An example of an incumbent in office is President Joe Biden, who has been serving as the President of the United States since January 20, 2021. Incumbents often have the advantage of name recognition, established political connections, and access to campaign resources. These factors contribute to a higher likelihood of reelection compared to challengers. In parliamentary systems, Angela Merkel served as the incumbent Chancellor of Germany for 16 years before stepping down in 2021. The role of an incumbent involves both the execution of governmental duties and the strategizing for upcoming electoral contests. Holding office offers a platform to influence policy and public opinion while campaigning for continued leadership.
Table of Comparison
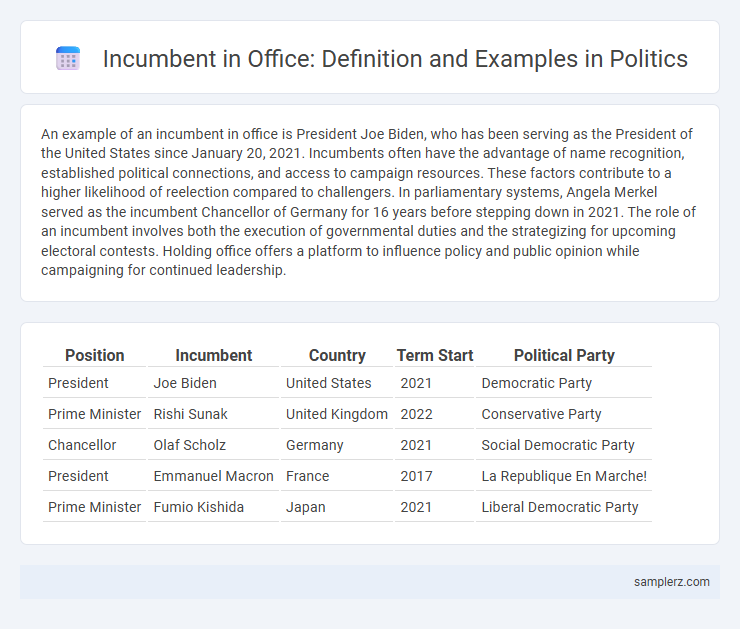
| Position | Incumbent | Country | Term Start | Political Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| President | Joe Biden | United States | 2021 | Democratic Party |
| Prime Minister | Rishi Sunak | United Kingdom | 2022 | Conservative Party |
| Chancellor | Olaf Scholz | Germany | 2021 | Social Democratic Party |
| President | Emmanuel Macron | France | 2017 | La Republique En Marche! |
| Prime Minister | Fumio Kishida | Japan | 2021 | Liberal Democratic Party |
Definition of an Incumbent in Political Office
An incumbent in political office refers to a current officeholder actively serving their term during an election period. This status often provides advantages such as greater name recognition, established political networks, and easier access to campaign funding. Incumbents typically leverage their legislative record and constituent services as key factors in their re-election campaigns.
Historical Overview: Notable Incumbents Worldwide
Franklin D. Roosevelt remains one of the most notable incumbents in office, serving as the 32nd President of the United States from 1933 to 1945 and implementing transformative New Deal policies during the Great Depression. Margaret Thatcher, as the UK's Prime Minister from 1979 to 1990, stands out for her strong conservative leadership and economic reforms known as Thatcherism. In recent history, Angela Merkel held the Chancellor of Germany position from 2005 to 2021, recognized for stabilizing the EU economy and managing the European migrant crisis.
The Role of Incumbency in Election Campaigns
Incumbency plays a critical role in election campaigns by providing candidates with name recognition, established donor networks, and a record of public service to showcase. Studies show that incumbents have a reelection rate exceeding 80% in U.S. congressional races due to advantages like media exposure and constituent services. The ability to leverage legislative achievements and secure government resources further strengthens an incumbent's position against challengers.
Advantages Held by Political Incumbents
Political incumbents often benefit from name recognition, established donor networks, and easier access to media coverage, providing them significant fundraising and visibility advantages. Their track record in office allows them to showcase accomplishments and policy experience, which can instill voter confidence relative to challengers. Furthermore, incumbents typically have institutional support and established campaign infrastructures that streamline their re-election efforts.
Challenges Faced by Incumbents in Office
Incumbents in office often contend with voter fatigue, where constituents seek change despite previous achievements. They face intense scrutiny over policy decisions and must balance the demands of diverse interest groups while managing limited resources. Campaign finance pressures and maintaining visibility amid emerging challengers further complicate re-election efforts.
Case Study: Successful Incumbents in Recent Elections
In the 2020 U.S. presidential election, incumbent Joe Biden prevailed by leveraging robust voter engagement and clear policy messaging. Similarly, German Chancellor Angela Merkel secured multiple terms through consistent economic growth and coalition-building strategies. These case studies illustrate how incumbents capitalize on established political capital and effective campaign dynamics to maintain office.
Incumbent Presidents: Influence and Impact
Incumbent presidents leverage their established political networks and policy achievements to influence legislative agendas and public opinion effectively. Their access to executive resources and media platforms amplifies their capacity to shape national discourse and maintain electoral advantages. Historical data shows that incumbent presidents often enjoy higher re-election rates due to the visibility and institutional support inherent in their office.
How Incumbency Shapes Political Landscape
Incumbency significantly shapes the political landscape by providing officeholders with advantages such as name recognition, established donor networks, and proven electoral success. For example, President Joe Biden's 2020 campaign leveraged his incumbent status to secure key endorsements and mobilize voter bases effectively. These factors often create high barriers for challengers, reinforcing the power dynamics within electoral politics.
Controversies Involving Political Incumbents
Political incumbents often face controversies such as allegations of corruption, misuse of public funds, and conflicts of interest that damage public trust and threaten their re-election prospects. For example, former Chicago Mayor Richard M. Daley encountered scrutiny over city contract awards perceived as favoring political allies. These controversies underscore the challenges incumbents face in maintaining ethical governance while balancing political pressures.
Voter Perception and the Incumbency Effect
Incumbent politicians often benefit from the incumbency effect, where voter perception is positively influenced by name recognition, proven experience, and established networks. Studies show that incumbents typically secure a re-election advantage of 5 to 10 percentage points due to perceived competence and access to resources. This phenomenon underscores how voter familiarity and trust can significantly impact electoral outcomes in democratic systems.
example of incumbent in office Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com