A loss leader in retail is a product sold at a price below its market cost to attract customers. An example is a popular brand of coffee sold at a reduced price in a supermarket, designed to bring shoppers into the store. Retailers use this strategy to increase foot traffic and boost sales of higher-margin items around the loss leader product. Walmart often uses loss leader tactics by offering low prices on staple items like milk or eggs. These deeply discounted products generate store visits, encouraging customers to purchase additional goods. The data shows that while the retailer incurs a loss on these specific items, overall revenue and profitability improve due to increased basket size.
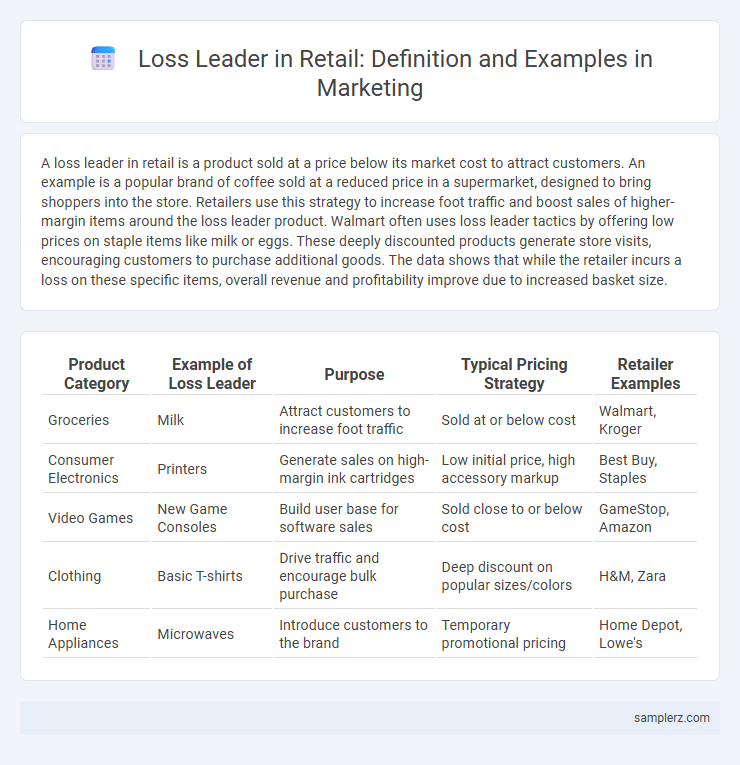
Table of Comparison
| Product Category | Example of Loss Leader | Purpose | Typical Pricing Strategy | Retailer Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groceries | Milk | Attract customers to increase foot traffic | Sold at or below cost | Walmart, Kroger |
| Consumer Electronics | Printers | Generate sales on high-margin ink cartridges | Low initial price, high accessory markup | Best Buy, Staples |
| Video Games | New Game Consoles | Build user base for software sales | Sold close to or below cost | GameStop, Amazon |
| Clothing | Basic T-shirts | Drive traffic and encourage bulk purchase | Deep discount on popular sizes/colors | H&M, Zara |
| Home Appliances | Microwaves | Introduce customers to the brand | Temporary promotional pricing | Home Depot, Lowe's |
Understanding the Loss Leader Strategy in Retail
Retailers often use popular products like printers or game consoles as loss leaders by selling them below cost to attract customers into the store. This strategy leverages customer traffic drawn by the discounted item to boost sales of higher-margin products such as ink cartridges or video games. Understanding the loss leader strategy in retail reveals how businesses balance short-term losses with long-term profit through increased overall sales volume and customer loyalty.
Classic Examples of Loss Leaders Used by Major Retailers
Retail giants like Walmart often use loss leaders such as milk or eggs to attract customers, knowing these staple items drive frequent store visits. Amazon offers discounted or free shipping on select products as a loss leader, boosting overall sales and customer loyalty. Best Buy strategically prices gaming consoles below cost to increase sales of high-margin accessories and services.
Grocery Stores Utilizing Loss Leaders to Drive Traffic
Grocery stores frequently use staple items like milk or bread as loss leaders to attract customers into the store, sacrificing profit on these products to boost overall sales volume. This strategy increases foot traffic, encouraging shoppers to purchase higher-margin items once inside. By pricing essential goods below cost, retailers enhance customer loyalty while improving sales of complementary products.
Black Friday Loss Leader Deals: Tactics and Impact
Black Friday loss leader deals often feature heavily discounted electronics and household appliances to drive massive customer traffic into retail stores. Retailers use these tactics to increase overall sales volume, knowing that consumers typically purchase additional full-priced items once inside. These strategic discounts create urgency and boost market share while absorbing short-term losses for long-term profitability.
Tech Giants Offering Gadgets Below Cost as Loss Leaders
Tech giants like Apple and Samsung strategically price select gadgets below cost as loss leaders to attract consumers and drive ecosystem sales. By offering popular devices such as smartphones and smart speakers at a loss, these companies increase user engagement and promote accessory and software purchases. This pricing tactic boosts market share while subsidizing initial hardware expenses through long-term service subscriptions.
Seasonal Products as Effective Retail Loss Leaders
Seasonal products such as holiday decorations and summer apparel often serve as effective retail loss leaders by attracting customers with significantly reduced prices. Retailers strategically price these items below cost to increase store traffic and encourage additional purchases of higher-margin merchandise. This tactic leverages consumer urgency tied to limited seasonal availability, maximizing overall sales and customer loyalty.
Loss Leaders in Clothing and Apparel Retail
Loss leaders in clothing and apparel retail often include popular wardrobe staples such as basic t-shirts, denim jeans, and seasonal accessories sold below cost to attract customers. Retailers like H&M and Zara use these items strategically to increase foot traffic and encourage purchasing of higher-margin fashion pieces. This approach enhances overall sales volume while reinforcing brand loyalty through affordable entry products.
How Pharmacies Use Loss Leaders to Attract Customers
Pharmacies often use popular over-the-counter medications and essential health products as loss leaders, pricing them below cost to attract foot traffic. This strategy increases customer visits, boosting sales of higher-margin items such as prescription drugs and wellness supplements. By leveraging loss leader pricing, pharmacies enhance overall profitability while maintaining competitive positioning.
Impact of Loss Leader Strategy on Customer Loyalty
Loss leader pricing in retail, such as selling popular products like printers at a minimal cost or below cost, drives increased store traffic and encourages customers to purchase higher-margin accessories. This strategy enhances customer loyalty by creating a perception of value and trust, prompting repeat visits and long-term brand engagement. Retailers leveraging loss leaders often experience higher customer retention rates and amplified word-of-mouth referrals, solidifying market position.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Loss Leader Pricing in Modern Retail
Loss leader pricing in modern retail is exemplified by supermarkets offering staple items like milk or bread at significantly reduced prices to attract customers. Evaluating its effectiveness involves analyzing increased foot traffic, customer purchasing behavior on higher-margin products, and overall impact on store profitability. Retailers use data analytics to measure conversion rates and average transaction values, ensuring that loss leader strategies drive long-term sales growth rather than just short-term discounts.
example of loss leader in retail Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com