Remarketing in marketing involves targeting users who have previously interacted with a brand but did not complete a desired action. For example, an e-commerce company can use remarketing by displaying ads to visitors who added products to their shopping cart but did not make a purchase. These targeted ads often appear on social media platforms or other websites within the Google Display Network, increasing the chances of conversion. This strategy leverages customer data such as browsing history and engagement patterns to create personalized ad experiences. By analyzing user behavior, marketers can tailor messages that encourage users to return and finalize transactions. Remarketing campaigns drive higher ROI by focusing efforts on warm leads, reducing the cost of customer acquisition.
Table of Comparison
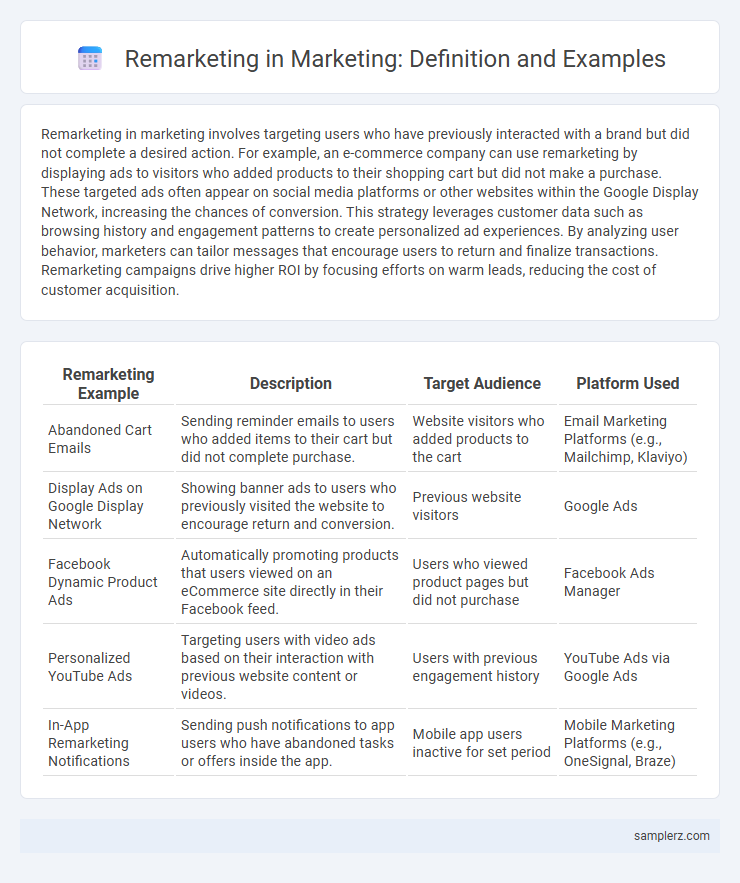
| Remarketing Example | Description | Target Audience | Platform Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abandoned Cart Emails | Sending reminder emails to users who added items to their cart but did not complete purchase. | Website visitors who added products to the cart | Email Marketing Platforms (e.g., Mailchimp, Klaviyo) |
| Display Ads on Google Display Network | Showing banner ads to users who previously visited the website to encourage return and conversion. | Previous website visitors | Google Ads |
| Facebook Dynamic Product Ads | Automatically promoting products that users viewed on an eCommerce site directly in their Facebook feed. | Users who viewed product pages but did not purchase | Facebook Ads Manager |
| Personalized YouTube Ads | Targeting users with video ads based on their interaction with previous website content or videos. | Users with previous engagement history | YouTube Ads via Google Ads |
| In-App Remarketing Notifications | Sending push notifications to app users who have abandoned tasks or offers inside the app. | Mobile app users inactive for set period | Mobile Marketing Platforms (e.g., OneSignal, Braze) |
What is Remarketing?
Remarketing in marketing involves targeting users who have previously interacted with a brand's website or app by displaying tailored ads to encourage them to return and complete a purchase. It uses cookies and tracking pixels to identify these visitors and serves personalized ads across platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads. This strategy increases conversion rates by focusing on an audience already familiar with the brand's products or services.
Benefits of Remarketing in Marketing
Remarketing in marketing significantly boosts conversion rates by targeting users who have previously engaged with a brand but did not complete a purchase. It enhances brand recall through personalized ads, increasing the likelihood of customer return and higher lifetime value. This strategy reduces acquisition costs by focusing marketing spend on audience segments with proven interest, leading to better ROI.
How Remarketing Works: A Simple Overview
Remarketing targets users who have previously interacted with a brand's website or app by displaying tailored ads as they browse other online platforms, increasing brand recall and conversion rates. It employs browser cookies or mobile device IDs to track visitor behavior and segment audiences based on their engagement level or specific actions, such as cart abandonment. This precise targeting allows marketers to deliver personalized ad content that encourages users to revisit and complete desired actions, enhancing overall campaign effectiveness.
Remarketing vs. Retargeting: Key Differences
Remarketing primarily uses email campaigns to reconnect with previous customers, while retargeting relies on display ads to attract visitors who have interacted with a website but did not convert. Remarketing targets known audiences with personalized messages, enhancing customer loyalty, whereas retargeting targets anonymous users based on their online behavior to increase site visits and conversions. Understanding these distinctions helps marketers allocate budget effectively and optimize customer acquisition strategies.
Google Ads Remarketing: A Practical Example
Google Ads Remarketing targets users who previously visited a website by displaying tailored ads as they browse other sites within the Google Display Network. For instance, an online retailer can use Google Ads Remarketing to show personalized product ads to customers who abandoned their shopping cart, increasing the chances of conversion. This strategy boosts ROI by re-engaging potential buyers with relevant offers based on their prior interactions.
Social Media Remarketing Campaigns
Social media remarketing campaigns target users who previously engaged with a brand's content, increasing conversion rates by presenting tailored ads on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn. These campaigns use pixel tracking and custom audience segmentation to deliver personalized offers and reminders, boosting customer retention and brand recall. Brands leveraging dynamic product ads in social media remarketing often experience higher click-through rates and improved return on ad spend (ROAS).
Email Remarketing: Turning Abandoned Carts into Sales
Email remarketing targets users who have abandoned their shopping carts by sending personalized follow-up emails featuring the exact items left behind. Incorporating incentives such as limited-time discounts or free shipping in these emails can significantly increase conversion rates. Retailers leveraging automated email sequences for cart abandonment have seen an average 10-15% uplift in recovered sales.
Dynamic Remarketing: Personalizing the Customer Experience
Dynamic Remarketing leverages user behavior data to deliver personalized ads featuring products or services previously viewed, significantly increasing conversion rates. By integrating real-time product feeds with customer interaction history, marketers create highly relevant ad experiences tailored to individual preferences. This targeted approach enhances engagement, drives repeat visits, and optimizes ROI through customized recommendations.
Best Practices for Successful Remarketing Strategies
Effective remarketing strategies leverage personalized ad content tailored to user behavior by segmenting audiences based on interactions, which significantly increases conversion rates. Utilizing frequency capping prevents ad fatigue, ensuring customers are not overwhelmed while maintaining brand presence across multiple platforms. Employing dynamic remarketing with real-time product updates enhances user experience and drives higher engagement through relevant, timely offers.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Remarketing Efforts
Remarketing campaigns are measured by tracking key performance indicators such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and return on ad spend (ROAS) to evaluate user engagement and sales impact. Utilizing tools like Google Analytics and Facebook Pixel enables marketers to attribute conversions accurately and assess the incremental lift generated by remarketing ads. A/B testing different ad creatives and audience segments further refines targeting strategies and improves overall campaign effectiveness.
example of remarketing in marketing Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com