Slow food in the kitchen emphasizes the use of fresh, locally sourced ingredients to create meals that celebrate traditional cooking methods. This approach often involves preparing dishes such as homemade pasta, slow-cooked stews, or freshly baked bread. These recipes prioritize quality and flavor, encouraging a deeper connection to the origins of the food. Incorporating slow food practices promotes mindful eating and sustainability, reducing reliance on processed or mass-produced products. Examples include simmering soups over low heat for hours or fermenting vegetables at home to enhance natural flavors and nutritional benefits. The slow food movement supports local farmers and reduces environmental impact by focusing on seasonal produce.
Table of Comparison
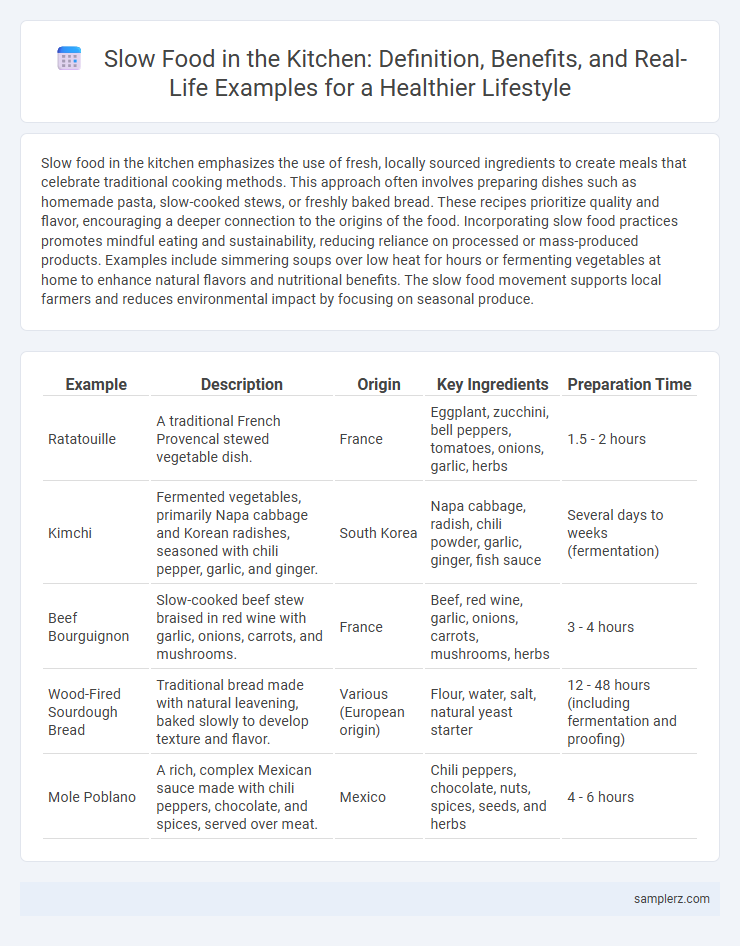
| Example | Description | Origin | Key Ingredients | Preparation Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratatouille | A traditional French Provencal stewed vegetable dish. | France | Eggplant, zucchini, bell peppers, tomatoes, onions, garlic, herbs | 1.5 - 2 hours |
| Kimchi | Fermented vegetables, primarily Napa cabbage and Korean radishes, seasoned with chili pepper, garlic, and ginger. | South Korea | Napa cabbage, radish, chili powder, garlic, ginger, fish sauce | Several days to weeks (fermentation) |
| Beef Bourguignon | Slow-cooked beef stew braised in red wine with garlic, onions, carrots, and mushrooms. | France | Beef, red wine, garlic, onions, carrots, mushrooms, herbs | 3 - 4 hours |
| Wood-Fired Sourdough Bread | Traditional bread made with natural leavening, baked slowly to develop texture and flavor. | Various (European origin) | Flour, water, salt, natural yeast starter | 12 - 48 hours (including fermentation and proofing) |
| Mole Poblano | A rich, complex Mexican sauce made with chili peppers, chocolate, and spices, served over meat. | Mexico | Chili peppers, chocolate, nuts, spices, seeds, and herbs | 4 - 6 hours |
Understanding Slow Food: A Kitchen Revolution
Embracing slow food in the kitchen emphasizes locally sourced, seasonal ingredients prepared with care to preserve natural flavors and nutrients. This approach fosters sustainable practices by reducing reliance on processed foods and minimizing waste, connecting chefs and home cooks to their culinary heritage. Techniques like slow roasting, fermenting, and handcrafting embody a kitchen revolution that prioritizes quality, mindfulness, and ecological balance.
Traditional Cooking Techniques That Embrace Slow Food
Traditional cooking techniques that embrace slow food emphasize methods such as slow braising, fermentation, and stone grinding to preserve flavors and nutrients. These approaches prioritize natural ingredients, minimal processing, and extended cooking times to enhance taste and promote sustainability. Utilizing cast iron pots for slow simmering or wooden tools for hand mixing fosters a connection to cultural heritage and mindful eating practices.
Farm-to-Table Ingredients for Slow Food Meals
Farm-to-table ingredients emphasize fresh, locally sourced produce and meats that form the cornerstone of slow food meals, enhancing flavor and nutritional value. Seasonal vegetables, free-range eggs, and grass-fed meats support sustainable farming practices while reducing the carbon footprint of meals. Incorporating these ingredients into cooking preserves traditional culinary techniques and fosters a deeper connection to the food's origin.
Homemade Bread: The Heart of Slow Food in the Kitchen
Homemade bread embodies the essence of slow food by emphasizing natural fermentation, high-quality ingredients, and mindful preparation. The process involves patiently allowing dough to rise, enhancing flavor and nutritional value while avoiding preservatives and artificial additives. This traditional practice fosters a deeper connection to food, promoting wellness and sustainable eating habits in the kitchen.
Simmering Soups and Stews: Classic Slow Food Dishes
Simmering soups and stews exemplify slow food by enhancing flavors through prolonged cooking at low temperatures, allowing ingredients like vegetables, herbs, and meats to meld naturally. Classic dishes such as beef stew, minestrone, and chicken noodle soup rely on simmering to develop rich textures and deep, harmonious tastes. This method preserves nutrients and promotes mindful eating, embodying the core principles of the slow food movement.
The Art of Fermentation: Slow Food Preserves and Pickles
The art of fermentation transforms fresh vegetables into flavorful slow food preserves and pickles, enhancing both taste and nutritional value. Fermented foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, and pickled cucumbers are rich in probiotics, supporting gut health and digestion. Embracing this time-honored method in the kitchen exemplifies sustainable, health-conscious living through slow food practices.
Pasta from Scratch: Authentic Slow Food Experience
Making pasta from scratch exemplifies the slow food movement by emphasizing traditional techniques and high-quality ingredients. Hand-kneading dough and allowing it to rest naturally enhances the texture and flavor, contrasting with mass-produced pasta. This process fosters a deeper connection to culinary heritage and encourages mindful cooking and eating habits.
Slow Roasting: Bringing Out Flavors in Meats and Vegetables
Slow roasting transforms meats and vegetables by cooking them at low temperatures over extended periods, enhancing natural flavors and tenderness. This method preserves juices and intensifies aromas, making dishes richer and more succulent. Slow roasting is a cornerstone of the slow food movement, emphasizing quality ingredients and mindful preparation for a flavorful dining experience.
Seasonal Cooking: Celebrating Slow Food with Local Produce
Seasonal cooking emphasizes using fresh, local produce that reflects the natural harvest cycle, promoting sustainability and nutrient-rich meals. Incorporating ingredients like heirloom tomatoes in summer or root vegetables in winter supports farmers and reduces carbon footprints. This slow food approach enriches flavor profiles and reconnects kitchens with the rhythms of nature.
Mindful Meal Preparation: The Ritual of Slow Food
Mindful meal preparation involves intentionally selecting fresh, seasonal ingredients and savoring each step from chopping to cooking, which enhances the sensory experience in the kitchen. This slow food ritual promotes nutritional awareness and reduces stress by encouraging a deeper connection with the food being prepared. Emphasizing traditional techniques like simmering, fermenting, or hand-grinding elevates the quality and flavor of meals while fostering sustainable eating habits.
example of slow food in kitchen Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com