Telecabines in ropeway systems provide an efficient and scenic mode of aerial transportation, commonly used in mountainous regions and urban settings. These enclosed cabins, suspended by cables, can transport passengers smoothly over difficult terrains, offering a reliable alternative to traditional ground transport. Telecabines enhance mobility by reducing travel time and minimizing environmental impact compared to road vehicles. Manufacturers design telecabines with advanced materials and engineering techniques to ensure safety, comfort, and energy efficiency. Data from ropeway operators show that telecabin systems handle high passenger volumes while maintaining consistent operational speeds. The integration of telecabine technology contributes to sustainable urban transit networks and promotes tourism by connecting remote locations seamlessly.
Table of Comparison
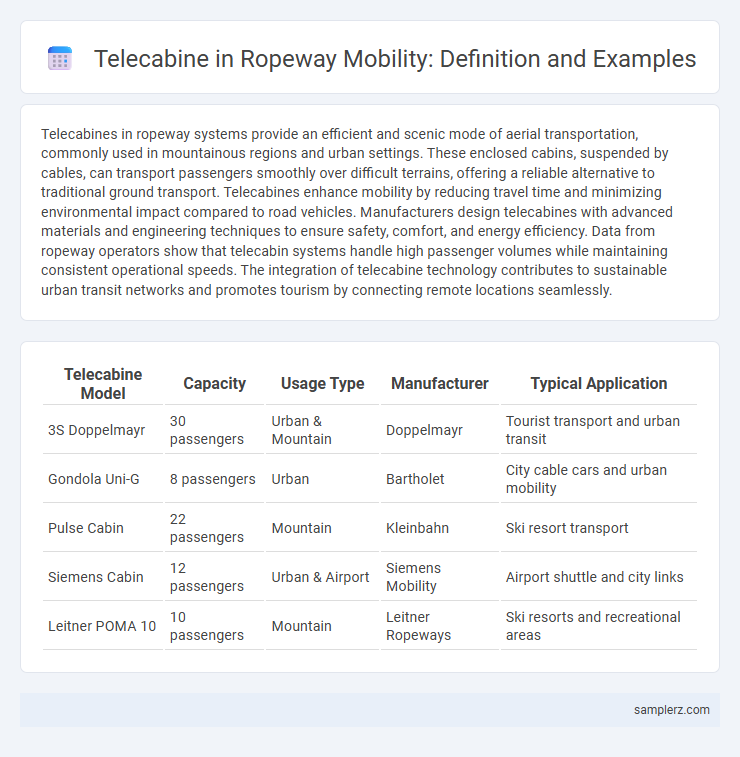
| Telecabine Model | Capacity | Usage Type | Manufacturer | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3S Doppelmayr | 30 passengers | Urban & Mountain | Doppelmayr | Tourist transport and urban transit |
| Gondola Uni-G | 8 passengers | Urban | Bartholet | City cable cars and urban mobility |
| Pulse Cabin | 22 passengers | Mountain | Kleinbahn | Ski resort transport |
| Siemens Cabin | 12 passengers | Urban & Airport | Siemens Mobility | Airport shuttle and city links |
| Leitner POMA 10 | 10 passengers | Mountain | Leitner Ropeways | Ski resorts and recreational areas |
Introduction to Telecabines in Ropeway Mobility
Telecabines in ropeway mobility represent an innovative mode of transportation, utilizing suspended cabins attached to cables to efficiently navigate steep or challenging terrains. This system enhances urban and mountainous transit by providing safe, eco-friendly, and reliable connections that reduce traffic congestion and minimize environmental impact. Advanced telecabine technologies incorporate automated controls and panoramic designs, optimizing passenger comfort and operational efficiency.
Iconic Telecabine Systems Around the World
Iconic telecabine systems such as the Roosevelt Island Tramway in New York City, the Table Mountain Cableway in South Africa, and the Ngong Ping 360 in Hong Kong highlight advancements in urban and tourist mobility. These ropeway systems offer efficient, scenic transportation options that reduce traffic congestion and carbon emissions. Integrating cutting-edge technology, they provide reliable and safe transit while enhancing the appeal of their respective destinations.
Urban Applications of Telecabine Ropeways
Telecabine ropeways in urban settings enhance mobility by offering efficient, congestion-free transportation across challenging terrains and dense cityscapes. Cities like Medellin and La Paz utilize these aerial cable cars to connect underserved neighborhoods, reducing commute times and lowering emissions. The integration of telecabine systems supports sustainable urban development by providing a scalable, eco-friendly transit alternative.
Telecabines in Mountainous Regions
Telecabines in mountainous regions provide efficient, eco-friendly transportation by navigating steep terrains and connecting remote areas with urban centers. These ropeway systems reduce travel time while offering panoramic views, making them popular for both commuting and tourism. Advanced cable car technologies ensure safety and comfort, even in harsh weather conditions.
Eco-Friendly Benefits of Telecabine Ropeways
Telecabine ropeways significantly reduce carbon emissions by relying on electric power instead of fossil fuels, making them an eco-friendly alternative for urban and mountainous mobility. Their energy efficiency is enhanced by regenerative braking systems that recycle energy during descent, minimizing overall consumption. By decreasing ground traffic congestion, telecabine ropeways help lower air pollution levels and promote sustainable transportation solutions.
Technological Innovations in Telecabine Systems
Telecabine systems in ropeways have pioneered advances such as automated grip technology that enhances safety and operational efficiency while minimizing maintenance needs. Modern cabins integrate real-time monitoring sensors and IoT connectivity, enabling predictive maintenance and improved passenger experience through seamless communication. Innovations in aerodynamic cabin design and energy-efficient motor systems reduce environmental impact and maximize performance in diverse terrains.
Safety Features in Modern Telecabine Ropeways
Modern telecabine ropeways prioritize safety through advanced braking systems and continuous monitoring technology, ensuring secure transportation even in adverse weather conditions. Emergency communication devices within cabins enable instant contact with operators during unexpected situations. Structural reinforcements and automated rescue protocols further enhance passenger protection in contemporary ropeway designs.
Accessibility of Telecabines for All Passengers
Telecabines in ropeway systems enhance mobility by providing accessible transportation options for passengers with varying mobility needs, including wheelchair users and elderly travelers. These cabins feature level boarding, spacious interiors, and secure restraint systems to ensure safety and comfort. Designed to comply with universal access standards, telecabines improve inclusivity and offer reliable transit across challenging terrains.
Case Studies: Successful Telecabine Implementations
The Medellin Metrocable system in Colombia exemplifies successful telecabine implementation, dramatically improving urban mobility in steep, underserved neighborhoods by integrating cable cars with existing public transit. The Emirates Air Line in London showcases telecabine technology enhancing river crossings while promoting tourism and daily commuting efficiency. In La Paz, Bolivia, the Mi Teleferico network connects sprawling, mountainous urban areas, reducing travel times by over 50% and demonstrating effective cableway integration within complex terrains.
Future Trends in Telecabine Ropeway Mobility
Future trends in telecabine ropeway mobility emphasize the integration of smart technologies such as IoT sensors and AI-powered predictive maintenance to enhance safety and operational efficiency. Renewable energy sources, especially solar and wind power, are increasingly utilized to reduce the carbon footprint of ropeway systems. Autonomous cabin control and seamless digital ticketing solutions are set to improve passenger experience and streamline urban mobility networks.
example of telecabine in ropeway Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com