A locavore is a person who prioritizes purchasing and consuming food that is grown or produced locally, typically within a 100-mile radius. In a grocery store setting, examples of locavore practices include buying seasonal fruits and vegetables from local farmers' markets or selecting meat and dairy products sourced from nearby farms. This approach supports local economies and reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance food transportation. Grocery stores that cater to locavores often feature dedicated sections for local produce, handmade goods, and artisanal items. Data shows that locavore consumers tend to prefer organic and minimally processed foods, reflecting a commitment to sustainability and health. Emphasizing local sourcing helps stores meet the growing demand for transparency in food origins and traceability.
Table of Comparison
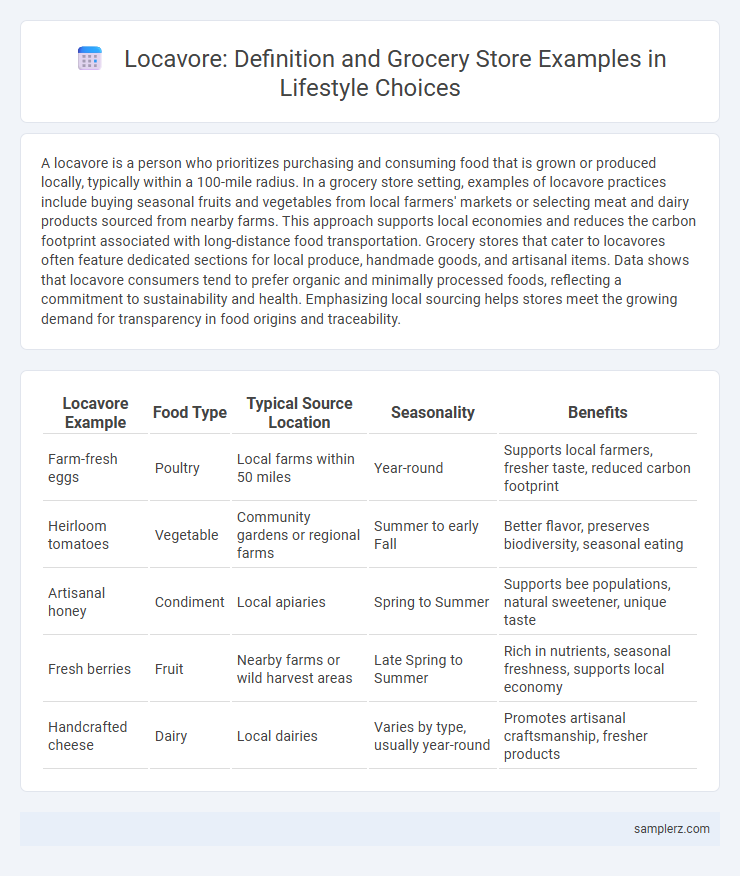
| Locavore Example | Food Type | Typical Source Location | Seasonality | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm-fresh eggs | Poultry | Local farms within 50 miles | Year-round | Supports local farmers, fresher taste, reduced carbon footprint |
| Heirloom tomatoes | Vegetable | Community gardens or regional farms | Summer to early Fall | Better flavor, preserves biodiversity, seasonal eating |
| Artisanal honey | Condiment | Local apiaries | Spring to Summer | Supports bee populations, natural sweetener, unique taste |
| Fresh berries | Fruit | Nearby farms or wild harvest areas | Late Spring to Summer | Rich in nutrients, seasonal freshness, supports local economy |
| Handcrafted cheese | Dairy | Local dairies | Varies by type, usually year-round | Promotes artisanal craftsmanship, fresher products |
Understanding the Locavore Movement in Modern Groceries
The locavore movement emphasizes purchasing groceries sourced within a 100-mile radius to support local farmers and reduce carbon footprints. Modern grocery stores increasingly feature dedicated sections with seasonal, locally grown produce and artisanal products reflecting regional agricultural heritage. Consumer demand for transparency and sustainability drives the growth of farmers' markets and community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs integrated into contemporary retail spaces.
How Grocery Stores Source Local Produce for Consumers
Grocery stores source local produce by partnering with nearby farms and regional cooperatives to ensure fresh, seasonal fruits and vegetables reach consumers quickly. Utilizing direct procurement and farm-to-shelf logistics reduces transportation time and carbon emissions while supporting local economies. Implementing traceability systems, stores provide transparency about the origin of products, enhancing trust and encouraging sustainable consumption among locavore shoppers.
Seasonal Fruits and Vegetables: A Locavore’s Guide
Seasonal fruits and vegetables are the cornerstone of a locavore grocery strategy, emphasizing fresh, locally sourced produce that aligns with regional harvest cycles. Examples include ripe heirloom tomatoes and sweet corn in summer, crisp apples and root vegetables in fall, and hearty kale and Brussels sprouts in winter, ensuring nutrient-rich choices that support sustainable agriculture. Shopping at farmers' markets or community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs enhances access to these seasonal gems, reducing carbon footprint and promoting local economies.
Spotlight on Local Dairy and Farm-Fresh Eggs
Locavores prioritize purchasing local dairy products such as artisan cheeses, fresh milk, and yogurt sourced directly from nearby farms, ensuring maximum freshness and supporting regional agriculture. Farm-fresh eggs, often available at farmers' markets or local co-ops, offer higher nutritional value and superior taste compared to mass-produced options. Emphasizing local dairy and eggs reduces carbon footprints and fosters sustainable food systems within the community.
Locally Sourced Meat and Sustainable Seafood Options
Locavores prioritize grocery shopping at farmers' markets and specialty stores that offer locally sourced meat from regional farms practicing ethical animal husbandry. Sustainable seafood options often include species certified by organizations like the Marine Stewardship Council, ensuring responsible fishing practices within nearby waters. Choosing these products supports local economies, reduces carbon footprints, and promotes environmental stewardship.
The Role of Farmers’ Partnerships in Grocery Supply Chains
Farmers' partnerships play a crucial role in grocery supply chains by enabling locavores to access fresh, locally grown produce directly from nearby farms. These collaborations reduce transportation emissions and support sustainable agriculture, ensuring higher quality and seasonal variety in grocery stores. Strengthening these connections fosters community resilience and promotes transparency in food sourcing.
Locavore Shopping Tips for the Conscious Consumer
Choosing seasonal produce from local farmers' markets supports sustainability and ensures fresher, nutrient-rich foods. Prioritize grocery items labeled with regional origin or certified local stamps to reduce carbon footprint and bolster community agriculture. Incorporate whole grains, dairy, and meats sourced within a 100-mile radius to maximize the impact of locavore shopping habits for eco-conscious consumers.
Benefits of Buying Local Products from Your Grocery Store
Purchasing local products from your grocery store supports regional farmers and reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. Locally sourced foods often have higher nutritional value due to shorter storage times and fresher harvesting practices. Buying local also boosts the local economy by keeping money within the community and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Identifying Locavore Products: Labeling and Certifications
Locavore products at grocery stores are often identified through specific labeling such as "Locally Grown," "Farm Fresh," or geographic certifications like the USDA Organic seal combined with regional tags. Certifications from local agricultural boards or community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs also indicate products sourced within a defined local radius. Consumers seeking locavore items should look for produce and goods with clear origin information, emphasizing freshness, sustainability, and reduced carbon footprint.
Supporting Community: The Economic Impact of Locavore Choices
Locavores who prioritize purchasing fruits, vegetables, and dairy products from local farmers' markets directly support small-scale producers and keep money circulating within the community. Choosing locally sourced groceries reduces dependency on large agribusinesses and fosters economic resilience by creating jobs and sustaining local agriculture. This consumer behavior strengthens the regional economy and promotes sustainable development through community-centered practices.
example of locavore in grocery Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com