The tuktuk is a popular mode of mobility in many urban areas, especially in cities across Southeast Asia. This three-wheeled vehicle serves as an efficient and affordable alternative to traditional taxis and public transport. Data from cities like Bangkok and Manila show that tuktuks significantly reduce travel time in congested streets, offering a practical solution for short-distance commutes. In urban mobility, the tuktuk plays a crucial role in addressing last-mile connectivity challenges. Its compact size allows it to navigate narrow alleyways and heavy traffic, making it ideal for densely populated areas. City transportation statistics indicate that tuktuks contribute to reducing carbon emissions by using fuel-efficient engines or electric models, aligning with sustainable urban mobility goals.
Table of Comparison
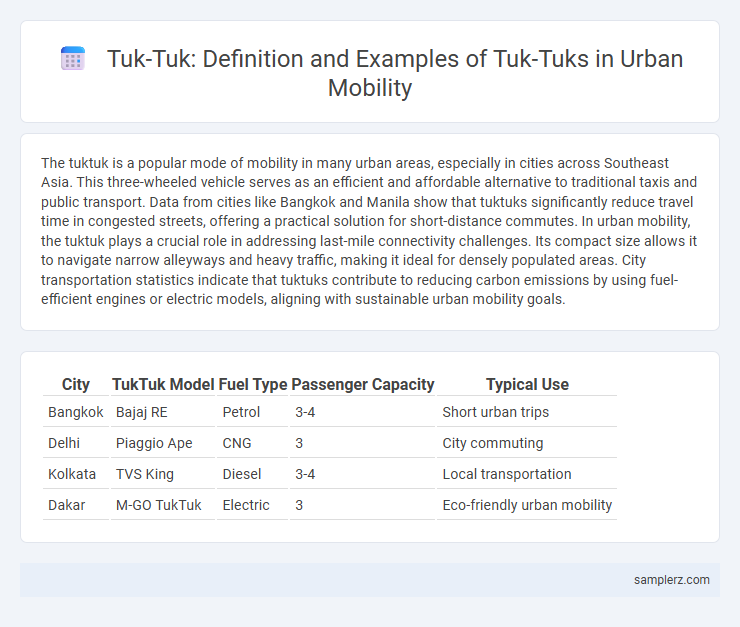
| City | TukTuk Model | Fuel Type | Passenger Capacity | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bangkok | Bajaj RE | Petrol | 3-4 | Short urban trips |
| Delhi | Piaggio Ape | CNG | 3 | City commuting |
| Kolkata | TVS King | Diesel | 3-4 | Local transportation |
| Dakar | M-GO TukTuk | Electric | 3 | Eco-friendly urban mobility |
Introduction to TukTuk Mobility Solutions
TukTuk mobility solutions offer an efficient, eco-friendly mode of transportation in congested urban areas, reducing traffic congestion and lowering emissions. These three-wheeled vehicles can navigate narrow streets and crowded neighborhoods where traditional cars struggle, improving accessibility and last-mile connectivity. Growing adoption of electric TukTuks enhances sustainable urban transit, supporting smart city initiatives and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Urban Integration of TukTuks
TukTuks play a key role in urban mobility by providing flexible, last-mile transportation that complements existing public transit systems. Their compact size and maneuverability reduce traffic congestion and improve accessibility in narrow city streets and densely populated neighborhoods. Integrating TukTuks with multimodal transport hubs enhances efficient urban connectivity and supports sustainable mobility solutions.
Environmental Impact of City TukTuks
City tuk-tuks contribute significantly to urban air pollution due to their reliance on two-stroke engines that emit high levels of carbon monoxide and particulate matter. Recent studies indicate that replacing conventional tuk-tuks with electric models can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70%. Implementing electric tuk-tuks in dense urban areas improves air quality and lowers the overall carbon footprint of city transportation systems.
TukTuks vs Traditional Urban Transport
TukTuks offer agile and affordable mobility solutions in congested city centers, outperforming traditional urban transport options like buses and taxis in maneuverability and fuel efficiency. Their compact size reduces traffic bottlenecks and parking challenges, making them ideal for short-distance trips within dense urban environments. While conventional public transit provides higher passenger capacity, TukTuks uniquely blend convenience with cost-effectiveness for first- and last-mile connectivity.
Affordability and Accessibility of TukTuks
TukTuks offer an affordable urban mobility solution, with fares significantly lower than traditional taxis and ride-sharing services, making them accessible to low-income populations. Their compact size enables them to navigate congested city streets efficiently, reducing travel times and increasing accessibility in densely populated areas. This combination of cost-effectiveness and maneuverability makes TukTuks a popular choice for short-distance travel in many developing cities worldwide.
Smart City Adoption of Electric TukTuks
Electric tuk-tuks are transforming urban mobility in smart cities by reducing emissions and traffic congestion. Cities like Bangkok and Manila implement electric tuk-tuk fleets integrated with IoT systems for real-time monitoring and route optimization. These eco-friendly vehicles enhance sustainable transportation by leveraging smart charging infrastructure and mobile payment solutions.
Case Studies: Successful TukTuk Implementation
TukTuks have dramatically improved urban mobility in cities like Bangkok and Jakarta, offering affordable and eco-friendly transport options that reduce traffic congestion and emissions. Case studies reveal that integrating TukTuks with existing public transit systems enhances last-mile connectivity and boosts local economies by supporting informal transport sectors. Data from these implementations show increased passenger satisfaction and a notable decrease in carbon footprint compared to traditional vehicle use.
Challenges in TukTuk Urban Operations
TukTuk urban operations face significant challenges including limited passenger capacity, safety concerns in high-traffic areas, and inadequate integration with existing public transportation networks. Engine emissions contribute to urban air pollution, necessitating cleaner energy solutions to meet environmental regulations. Navigating narrow streets and congested zones further complicates efficient route planning and increases downtime.
Future Trends in TukTuk-based Mobility
Future trends in tuk-tuk based mobility emphasize electric powertrains to reduce urban air pollution and carbon emissions. Integration with smart city infrastructure enables real-time route optimization and seamless ridesharing through mobile apps, enhancing commuter efficiency. Autonomous driving technology is also being tested to improve safety and reduce operational costs in densely populated urban environments.
Policy and Regulation for TukTuks in Cities
TukTuks in cities face diverse policy and regulatory frameworks aimed at balancing urban mobility and safety. Many municipalities implement specific licensing requirements, emission standards, and operational zones to integrate TukTuks into public transport systems effectively. Enforcement of these regulations ensures reduced congestion and pollution while promoting sustainable micro-mobility solutions in densely populated urban centers.
example of tuktuk in city Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com