Churn in SaaS refers to the rate at which customers cancel or stop using a software subscription service within a given period. This metric is critical for SaaS companies as it directly impacts recurring revenue and growth projections. High churn rates indicate potential issues with product value, customer satisfaction, or competitive pressures. Data shows that SaaS companies with a monthly churn rate exceeding 5% often struggle to maintain profitability and market share. An example includes a SaaS provider experiencing a 7% churn rate due to poor onboarding experiences and lack of feature adoption. Monitoring churn alongside customer engagement data helps marketers identify retention strategies and improve overall customer lifetime value.
Table of Comparison
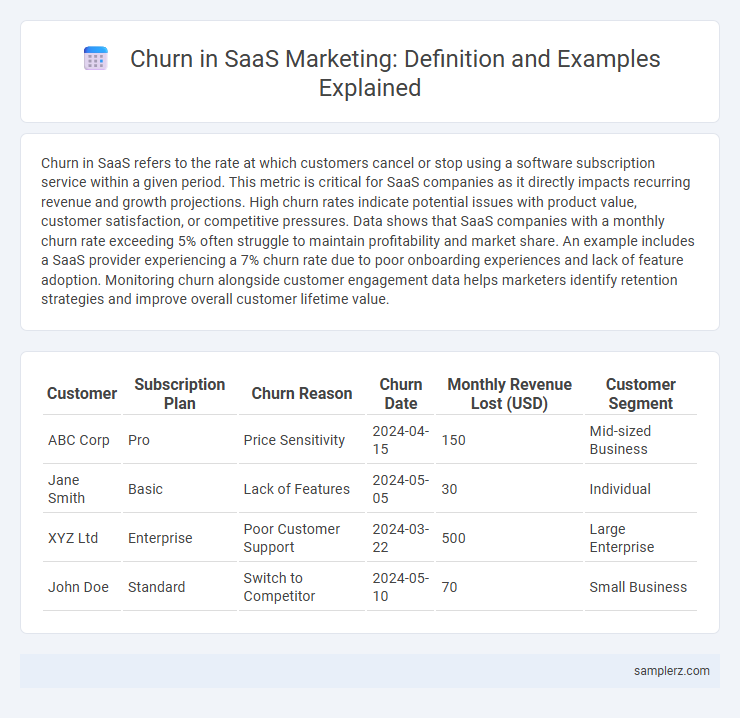
| Customer | Subscription Plan | Churn Reason | Churn Date | Monthly Revenue Lost (USD) | Customer Segment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Corp | Pro | Price Sensitivity | 2024-04-15 | 150 | Mid-sized Business |
| Jane Smith | Basic | Lack of Features | 2024-05-05 | 30 | Individual |
| XYZ Ltd | Enterprise | Poor Customer Support | 2024-03-22 | 500 | Large Enterprise |
| John Doe | Standard | Switch to Competitor | 2024-05-10 | 70 | Small Business |
Understanding Churn in SaaS: Key Definitions
Churn in SaaS refers to the rate at which customers cancel or do not renew their subscriptions within a given period, directly impacting recurring revenue and growth metrics. Customer churn rate, typically expressed as a percentage, is calculated by dividing the number of lost subscribers by the total active subscribers at the start of the period. Understanding key definitions such as voluntary churn, involuntary churn, and revenue churn enables SaaS companies to identify root causes and implement targeted retention strategies effectively.
Common Causes of SaaS Customer Churn
High customer churn in SaaS often stems from poor onboarding experiences, limited product value, and inadequate customer support. Customers frequently leave due to confusing user interfaces, unmet expectations, or lack of ongoing engagement. Identifying these common causes allows SaaS businesses to tailor retention strategies and improve customer lifetime value.
Real-World Example: Churn Triggered by Poor Onboarding
A SaaS company experienced a 25% churn rate within the first three months due to inadequate onboarding processes that left users confused about key features. Customers frequently reported difficulty navigating the platform, leading to early cancellations and negative reviews. Improving onboarding with personalized tutorials and proactive support reduced churn by 40% in the following quarter.
Case Study: Feature Gaps Leading to SaaS Churn
A SaaS company experienced a 25% churn rate after failing to address critical feature gaps in its product, leading users to switch to competitors with more comprehensive offerings. Customer feedback highlighted the absence of advanced analytics and integration capabilities as primary reasons for dissatisfaction. This case demonstrates how unmet feature expectations directly impact customer retention in the SaaS market.
Price Sensitivity: Example of Churn from Pricing Changes
A significant example of churn in SaaS occurs when price sensitivity leads customers to cancel subscriptions after unexpected pricing hikes. For instance, a 15% increase in monthly fees can trigger a 20% rise in churn rates among budget-conscious users. Companies that implement transparent communication and flexible pricing tiers can mitigate churn caused by price sensitivity.
Churn Due to Weak Customer Support in SaaS
Churn due to weak customer support in SaaS significantly impacts revenue and customer lifetime value, as dissatisfied users often switch to competitors with more responsive service. High churn rates are frequently linked to unresolved technical issues, slow response times, and lack of personalized assistance, undermining user trust and satisfaction. Investing in robust, 24/7 customer support systems and proactive communication can reduce churn by enhancing user retention and loyalty.
Impact of Competitor Offerings on SaaS Customer Retention
Competitor offerings with lower pricing and enhanced features significantly increase churn rates in SaaS businesses, directly impacting customer retention and lifetime value. When rivals introduce innovative functionalities or flexible subscription models, customers often switch, causing revenue decline and higher acquisition costs. Effective differentiation and continuous value delivery are critical to mitigating churn driven by competitive pressures.
Analyzing Voluntary vs Involuntary Churn in SaaS
Voluntary churn in SaaS occurs when customers actively cancel subscriptions due to dissatisfaction or better alternatives, driven by factors such as product usability or pricing. Involuntary churn results from payment failures, expired credit cards, or billing errors, often unnoticed without proactive monitoring. Differentiating these churn types enables targeted retention strategies, such as improving customer experience for voluntary churn and optimizing payment processes for involuntary churn.
Example: Churn Stemming from Product Downtime
Churn in SaaS often occurs due to product downtime, which disrupts user experience and leads to customer dissatisfaction. When a cloud-based software solution experiences frequent outages, users may lose critical access to features, causing a decline in trust and potential subscription cancellations. Monitoring uptime metrics and implementing robust infrastructure can significantly reduce churn caused by product downtime.
Turnaround Stories: Successful SaaS Churn Reduction Strategies
Customer churn in SaaS can drastically impact recurring revenue, with typical rates averaging 5-7% monthly. One notable turnaround story involves a SaaS company that reduced its churn rate from 8% to 2% by implementing personalized onboarding, proactive customer support, and usage analytics to identify at-risk users. These targeted strategies not only stabilized revenue but also enhanced customer lifetime value and overall growth.
example of churn in SaaS Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com