Zerging is a common tactic in real-time strategy games where a player floods the enemy with a large number of low-cost units to overwhelm their defenses. This strategy is named after the Zerg race in StarCraft, known for quickly producing numerous weak units to overpower opponents. Effective zerging relies on rapid resource gathering and continuous unit production to maintain pressure on the enemy. In games like StarCraft, zerging typically involves building multiple Hatcheries to increase unit output and aggressively attacking before the opponent can build a strong defense. Data from competitive matches shows that zerging can be highly successful in early to mid-game phases when the opponent's economy and army size are still developing. Zerging requires precise micromanagement and map control to efficiently sustain the large unit numbers and capitalize on numerical superiority.
Table of Comparison
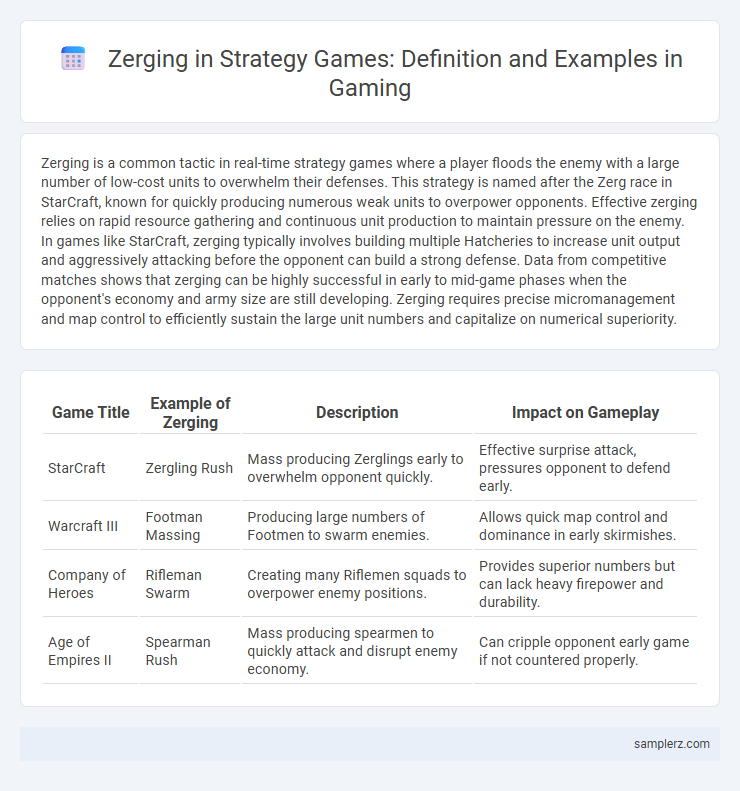
| Game Title | Example of Zerging | Description | Impact on Gameplay |
|---|---|---|---|
| StarCraft | Zergling Rush | Mass producing Zerglings early to overwhelm opponent quickly. | Effective surprise attack, pressures opponent to defend early. |
| Warcraft III | Footman Massing | Producing large numbers of Footmen to swarm enemies. | Allows quick map control and dominance in early skirmishes. |
| Company of Heroes | Rifleman Swarm | Creating many Riflemen squads to overpower enemy positions. | Provides superior numbers but can lack heavy firepower and durability. |
| Age of Empires II | Spearman Rush | Mass producing spearmen to quickly attack and disrupt enemy economy. | Can cripple opponent early game if not countered properly. |
Introduction to Zerging in Strategy Games
Zerging in strategy games refers to the tactic where a player rapidly amasses a large number of low-cost units to overwhelm opponents with sheer numbers. Popularized in games like StarCraft, this strategy relies on speed and quantity rather than unit strength or technology upgrades. Mastering zerging requires efficient resource management and quick unit production to maintain relentless pressure on adversaries.
Classic Zerg Rush in StarCraft
The Classic Zerg Rush in StarCraft exemplifies zerging by overwhelming opponents with a massive swarm of low-cost Zerglings early in the game. This tactic leverages rapid unit production from multiple Hatcheries to flood enemy defenses before they can effectively respond. Mastering the timing and execution of this rush is crucial for dominating early-game strategy and gaining map control.
Mass Infantry Swarms in Command & Conquer
Mass infantry swarms, or "zerging," in Command & Conquer involve overwhelming opponents with large groups of low-cost units to quickly control territory and resources. This tactic relies on rapid unit production and aggressive map control to outnumber and outmaneuver enemy forces. Effective mass infantry swarming exploits the game's unit production speed and terrain advantages to disrupt enemy strategies and secure victory.
Overwhelming Numbers in Age of Empires
Zerging in strategy games like Age of Empires involves overwhelming opponents with large armies to quickly dominate the map. Players mass units such as infantry, archers, and cavalry in high quantities, exploiting the advantage of sheer numbers to break enemy defenses. This tactic often forces opponents into defensive play, enabling rapid territorial expansion and resource control.
Early Scout Rushes in Warcraft III
Early scout rushes in Warcraft III exemplify zerging by overwhelming opponents with a fast, concentrated attack using multiple low-level units. This tactic involves rapidly producing and deploying scouts to scout enemy positions and apply pressure before they can build defense. Mastering early scout rushes exploits the game's fast-paced resource management and unit production mechanics, often forcing early game advantages or errors from opponents.
Swarm Tactics in Total War Series
Swarm tactics in the Total War series exemplify zerging through overwhelming enemy forces with large, fast-moving units to exploit weaknesses and disrupt formations. Players often mass low-cost infantry or archers to saturate battlefields, utilizing numerical superiority to break enemy lines before they can organize a counterattack. This aggressive, high-volume approach mirrors classic zerging strategies, emphasizing volume and speed over individual unit strength for battlefield dominance.
Zerging in Multiplayer Online Battle Arenas
Zerging in Multiplayer Online Battle Arenas (MOBAs) involves overwhelming opponents with large numbers of low-level units or heroes, often sacrificing individual skill for sheer quantity. This tactic is exemplified by players massing minions or repeatedly grouping multiple heroes to push lanes aggressively and control map objectives. Zerg rushing in MOBAs can disrupt enemy strategies by applying constant pressure, forcing defensive play and potential mispositioning.
Automated Unit Production in Real-Time Strategy
Zerging in real-time strategy games exemplifies automated unit production by rapidly generating large numbers of low-cost units to overwhelm opponents. This tactic relies on efficient resource management and continuous unit spawning from multiple production buildings to maintain relentless pressure. Automated production systems enable players to sustain high-volume attacks, forcing opponents into defensive play and disrupting their economy.
Zerg Tactics in Mobile Strategy Games
Zerging in mobile strategy games involves overwhelming opponents by mass-producing low-cost units rapidly, mimicking the aggressive swarm tactics of the Zerg race from StarCraft. This approach capitalizes on numerical superiority to disrupt enemy defenses and control key map areas before more advanced units can be deployed. Effective Zerg tactics require fast resource management and continuous unit production to maintain relentless pressure on opponents.
Balancing Against Zerg Playstyles
Zerging in strategy games involves overwhelming opponents with large numbers of low-cost units, a tactic popularized in titles like StarCraft. Effective balancing against zerg playstyles requires developers to introduce unit diversity and strategic countermeasures such as area-of-effect damage and economic penalties for mass unit production. Implementing cooldowns on unit spawning and enhancing micro-management mechanics also helps maintain competitive fairness and tactical depth.
example of zerging in strategy game Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com