A common dark pattern in marketing is the use of hidden fees that only appear during the final stages of checkout. This tactic involves displaying a lower initial price to attract customers and then revealing additional charges such as taxes, service fees, or shipping costs before completing the purchase. Companies employing these deceptive strategies aim to increase conversion rates by misleading consumers about the true cost of products or services. Another dark pattern is the manipulation of urgency through fake countdown timers to pressure buyers into making quick decisions. These timers suggest limited-time offers or scarcity, even when inventory is plentiful or the deal is constantly available. This approach exploits consumer psychology by creating a false sense of urgency, driving impulse purchases without allowing adequate time for consideration.
Table of Comparison
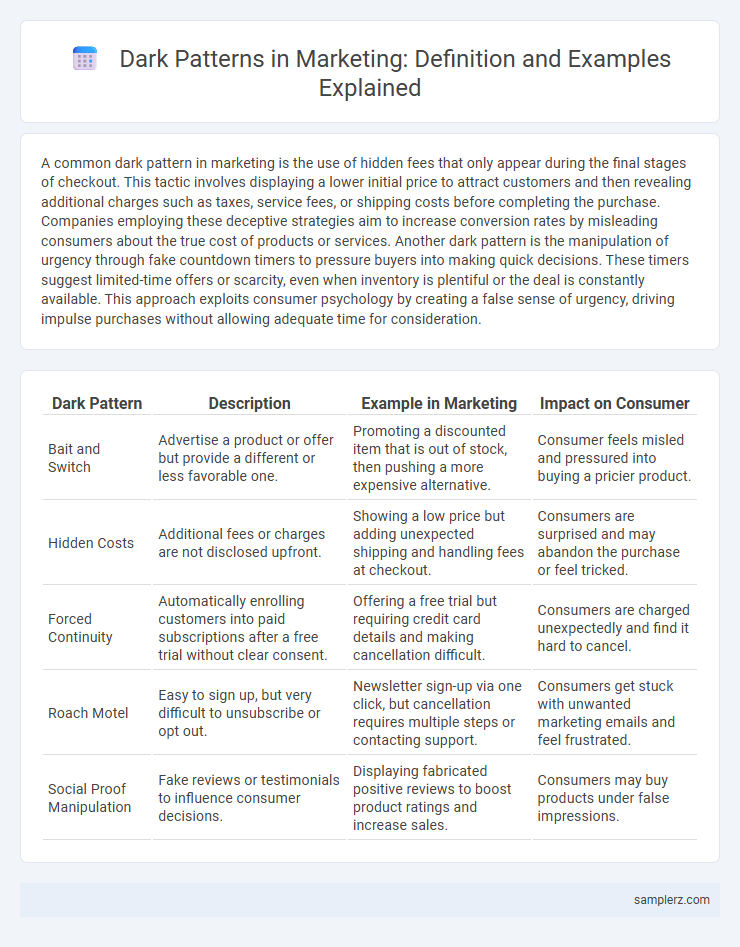
| Dark Pattern | Description | Example in Marketing | Impact on Consumer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bait and Switch | Advertise a product or offer but provide a different or less favorable one. | Promoting a discounted item that is out of stock, then pushing a more expensive alternative. | Consumer feels misled and pressured into buying a pricier product. |
| Hidden Costs | Additional fees or charges are not disclosed upfront. | Showing a low price but adding unexpected shipping and handling fees at checkout. | Consumers are surprised and may abandon the purchase or feel tricked. |
| Forced Continuity | Automatically enrolling customers into paid subscriptions after a free trial without clear consent. | Offering a free trial but requiring credit card details and making cancellation difficult. | Consumers are charged unexpectedly and find it hard to cancel. |
| Roach Motel | Easy to sign up, but very difficult to unsubscribe or opt out. | Newsletter sign-up via one click, but cancellation requires multiple steps or contacting support. | Consumers get stuck with unwanted marketing emails and feel frustrated. |
| Social Proof Manipulation | Fake reviews or testimonials to influence consumer decisions. | Displaying fabricated positive reviews to boost product ratings and increase sales. | Consumers may buy products under false impressions. |
Introduction to Dark Patterns in Marketing
Dark patterns in marketing manipulate consumer behavior through deceptive design tactics such as hidden costs, forced continuity, and sneaking items into shopping carts. These strategies exploit cognitive biases by creating urgency or confusing navigation to increase sales without transparent consent. Recognizing these dark patterns is essential for ethical marketing and maintaining consumer trust.
Hidden Costs: Surprise Fees at Checkout
Hidden costs, such as surprise fees at checkout, are a common dark pattern in marketing that misleads consumers by initially advertising low prices but adding unexpected charges later. These fees often include shipping surcharges, handling costs, or mandatory insurance that appear only at the final payment stage. This manipulative tactic undermines transparency and can lead to negative customer experiences and decreased trust in the brand.
Forced Continuity: Sneaky Free Trial Traps
Forced continuity in marketing often occurs through sneaky free trial traps, where users sign up for a trial without clear disclosure that their credit card will be charged automatically once the trial ends. Companies employ misleading cancellation processes and obscure terms to make it difficult for consumers to unsubscribe, resulting in unexpected charges. This dark pattern exploits user trust, increasing customer churn and damaging brand reputation while boosting short-term revenue.
Roach Motel: Easy to Sign Up, Hard to Cancel
The Roach Motel dark pattern in marketing traps users by making the sign-up process simple and fast while intentionally complicating cancellation or opt-out procedures. Subscription services often implement hidden cancellation steps, such as requiring phone calls, extended wait times, or navigating through multiple web pages to discourage users from leaving. These tactics increase customer retention artificially but damage brand trust and can lead to regulatory scrutiny.
Trick Questions: Confusing Opt-In/Opt-Out Forms
Trick questions in marketing often appear through confusing opt-in/opt-out forms designed to mislead users into subscribing or sharing personal data unintentionally. These dark patterns obscure the true intent of consent by using double negatives or ambiguous language, making it difficult for users to opt-out effectively. Studies reveal that nearly 60% of online users encounter such deceptive forms, highlighting the urgency for transparent consent mechanisms in digital marketing strategies.
Bait and Switch: Misleading Advertisements
Bait and switch is a deceptive marketing tactic where consumers are lured with an attractive offer that is unavailable or not intended to be honored, leading them to purchase a more expensive or different product. Retailers often advertise a popular item at a low price, only to claim it's out of stock upon customer interest, steering buyers toward higher-priced alternatives. This practice undermines trust, violates advertising standards, and can result in legal consequences under consumer protection laws.
Scarcity Tactics: Fake Limited Stock Alerts
Scarcity tactics in marketing often employ fake limited stock alerts to manipulate consumer behavior and drive impulsive purchases. By falsely indicating that a product is nearly sold out or available only for a short time, brands create a sense of urgency that pressures customers into making hasty decisions. This dark pattern exploits psychological triggers, undermining trust and potentially damaging long-term brand reputation.
Confirmshaming: Guilt-Driven Opt-Out Choices
Confirmshaming in marketing manipulates users by framing opt-out choices with guilt-inducing language, such as "No, I prefer to miss out on exclusive deals." This dark pattern pressures consumers into subscribing or purchasing by exploiting their fear of loss or social judgment. Brands employing confirmshaming undermine trust, leading to negative user experiences and potential backlash.
Sneak Into Basket: Preselected Add-Ons
Sneak Into Basket dark patterns manipulate consumers by automatically adding preselected add-ons to their shopping carts without explicit consent, inflating purchase costs. This tactic exploits user inattention and urgency, often misleading buyers into paying for unnecessary products or services. Marketing strategies that employ such covert upselling undermine trust and can result in negative brand perception and customer churn.
Social Proof Manipulation: Fake Urgency and Popularity
Marketers often exploit social proof manipulation by creating fake urgency through countdown timers and limited-time offers that are not genuinely time-sensitive. They inflate perceived popularity by displaying fabricated purchase numbers or fake user reviews to pressure consumers into quick decisions. These dark patterns distort consumer trust and drive impulsive buying behavior, undermining ethical marketing standards.
example of dark pattern in marketing Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com