A writ in judicature is a formal written order issued by a court or a judicial authority directing a specific action or forbidding certain acts. Typical examples include writs of habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, certiorari, and quo warranto. These writs serve as crucial tools in safeguarding the rule of law and ensuring that government authorities act within their legal boundaries. The writ of habeas corpus commands the release of a person unlawfully detained, protecting individual liberty against arbitrary imprisonment. The writ of mandamus compels a public official or government body to perform a statutory duty that has been neglected. Such writs play a pivotal role in maintaining checks and balances within governmental institutions and upholding citizens' constitutional rights.
Table of Comparison
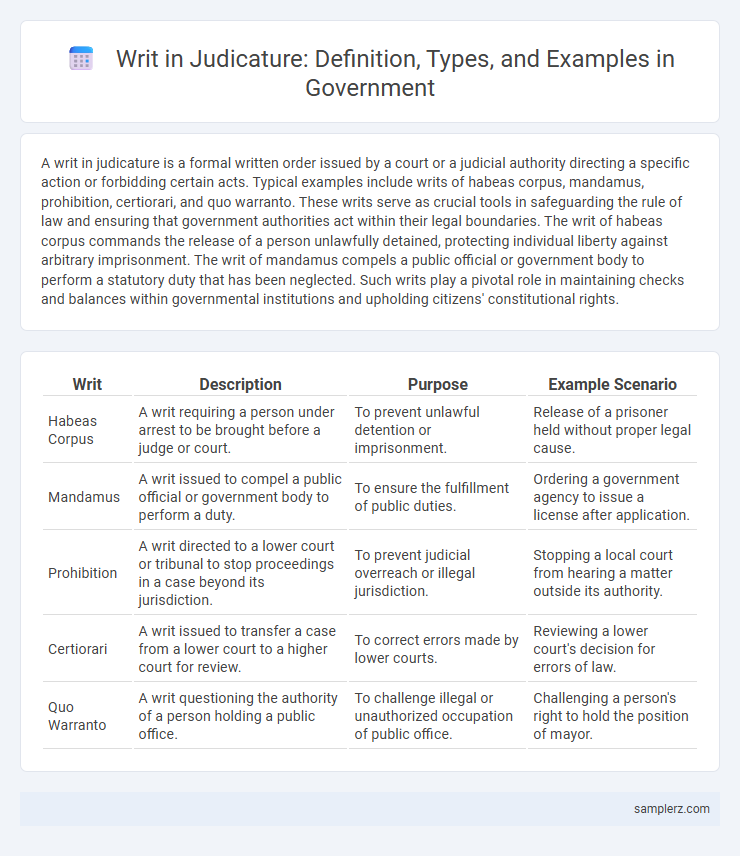
| Writ | Description | Purpose | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Habeas Corpus | A writ requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a judge or court. | To prevent unlawful detention or imprisonment. | Release of a prisoner held without proper legal cause. |
| Mandamus | A writ issued to compel a public official or government body to perform a duty. | To ensure the fulfillment of public duties. | Ordering a government agency to issue a license after application. |
| Prohibition | A writ directed to a lower court or tribunal to stop proceedings in a case beyond its jurisdiction. | To prevent judicial overreach or illegal jurisdiction. | Stopping a local court from hearing a matter outside its authority. |
| Certiorari | A writ issued to transfer a case from a lower court to a higher court for review. | To correct errors made by lower courts. | Reviewing a lower court's decision for errors of law. |
| Quo Warranto | A writ questioning the authority of a person holding a public office. | To challenge illegal or unauthorized occupation of public office. | Challenging a person's right to hold the position of mayor. |
Definition and Importance of Writs in Judicature
Writs in judicature are formal written orders issued by a court directing an individual or authority to perform or refrain from performing a specific act, serving as crucial instruments in upholding the rule of law. These legal commands ensure protection of fundamental rights and prevent miscarriage of justice by compelling government bodies to act within their jurisdiction. Examples of writs include habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, certiorari, and quo warranto, each playing a vital role in maintaining judicial oversight and accountability.
Overview of Constitutional Provisions for Writs
The Indian Constitution explicitly empowers the Supreme Court and High Courts under Articles 32 and 226 respectively to issue writs for the enforcement of fundamental rights and for any other purpose. These writs include habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto, and certiorari, each serving specific legal functions such as protecting personal liberty or preventing unlawful authority action. The constitutional provisions provide a vital mechanism for judicial review, ensuring government accountability and safeguarding citizens' constitutional rights.
Types of Writs Available in Judicial System
The judiciary issues several types of writs to protect fundamental rights and ensure justice, including habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, certiorari, and quo warranto. Habeas corpus safeguards individual liberty by preventing unlawful detention, while mandamus commands public authorities to perform their duties. Prohibition restrains lower courts from exceeding jurisdiction, certiorari reviews and quashes unlawful orders, and quo warranto challenges a person's right to hold a public office.
Habeas Corpus: Safeguarding Individual Liberty
Habeas Corpus is a fundamental writ in the judicial system that protects individual liberty by ensuring a person's right to challenge unlawful detention before a court. This writ mandates authorities to present the detained individual and justify the legality of their confinement, preventing arbitrary imprisonment and abuse of state power. The enforcement of Habeas Corpus upholds constitutional guarantees and serves as a critical mechanism for maintaining the rule of law and human rights.
Mandamus: Enforcing Public Duties
A writ of mandamus serves as a judicial order compelling government officials or public authorities to fulfill their mandatory duties as prescribed by law. This writ ensures accountability by directing public officers to perform non-discretionary acts crucial for upholding citizens' rights and administrative justice. Courts employ mandamus to maintain the rule of law and prevent governmental abuse or neglect of statutory obligations.
Prohibition: Preventing Excess of Jurisdiction
The writ of Prohibition serves as a crucial judicial instrument to prevent lower courts or tribunals from exceeding their jurisdiction and acting beyond their legal authority. It restrains unlawful exercise of power by prohibiting the continuation of proceedings that violate jurisdictional limits, thus ensuring adherence to the rule of law. This writ safeguards against judicial overreach and protects the integrity of administrative and judicial functions within the government framework.
Certiorari: Reviewing Lower Court Decisions
Certiorari is a judicial writ issued by higher courts to review and potentially nullify decisions made by lower courts when a significant legal error or jurisdictional issue is identified. This writ ensures the proper application of law and protects against miscarriages of justice by scrutinizing lower court rulings. It is commonly invoked in constitutional cases where the interpretation of fundamental rights or statutory mandates requires clarification.
Quo Warranto: Challenging Authority Legitimacy
Quo warranto is a legal writ used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise authority, questioning the legitimacy of their claim. It requires the accused to show by what warrant they hold the position, ensuring government officials comply with legal qualifications. This writ serves as a critical tool in judicial review to prevent unauthorized or unconstitutional occupancy of public offices.
Landmark Cases Involving Judicial Writs
The writ of habeas corpus played a pivotal role in the landmark case of Boumediene v. Bush (2008), where the Supreme Court affirmed detainees' constitutional right to challenge unlawful detention. Marbury v. Madison (1803) established the writ of mandamus as a tool for judicial review, solidifying the judiciary's power to invalidate unconstitutional government actions. In Ex parte McCardle (1869), the Court emphasized limits on habeas corpus jurisdiction, shaping the balance of power between the legislature and judiciary.
Impact of Writ Jurisdiction on Good Governance
Writ jurisdiction plays a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights by enabling courts to issue orders such as habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto, and certiorari, ensuring government accountability and adherence to the rule of law. The enforcement of these writs acts as a powerful mechanism to check arbitrary actions by public authorities, promoting transparency and integrity in governance structures. Consequently, writ jurisdiction significantly strengthens good governance by safeguarding citizens' rights and reinforcing administrative discipline.
example of writ in judicature Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com