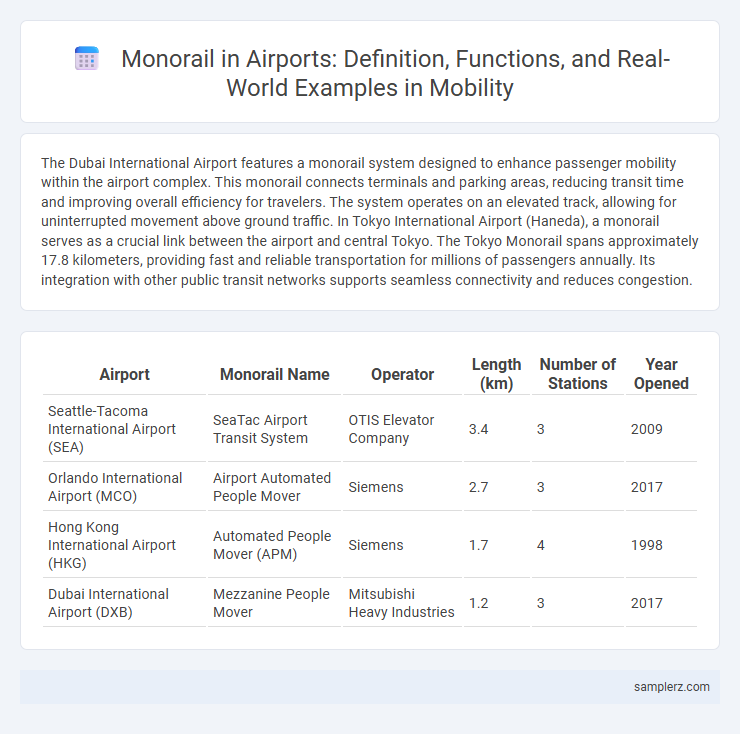
The Dubai International Airport features a monorail system designed to enhance passenger mobility within the airport complex. This monorail connects terminals and parking areas, reducing transit time and improving overall efficiency for travelers. The system operates on an elevated track, allowing for uninterrupted movement above ground traffic. In Tokyo International Airport (Haneda), a monorail serves as a crucial link between the airport and central Tokyo. The Tokyo Monorail spans approximately 17.8 kilometers, providing fast and reliable transportation for millions of passengers annually. Its integration with other public transit networks supports seamless connectivity and reduces congestion.
Table of Comparison
| Airport | Monorail Name | Operator | Length (km) | Number of Stations | Year Opened |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seattle-Tacoma International Airport (SEA) | SeaTac Airport Transit System | OTIS Elevator Company | 3.4 | 3 | 2009 |
| Orlando International Airport (MCO) | Airport Automated People Mover | Siemens | 2.7 | 3 | 2017 |
| Hong Kong International Airport (HKG) | Automated People Mover (APM) | Siemens | 1.7 | 4 | 1998 |
| Dubai International Airport (DXB) | Mezzanine People Mover | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | 1.2 | 3 | 2017 |
Introduction to Airport Monorail Systems
Airport monorail systems provide efficient, elevated transportation connecting terminals, parking areas, and rental car facilities, reducing ground traffic congestion. These automated transit solutions enhance passenger flow and minimize transfer times, supporting seamless airport mobility. Advanced monorail infrastructure integrates real-time monitoring and energy-efficient technologies to optimize operational reliability and sustainability.
Key Features of Airport Monorails
Airport monorails feature elevated tracks that provide seamless, congestion-free transit between terminals, parking areas, and rental car centers. They utilize automated, driverless trains equipped with real-time tracking systems and energy-efficient technologies, enhancing operational efficiency and passenger convenience. Advanced safety mechanisms and frequent service intervals further contribute to reducing airport transit times and improving overall traveler experience.
Benefits of Monorail Integration in Airports
Monorail integration in airports enhances passenger flow by providing efficient, reliable, and rapid transit between terminals and parking areas, reducing congestion and wait times. The compact design of monorail systems minimizes land use and infrastructure costs while supporting sustainable transportation through lower emissions. Improved connectivity and seamless transfers elevate the overall airport experience, contributing to increased operational efficiency and traveler satisfaction.
Notable Airports with Monorail Services
Notable airports with monorail services include Kuala Lumpur International Airport, which utilizes its Aerotrain system to connect terminals efficiently and reduce transit time. Tokyo International Airport (Haneda) features an advanced monorail that links the airport directly to central Tokyo, enhancing passenger mobility across the metropolitan area. Miami International Airport operates a people mover monorail system that streamlines passenger movement between terminals while improving overall airport connectivity.
Case Study: Changi Airport Skytrain (Singapore)
The Changi Airport Skytrain in Singapore exemplifies advanced airport mobility by efficiently connecting terminals with a fully automated monorail system. Handling millions of passengers annually, it reduces transit times and enhances the overall travel experience through seamless, sustainable transportation technology. This case study highlights how integrated monorail solutions optimize airport operations and passenger flow in high-traffic hubs.
Case Study: Newark Liberty AirTrain (USA)
Newark Liberty AirTrain is a prime example of an efficient airport monorail system, connecting terminals, parking lots, and rental car facilities seamlessly. The system enhances passenger mobility by reducing transit times and improving access to New Jersey Transit and Amtrak stations. Its automated, elevated monorail design minimizes ground traffic congestion while providing reliable, rapid transit within Newark Liberty International Airport.
Case Study: Tokyo Haneda Airport Monorail (Japan)
Tokyo Haneda Airport's monorail system exemplifies efficient airport mobility, connecting the terminal directly to central Tokyo with rapid transit and minimal delays. The 17.8-kilometer-long Tokyo Monorail, operating since 1964, handles over 300,000 passengers daily, showcasing advanced automation and environmental sustainability in urban transit. Its integration with multiple train lines and real-time scheduling optimizes passenger flow and reduces congestion, setting a global standard for airport transit infrastructure.
Technological Advancements in Airport Monorails
Airport monorails have integrated cutting-edge automation systems that enhance operational efficiency and passenger safety, utilizing AI-powered predictive maintenance to reduce downtime. Advanced propulsion technologies, such as linear motors, enable smooth and energy-efficient transit between terminals. Real-time data analytics optimize scheduling and crowd management, ensuring seamless connectivity in high-traffic airport environments.
Passenger Experience on Airport Monorails
Airport monorails significantly enhance passenger experience by providing fast, reliable, and seamless transit between terminals and parking areas. Their elevated design reduces ground-level congestion, ensuring smooth, stress-free transfers even during peak travel times. Advanced automation and real-time information systems improve accessibility and convenience, making airport navigation efficient and comfortable for all travelers.
Future Trends in Airport Monorail Mobility
Future trends in airport monorail mobility emphasize the integration of autonomous driving technology and AI-powered traffic management systems to enhance efficiency and passenger experience. Sustainable energy sources, such as solar and hydrogen fuel cells, are increasingly adopted to reduce carbon emissions and operational costs. Advanced real-time data analytics improve predictive maintenance and optimize scheduling, ensuring seamless connections within airport terminals and surrounding transportation networks.
example of monorail in airport Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com