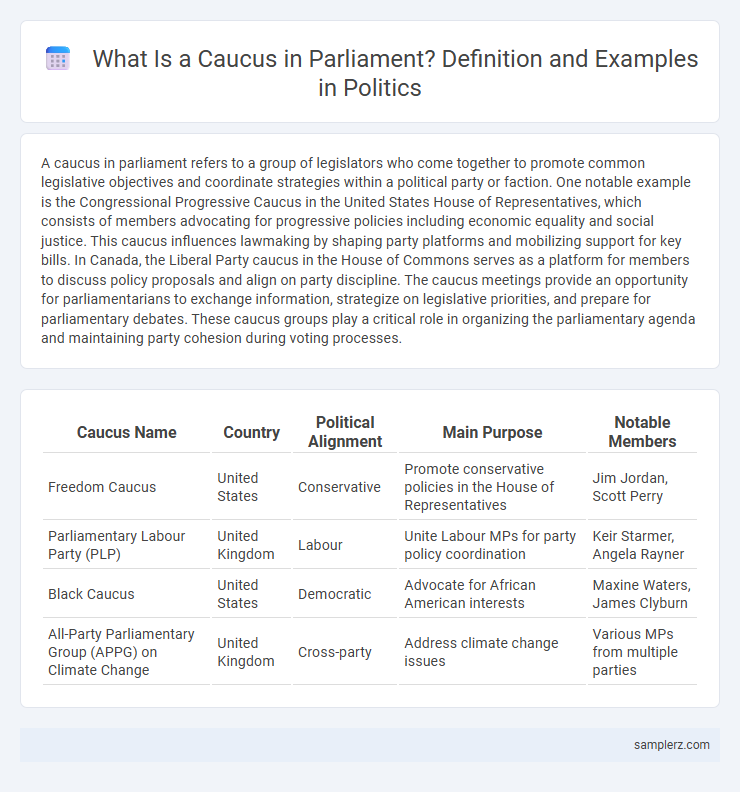
| Caucus Name | Country | Political Alignment | Main Purpose | Notable Members |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freedom Caucus | United States | Conservative | Promote conservative policies in the House of Representatives | Jim Jordan, Scott Perry |
| Parliamentary Labour Party (PLP) | United Kingdom | Labour | Unite Labour MPs for party policy coordination | Keir Starmer, Angela Rayner |
| Black Caucus | United States | Democratic | Advocate for African American interests | Maxine Waters, James Clyburn |
| All-Party Parliamentary Group (APPG) on Climate Change | United Kingdom | Cross-party | Address climate change issues | Various MPs from multiple parties |
Definition and Role of a Caucus in Parliament
A caucus in parliament is a formal group of members from the same political party or with shared interests who meet to discuss policy, strategy, and legislative agendas. This group plays a critical role in shaping party positions, coordinating voting, and influencing the legislative process to ensure unified action within parliament. Caucuses help streamline decision-making, strengthen party discipline, and facilitate communication between party leaders and rank-and-file members.
Historical Examples of Parliamentary Caucuses
The Congressional Progressive Caucus, founded in 1991, stands as a prominent historical example of a parliamentary caucus in the U.S. House of Representatives, championing progressive policies and social justice initiatives. Another significant example is the Blue Dog Coalition, established in 1995 by moderate and conservative Democrats aiming to influence fiscal policy and promote bipartisan legislation. The Parliamentary Labour Party's Socialist Campaign Group in the UK, formed in 1982, represents a notable caucus advocating left-wing policies within the Labour Party.
How Caucuses Influence Legislative Decision-Making
Caucuses in parliament, such as the Congressional Progressive Caucus in the U.S. House of Representatives, play a crucial role in shaping legislative agendas by consolidating members around shared policy goals and strategies. These groups coordinate voting, draft bills, and leverage collective influence to negotiate with party leadership and other caucus groups, impacting the legislative decision-making process significantly. Through targeted advocacy and strategic alliances, caucuses help define priorities and drive policy outcomes within complex parliamentary systems.
Case Studies: Party Caucuses in the UK Parliament
The UK Parliament features prominent party caucuses such as the Conservative 1922 Committee, which influences leadership decisions and policy directions within the Conservative Party. The Labour Party's Parliamentary Labour Party (PLP) caucus serves as a key forum for coordinating party strategy and maintaining discipline among MPs. These caucuses exemplify organized intra-party groups that shape legislative agendas and internal governance in the UK political system.
The Role of Cross-Party Caucuses in Policy Development
Cross-party caucuses in parliament play a crucial role in policy development by fostering collaboration among members from different political parties to address complex issues such as climate change, healthcare, and education reform. These caucuses facilitate bipartisan dialogue, enabling the sharing of diverse perspectives and the creation of comprehensive policy proposals that reflect a broader consensus. Examples include the Climate Solutions Caucus in the U.S. House of Representatives, which unites Democrats and Republicans in advancing sustainable environmental legislation.
Impact of Parliamentary Caucuses on Voting Behavior
Parliamentary caucuses, such as the Congressional Black Caucus in the U.S. House of Representatives, significantly shape voting behavior by consolidating member support around specific policy agendas. These caucuses facilitate coordinated strategies that influence legislative outcomes and party cohesion, often swaying key votes on social justice and economic issues. Research shows that caucus membership increases the likelihood of aligned voting patterns, reflecting the caucus's role as an influential actor within parliamentary decision-making processes.
Caucus Leadership and Organizational Structure
Caucus leadership in parliament typically includes a chairperson, vice-chair, and secretary who coordinate meetings and set agendas to represent party members' interests effectively. The organizational structure involves specialized subcommittees focused on policy areas such as finance, health, and foreign relations, enabling targeted legislative strategies and member engagement. Strong caucus leadership ensures cohesive decision-making and unified parliamentary voting within the party.
Case Example: The Women’s Caucus in Parliament
The Women's Caucus in Parliament serves as a vital platform advocating for gender equality and women's rights within legislative processes. It unites female parliamentarians across party lines to influence policy on issues such as gender-based violence, healthcare, and economic empowerment. The caucus has successfully pushed for laws enhancing women's political participation and addressing social inequalities.
Differences Between Caucuses and Parliamentary Committees
Caucuses in parliament are informal groups formed by members sharing common interests or goals, whereas parliamentary committees are formal bodies established by parliamentary rules to investigate specific issues or legislation. Caucuses focus on advocacy and influencing party policies, while committees have official mandates to scrutinize government actions and draft reports. Unlike committees that operate under strict procedural guidelines, caucuses provide flexible platforms for consensus-building and strategizing within the legislature.
Notable International Examples of Parliamentary Caucuses
The Congressional Black Caucus in the United States House of Representatives exemplifies a powerful parliamentary caucus advocating for African American interests and social justice policies. In the UK Parliament, the All-Party Parliamentary Group on Climate Change serves as a non-partisan caucus promoting environmental legislation and sustainability initiatives. Canada's Parliamentary Black Caucus focuses on equity and inclusion, influencing national policy on racial justice and systemic discrimination.
example of caucus in parliament Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com