Laddering in marketing involves identifying the deeper values and motivations behind consumer purchasing decisions. For example, a company selling eco-friendly water bottles may start by understanding that customers value sustainability. By asking why sustainability is important, the marketer uncovers that customers want to protect the environment for future generations, which connects to their broader personal values. This technique helps marketers create messaging that resonates on an emotional level. Instead of just promoting product features like BPA-free materials, the communication focuses on the higher-order benefit of contributing to a healthier planet. Using laddering, brands can develop targeted campaigns that link product attributes to consumers' core beliefs, increasing engagement and loyalty.
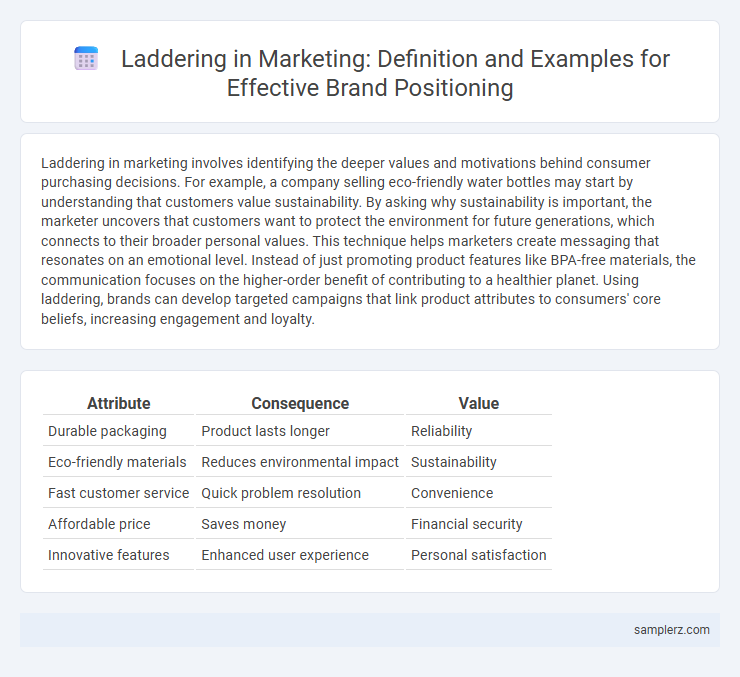
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Consequence | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Durable packaging | Product lasts longer | Reliability |
| Eco-friendly materials | Reduces environmental impact | Sustainability |
| Fast customer service | Quick problem resolution | Convenience |
| Affordable price | Saves money | Financial security |
| Innovative features | Enhanced user experience | Personal satisfaction |
Understanding Laddering in Marketing
Laddering in marketing involves uncovering the deeper motivations behind consumer behavior by linking product attributes to personal values through a structured interview technique. For example, a marketer might discover that a customer buys organic snacks not just for health benefits (attribute) but because it aligns with their value of environmental sustainability and well-being. This insight helps brands create targeted messaging that resonates on an emotional level, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
The Basics: What Is Laddering?
Laddering in marketing is a qualitative research technique used to uncover the underlying values and motivations driving consumer behavior by linking product attributes to personal consequences and core values. This method involves in-depth interviews that move from specific product features to the emotional benefits and eventual personal values that influence purchasing decisions. Understanding these hierarchical connections helps marketers create targeted messaging that resonates deeply with their audience.
Step-by-Step Laddering Example
Step-by-step laddering in marketing begins by identifying a product attribute, such as "eco-friendly packaging," then exploring the consequences of that attribute, like reducing environmental impact and enhancing brand reputation. Next, marketers connect these consequences to personal values, such as sustainability and social responsibility, to create a strong emotional appeal. This method deepens customer insight, enabling targeted messaging that aligns product features with consumer motivations effectively.
Laddering in Consumer Purchasing Decisions
Laddering in consumer purchasing decisions involves uncovering the underlying values and motivations that drive buyers through a sequence of attribute-consequence-value connections. For example, a customer choosing an eco-friendly detergent may prioritize its environmental benefits (attribute), leading to a sense of personal responsibility (consequence), which ultimately aligns with their core value of sustainability. Marketers leverage this insight by tailoring messages that resonate with the deeper emotional needs behind product choices, enhancing the effectiveness of marketing strategies.
Case Study: Laddering in the Beverage Industry
Laddering in marketing, exemplified by PepsiCo's campaign for Mountain Dew, reveals how consumer attributes link to emotional values driving purchase decisions. Through in-depth interviews, researchers identified that customers associated Mountain Dew not just with refreshment but with excitement and adventure, elevating brand positioning beyond taste. This strategic approach enhanced targeted messaging, increasing market share by aligning product features with deeper lifestyle aspirations.
How Laddering Reveals Core Brand Values
Laddering in marketing uncovers core brand values by linking product attributes to emotional benefits and personal motivations, revealing why consumers choose a brand beyond its features. For example, a sports apparel brand may connect durability (attribute) to confidence in performance (functional benefit) and ultimately to a sense of achievement and self-identity (emotional value). This technique helps marketers shape targeted messaging that resonates deeply with consumers' intrinsic desires, fostering stronger brand loyalty.
Laddering Techniques in Market Research
Laddering techniques in market research involve uncovering consumers' deep-seated values by linking product attributes to personal motivations through structured interviews. This method helps marketers understand why specific features matter by tracing the connections from tangible benefits to emotional benefits and core values. By applying laddering, brands can create targeted messaging that resonates on a psychological level, driving more effective engagement and loyalty.
Using Laddering to Refine Brand Messaging
Using laddering in marketing helps uncover underlying customer values by linking product features to emotional benefits, enabling brands to craft more resonant messaging. By systematically exploring why consumers choose a product, marketers identify core motivations that drive purchase decisions, refining brand narratives to emphasize these emotional connections. This approach enhances messaging effectiveness by aligning brand promises with the deeper aspirations and needs of target audiences.
Laddering Example: Cosmetics Market Insights
Laddering in the cosmetics market reveals that consumers often choose products based on functional attributes like moisturizing effects and natural ingredients, linking these features to higher-level personal values such as self-confidence and beauty enhancement. For instance, a customer may select a skincare brand emphasizing organic components because it aligns with their desire for health-conscious and sustainable lifestyles. By uncovering these attribute-consequence-value connections, marketers can tailor messaging that resonates deeply with target audiences and drives brand loyalty.
Laddering and Emotional Drivers in Customer Choices
Laddering in marketing uncovers the emotional drivers behind customer choices by linking product attributes to personal values, such as security, self-esteem, or belonging. For example, a car brand highlighting safety features connects to the deeper emotional need for family protection, influencing purchase decisions. This technique helps marketers craft messages that resonate on an emotional level, enhancing brand loyalty and customer engagement.
example of laddering in marketing Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com