Attribution in marketing refers to the process of identifying and assigning credit to different touchpoints that contribute to a customer's decision to convert. One common example is multi-touch attribution, where marketers analyze various interactions such as email clicks, social media engagement, and paid search ads to understand their impact on the buyer journey. This data-driven approach helps marketers allocate budget more efficiently by highlighting which channels and campaigns drive the most conversions. Another example is first-touch attribution, which assigns all the credit to the initial interaction a customer has with a brand, such as a display ad or organic search. This method provides insights into which marketing efforts are most effective at generating initial interest and awareness. Marketers use this data to optimize campaigns focused on attracting new prospects and increasing brand visibility.
Table of Comparison
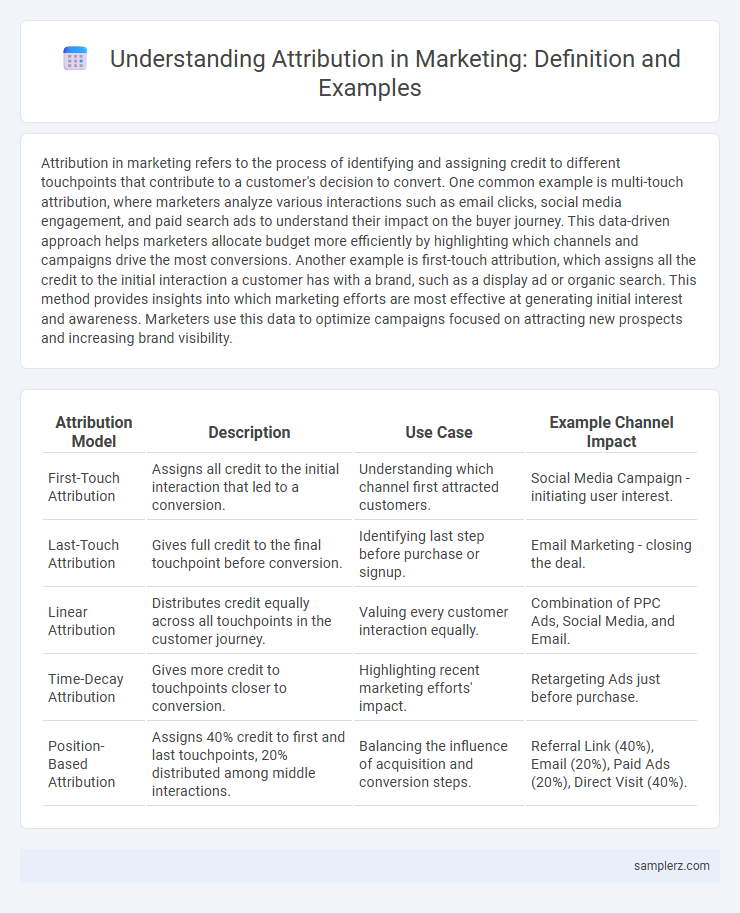
| Attribution Model | Description | Use Case | Example Channel Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-Touch Attribution | Assigns all credit to the initial interaction that led to a conversion. | Understanding which channel first attracted customers. | Social Media Campaign - initiating user interest. |
| Last-Touch Attribution | Gives full credit to the final touchpoint before conversion. | Identifying last step before purchase or signup. | Email Marketing - closing the deal. |
| Linear Attribution | Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints in the customer journey. | Valuing every customer interaction equally. | Combination of PPC Ads, Social Media, and Email. |
| Time-Decay Attribution | Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to conversion. | Highlighting recent marketing efforts' impact. | Retargeting Ads just before purchase. |
| Position-Based Attribution | Assigns 40% credit to first and last touchpoints, 20% distributed among middle interactions. | Balancing the influence of acquisition and conversion steps. | Referral Link (40%), Email (20%), Paid Ads (20%), Direct Visit (40%). |
Understanding Attribution in Marketing
Understanding attribution in marketing involves identifying how different channels contribute to customer conversions, such as tracking interactions through email campaigns, social media ads, and paid search. Multi-touch attribution models allocate credit across multiple touchpoints, providing insights into the effectiveness of each marketing effort. Utilizing tools like Google Analytics and CRM software enhances accuracy in measuring channel performance and optimizing marketing strategies.
Types of Attribution Models
Types of attribution models in marketing include first-touch, last-touch, linear, time-decay, and position-based models, each distributing credit differently across customer interactions. First-touch attribution assigns full credit to the initial interaction, while last-touch attributes all credit to the final touchpoint before conversion. Linear models evenly distribute credit across all touchpoints, time-decay emphasizes recent interactions, and position-based typically allocates 40% credit to both the first and last interactions, with the remaining 20% spread across the middle touchpoints.
First-Touch Attribution Example
First-touch attribution in marketing assigns full credit to the initial interaction that introduced a customer to a brand, such as a social media ad or an email campaign, which sparked their interest. For example, if a user clicks on a Facebook ad and later makes a purchase after visiting the website directly, the conversion is attributed solely to the Facebook ad. This model helps marketers understand which channels effectively generate initial awareness and drive top-of-funnel engagement.
Last-Touch Attribution Example
Last-Touch Attribution in marketing assigns 100% of the credit for a conversion to the final interaction before the sale, such as clicking a paid search ad or completing a purchase on a website. For example, if a customer discovered a product through a social media ad but converted after clicking an email link, the email channel receives full credit for the sale. This model is particularly useful for campaigns focused on closing sales and measuring the direct impact of the last customer touchpoint.
Multi-Touch Attribution in Action
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) in marketing evaluates the impact of each customer interaction across various channels, such as email campaigns, social media ads, and paid search, to assign proportional credit for conversions. For example, a customer might first discover a product through a Facebook ad, receive a follow-up email, and then complete the purchase via a Google search ad; MTA uses algorithms to allocate value to each touchpoint. By leveraging data-driven MTA models, marketers gain deeper insights into campaign performance, optimize budget allocation, and enhance overall return on investment (ROI).
Linear Attribution Model Example
The Linear Attribution Model allocates equal credit to every touchpoint in a customer's journey, such as social media ads, email campaigns, and direct website visits, ensuring balanced insight into each channel's contribution. For instance, if a customer interacts with three ads before making a purchase, each interaction receives 33.3% of the conversion credit. This model aids marketers in understanding the overall impact of diverse marketing efforts without prioritizing a single touchpoint.
Time-Decay Attribution Case
Time-Decay Attribution in marketing assigns increasing credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion event, recognizing the growing influence of recent interactions. This model highlights channels such as retargeting ads or last-click email campaigns, which play a critical role in nudging customers toward purchase decisions. By emphasizing the temporal proximity of engagements, marketers can optimize budget allocation and enhance campaign performance through more accurate attribution.
U-Shaped Attribution Example
U-Shaped Attribution assigns 40% credit to both the first and last touchpoints in the customer journey, highlighting the significance of initial engagement and final conversion interactions. This model attributes the remaining 20% evenly across all middle touchpoints, balancing the influence of consideration activities such as product demos or email clicks. Marketers apply U-Shaped Attribution to optimize campaigns by emphasizing lead generation channels and closing tactics that drive revenue growth.
Data-Driven Attribution in Marketing
Data-driven attribution in marketing uses machine learning algorithms to analyze customer journeys and assign credit to various touchpoints based on their actual influence on conversions. By leveraging first-party data and real-time interaction metrics, this method provides a granular understanding of which channels and campaigns drive the highest ROI. Marketers utilize platforms like Google Attribution and Adobe Analytics to implement data-driven models, enabling more precise budget allocation and optimized marketing strategies.
Benefits of Attribution for Campaign Optimization
Attribution in marketing helps identify the most effective touchpoints driving conversions, allowing precise allocation of budget to high-performing channels. This data-driven approach enhances campaign optimization by improving ROI and reducing wasted spend. Marketers gain actionable insights that support continuous refinement of strategies for better audience engagement and increased revenue.
example of attribution in marketing Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com