Urban foraging refers to the practice of gathering edible plants and natural resources found within city environments. An example of urban foraging during a walk might include collecting wild berries, dandelion greens, or edible mushrooms growing in parks or along sidewalks. This activity highlights the availability of natural food sources amidst urban settings and promotes sustainable living. People engaging in urban foraging benefit from connecting with local ecosystems and discovering food that is fresh and free. Awareness of city-specific plant species and identification techniques is essential to safely harvest edible items and avoid toxic plants. Urban foraging also contributes data on plant distribution in metropolitan areas, offering insights into biodiversity and environmental health.
Table of Comparison
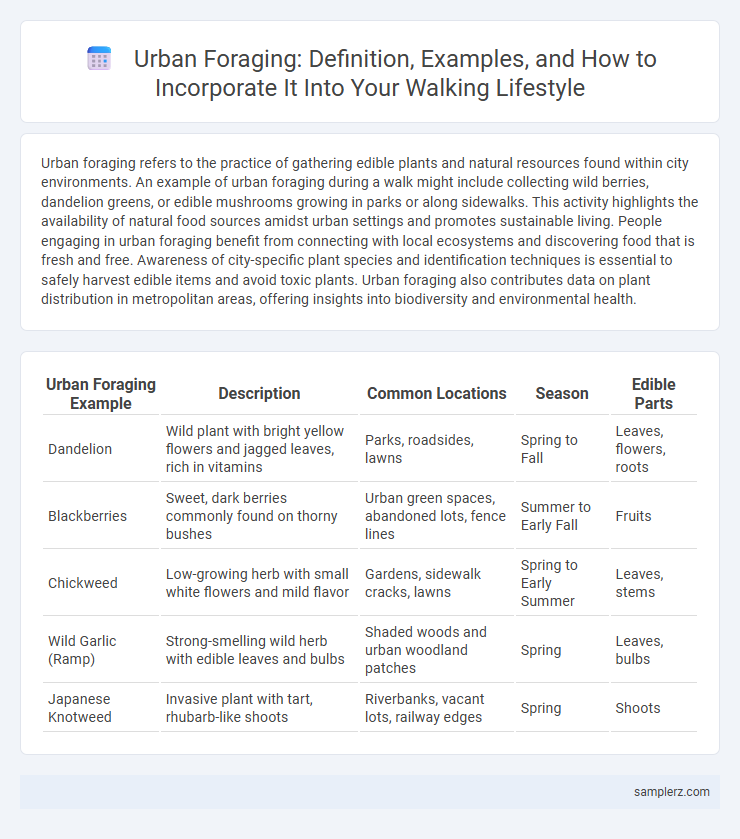
| Urban Foraging Example | Description | Common Locations | Season | Edible Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dandelion | Wild plant with bright yellow flowers and jagged leaves, rich in vitamins | Parks, roadsides, lawns | Spring to Fall | Leaves, flowers, roots |
| Blackberries | Sweet, dark berries commonly found on thorny bushes | Urban green spaces, abandoned lots, fence lines | Summer to Early Fall | Fruits |
| Chickweed | Low-growing herb with small white flowers and mild flavor | Gardens, sidewalk cracks, lawns | Spring to Early Summer | Leaves, stems |
| Wild Garlic (Ramp) | Strong-smelling wild herb with edible leaves and bulbs | Shaded woods and urban woodland patches | Spring | Leaves, bulbs |
| Japanese Knotweed | Invasive plant with tart, rhubarb-like shoots | Riverbanks, vacant lots, railway edges | Spring | Shoots |
Discovering Edible Plants Along City Sidewalks
Urban foraging along city sidewalks reveals a surprising abundance of edible plants such as dandelions, purslane, and wild garlic, offering fresh, nutritious options right in the heart of metropolitan areas. These common plants thrive in cracks and green patches, providing a sustainable source of vitamins and minerals while reducing food waste. Foragers can identify these species using plant identification apps and guidebooks, ensuring safe and responsible harvesting practices.
Foraging Wild Berries in Urban Parks
Foraging wild berries in urban parks offers a sustainable way to connect with nature while walking through city green spaces. Common edible species such as blackberries, raspberries, and elderberries thrive in many metropolitan areas, providing nutrient-rich snacks for urban foragers. Understanding local plant identification guidelines and seasonal harvesting practices ensures safe and responsible berry foraging in urban environments.
Finding Edible Weeds in Vacant Lots
Exploring vacant lots during urban walks reveals a surprising variety of edible weeds like dandelions, purslane, and chickweed, which are rich in vitamins and minerals. These commonly overlooked plants thrive in neglected spaces and can be foraged sustainably, providing a natural supplement to urban diets. Foragers should correctly identify each weed and ensure the area is free from pesticides or pollutants before harvesting.
Identifying Nut-Bearing Trees on City Streets
Observing city streets for urban foraging reveals nut-bearing trees such as black walnut, hackberry, and sweet chestnut, which thrive in many metropolitan areas. Identifying these trees requires attention to leaf shape, bark texture, and the distinctive nuts they produce, providing valuable foraging opportunities. Urban foragers benefit from using tree identification apps and field guides to safely and sustainably harvest nuts found along sidewalks and parks.
Harvesting Herbs from Community Garden Edges
Harvesting herbs from community garden edges offers urban foragers access to fresh, organic ingredients like mint, basil, and thyme growing naturally in shared green spaces. These herbs not only enhance culinary dishes with vibrant flavors but also promote sustainable living by reducing the need for store-bought produce. Engaging in this practice supports biodiversity and encourages connection with local ecosystems through mindful, seasonal harvesting.
Mushrooms Growing in Urban Green Spaces
Urban foraging has gained popularity as city dwellers seek sustainable food sources, with mushrooms flourishing in parks, community gardens, and neglected green spaces. Species like oyster mushrooms and shaggy ink caps thrive on decaying wood and organic debris found in these urban environments. Foragers emphasize proper identification and sustainable harvesting practices to ensure safety and ecological balance.
Edible Flowers Spotted on City Walks
Urban foraging on city walks reveals diverse edible flowers such as nasturtiums, violets, and dandelions, which thrive in parks and along sidewalks. These blossoms offer nutritional benefits, rich in vitamins and antioxidants, making them valuable for health-conscious urban dwellers. Identifying and safely harvesting these flowers enhances city living by connecting residents with natural food sources amid urban landscapes.
Collecting Wild Fruit from Overhanging Branches
Collecting wild fruit from overhanging branches during urban walks offers a sustainable way to connect with nature while exploring city landscapes. Neighborhoods with abundant trees such as cherry, mulberry, or crabapple provide accessible and nutritious snacks, promoting a healthy and eco-friendly lifestyle. This practice encourages mindfulness, reduces food waste, and supports community engagement through sharing locally foraged finds.
Foraging Tips for Rooftop Gardens
Urban foraging in rooftop gardens offers a sustainable way to harvest fresh herbs, edible flowers, and leafy greens in city environments. Focus on identifying safe, pesticide-free plants such as mint, basil, and nasturtiums while ensuring proper hygiene by washing foraged items thoroughly. Carry lightweight tools like scissors and a tote bag for efficient harvesting without damaging the rooftop ecosystem.
Urban Foraging Safety and Legal Considerations
When engaging in urban foraging during a walk, prioritize identifying edible plants that are free from pollutants and avoid areas treated with pesticides or heavy traffic pollution. Familiarize yourself with local regulations as some cities prohibit foraging on public property or protected land to preserve biodiversity and public safety. Carrying a plant identification guide or using a reputable app ensures you harvest only safe, legal, and non-toxic species, minimizing health risks and legal issues.
example of urban foraging in walk Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com