Rubberbanding in racing games occurs when AI opponents dynamically adjust their speed to maintain close proximity to the player. This technique ensures competitive gameplay by preventing players from gaining an overwhelming lead, often resulting in AI cars suddenly accelerating after falling behind. Data from popular titles like Mario Kart and Need for Speed reveal that rubberbanding algorithms monitor player position and adjust AI parameters in real time. This mechanic can impact player experience by creating unpredictable race outcomes, making it difficult to predict opponent behavior. Game designers balance rubberbanding intensity by analyzing telemetry data to optimize challenge without causing frustration. Studying telemetry from user sessions highlights how changes in AI speed relate directly to player progress, providing insights into the effectiveness of rubberbanding in maintaining engagement.
Table of Comparison
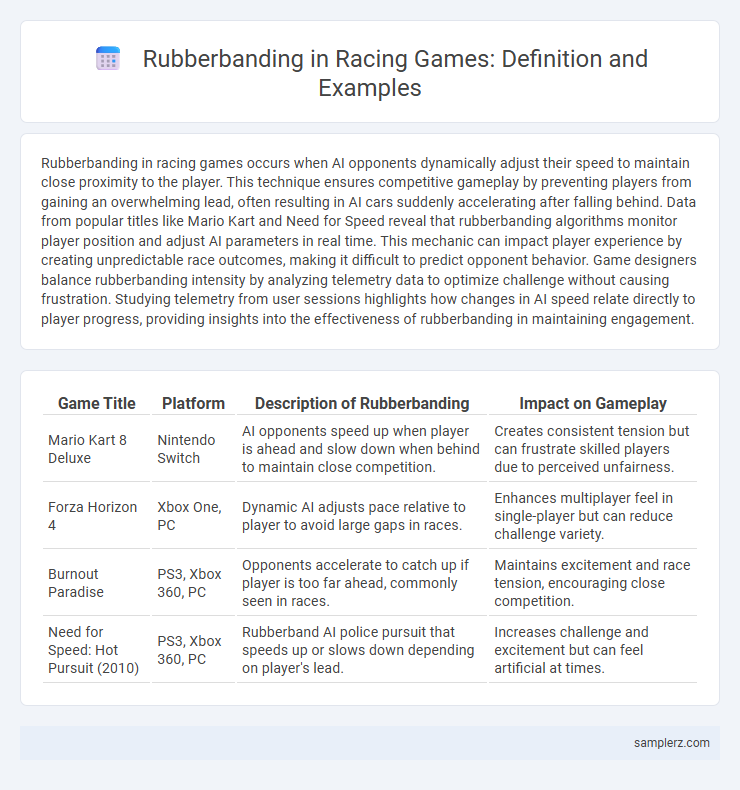
| Game Title | Platform | Description of Rubberbanding | Impact on Gameplay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mario Kart 8 Deluxe | Nintendo Switch | AI opponents speed up when player is ahead and slow down when behind to maintain close competition. | Creates consistent tension but can frustrate skilled players due to perceived unfairness. |
| Forza Horizon 4 | Xbox One, PC | Dynamic AI adjusts pace relative to player to avoid large gaps in races. | Enhances multiplayer feel in single-player but can reduce challenge variety. |
| Burnout Paradise | PS3, Xbox 360, PC | Opponents accelerate to catch up if player is too far ahead, commonly seen in races. | Maintains excitement and race tension, encouraging close competition. |
| Need for Speed: Hot Pursuit (2010) | PS3, Xbox 360, PC | Rubberband AI police pursuit that speeds up or slows down depending on player's lead. | Increases challenge and excitement but can feel artificial at times. |
Definition of Rubberbanding in Racing Games
Rubberbanding in racing games refers to the dynamic difficulty adjustment where AI opponents accelerate or slow down to maintain proximity to the player, preventing a race from becoming one-sided. This mechanic creates an artificial balance by allowing players who lag behind to catch up, enhancing engagement and challenge. Although it improves competitiveness, rubberbanding can sometimes cause frustration due to its unpredictable impact on race outcomes.
How Rubberbanding Impacts Gameplay Experience
Rubberbanding in racing games manipulates the speed of AI opponents to keep races competitive, often causing abrupt changes in difficulty and frustrating players. This mechanic can disrupt immersion by making player skill feel less impactful when AI cars unexpectedly catch up or fall behind. Such artificial balancing impacts gameplay experience by undermining the sense of achievement and altering strategic decision-making during races.
Classic Racing Titles Known for Rubberbanding
Classic racing titles like Mario Kart 64 and Diddy Kong Racing exemplify rubberbanding mechanics, where AI opponents dynamically adjust their speed to maintain close competition. This design choice enhances excitement but often frustrates players seeking consistent challenge levels. Rubberbanding ensures every race feels unpredictable, forcing racers to skillfully adapt to sudden AI speed changes.
Rubberbanding vs. Skill-Based Progression
Rubberbanding in racing games artificially adjusts AI difficulty to keep races competitive by improving opponents' speed when players lead, undermining skill-based progression that rewards consistent performance and strategic mastery. Skilled players often encounter frustration as their efforts are negated by rubberbanding mechanics designed to prevent runaway victories, diluting the value of practice and technique. Games prioritizing skill-based progression promote fairness and player satisfaction by enabling advancements through measurable improvements in racing precision and decision-making.
Notable Rubberbanding Moments in Mario Kart
Notable rubberbanding moments in Mario Kart often occur during intense races, where trailing players suddenly boost ahead due to AI speed adjustments, creating unpredictable race outcomes. Key examples include Nintendo's classic Mario Kart 64 and Mario Kart Wii, where rubberbanding AI rivals catch up rapidly near the finish line, maintaining competitive tension. This mechanic influences player strategies and race dynamics, making speed fluctuations a hallmark of the franchise's gameplay experience.
Rubberbanding in Need for Speed Series
Rubberbanding in the Need for Speed series is a common AI mechanic that adjusts the difficulty by allowing rival racers to catch up when players pull ahead, ensuring a competitive race. This dynamic pacing keeps gameplay engaging but can frustrate players who experience sudden, unrealistic speed boosts from opponents. The rubberbanding effect balances challenge and excitement, maintaining tension throughout high-speed races.
AI Opponents and Rubberbanding Behaviors
AI opponents in racing games often exhibit rubberbanding behaviors to maintain competitive balance by dynamically adjusting their speed relative to the player's position. This technique enables AI cars to catch up when lagging behind or slow down when too far ahead, creating a more engaging and challenging race experience. Rubberbanding helps simulate realistic competition and reduces player frustration during gameplay by keeping the race tight and unpredictable.
Rubberbanding Examples in Multiplayer Racing
Rubberbanding in multiplayer racing games occurs when AI opponents suddenly accelerate to catch up with the leading player, creating an unfair challenge. Classic examples include the "Mario Kart" series, where trailing racers frequently gain speed boosts to maintain competition intensity. This mechanic, while designed to keep races engaging, often frustrates skilled players seeking a pure test of racing ability.
Player Community Reactions to Rubberbanding
Rubberbanding in racing games often leads to frustration within the player community due to its impact on fair competition and skill-based outcomes. Gamers frequently express dissatisfaction on forums and social media, highlighting instances where AI opponents unpredictably catch up despite significant player leads, diminishing the sense of achievement. Persistent rubberbanding issues result in negative reviews and calls for developers to implement more balanced AI behavior and improved game mechanics.
Balancing Fun and Fairness: Alternatives to Rubberbanding
Rubberbanding in racing games occurs when AI opponents artificially adjust their speed to stay close to the player, often disrupting the balance between fun and fairness. Alternatives like dynamic difficulty adjustment, player performance tracking, and adaptive AI behaviors promote more genuine competition by responding naturally to player skill without forced catch-up mechanics. Implementing these methods enhances player engagement and maintains challenge without compromising the integrity of the racing experience.
example of rubberbanding in racing Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com