Translanguaging in bilingual education involves the strategic use of multiple languages within a single learning environment to enhance comprehension and communication. An example is a classroom where students read a science text in English, discuss their understanding in Spanish, and write summaries in both languages. This approach supports cognitive development by allowing students to draw on their full linguistic repertoire. In a bilingual program, translanguaging enables teachers to scaffold instruction by alternating between languages based on students' linguistic strengths. For instance, a math teacher might explain complex concepts in the students' native language, then reinforce those ideas with English terminology. Data show that such practices improve academic performance and language proficiency, fostering deeper engagement and confidence.
Table of Comparison
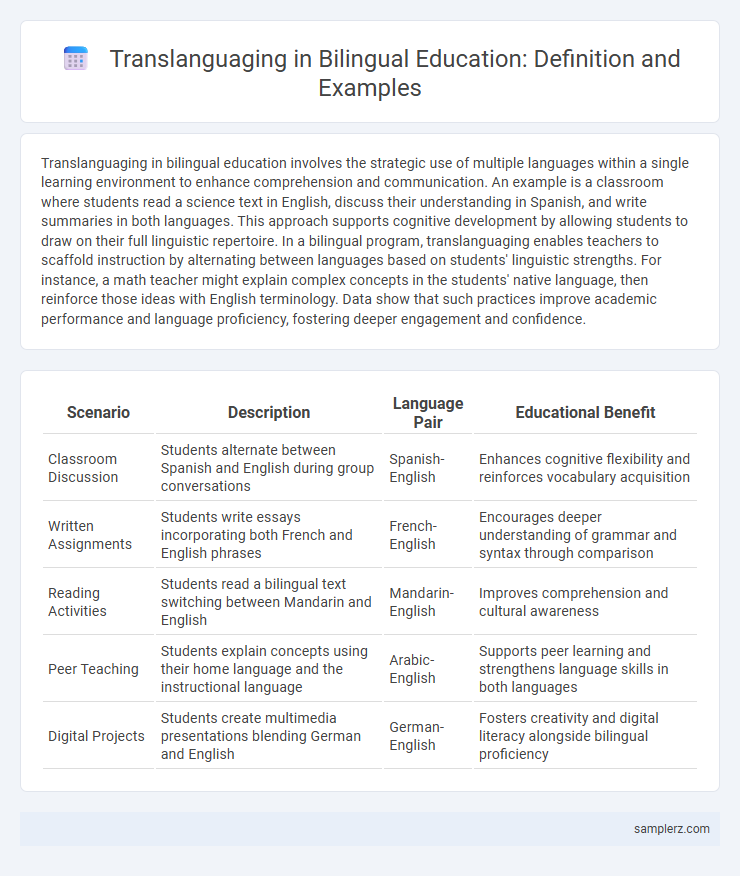
| Scenario | Description | Language Pair | Educational Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom Discussion | Students alternate between Spanish and English during group conversations | Spanish-English | Enhances cognitive flexibility and reinforces vocabulary acquisition |
| Written Assignments | Students write essays incorporating both French and English phrases | French-English | Encourages deeper understanding of grammar and syntax through comparison |
| Reading Activities | Students read a bilingual text switching between Mandarin and English | Mandarin-English | Improves comprehension and cultural awareness |
| Peer Teaching | Students explain concepts using their home language and the instructional language | Arabic-English | Supports peer learning and strengthens language skills in both languages |
| Digital Projects | Students create multimedia presentations blending German and English | German-English | Fosters creativity and digital literacy alongside bilingual proficiency |
Understanding Translanguaging in Bilingual Education
Translanguaging in bilingual education involves students strategically using all their language resources to enhance comprehension and communication, such as switching between English and Spanish during classroom discussions to clarify concepts. This dynamic practice supports deeper cognitive engagement by allowing learners to access background knowledge and express ideas more fully. Research shows that implementing translanguaging strategies boosts academic achievement and reinforces language development across both languages.
Classroom Strategies: Translanguaging in Action
Translanguaging in classroom strategies involves students actively switching between languages to enhance comprehension and expression, such as reading a text in one language and discussing it in another. Teachers encourage collaborative activities where bilingual learners pair up to solve problems using both languages, fostering deeper cognitive engagement and cultural connection. This approach supports linguistic diversity, promotes metalinguistic awareness, and improves academic achievement by validating students' full linguistic repertoires.
Enhancing Learning through Translanguaging Practices
Translanguaging in bilingual education leverages students' full linguistic repertoire, allowing them to alternate between languages within a single lesson or activity to deepen comprehension and expression. Research demonstrates that incorporating translanguaging practices boosts cognitive flexibility and content mastery, particularly in subjects like science and mathematics where conceptual understanding is critical. Teachers who strategically integrate translanguaging enable equitable participation and foster metalinguistic awareness, enhancing overall academic achievement in multilingual classrooms.
Teacher-Facilitated Translanguaging: Real-World Examples
Teacher-facilitated translanguaging in bilingual classrooms often involves educators encouraging students to use both languages fluidly to enhance comprehension and critical thinking. For example, a teacher might prompt students to explain complex concepts first in their native language before translating or discussing them in the second language, facilitating deeper understanding. This approach supports linguistic flexibility and academic achievement by validating students' entire linguistic repertoire.
Student-Centered Translanguaging Activities
Student-centered translanguaging activities include collaborative storytelling where bilingual students alternate languages to build narratives, enhancing comprehension and cultural expression. Peer teaching sessions enable learners to explain concepts in their dominant language, promoting deeper understanding and confidence. Interactive multilingual digital platforms support vocabulary acquisition and language flexibility through user-generated content in multiple languages.
Translanguaging as a Tool for Inclusive Education
Translanguaging in bilingual education enables students to use their full linguistic repertoire to enhance comprehension and expression, fostering an inclusive learning environment. Teachers encourage the strategic use of both languages during lessons to support cognitive development and cultural identity. Research shows translanguaging practices improve academic engagement and equity for diverse learners in multilingual classrooms.
Promoting Literacy with Translanguaging Techniques
Translanguaging in bilingual education enhances literacy by allowing students to leverage both languages fluently, improving comprehension and expression. Techniques such as dual-language journaling and cross-linguistic scaffolding actively engage learners in reading and writing across languages, reinforcing cognitive connections and vocabulary development. Research indicates that students using translanguaging strategies demonstrate higher literacy achievement and greater confidence in bilingual communication.
Translanguaging and Cognitive Development in Bilinguals
Translanguaging in bilingual education enhances cognitive development by allowing students to fluidly switch between languages, fostering metalinguistic awareness and problem-solving skills. Research shows that bilinguals engaging in translanguaging exhibit greater executive function control, which improves attention, memory, and task-switching abilities. Effective implementation of translanguaging strategies supports linguistic flexibility and deepens comprehension, contributing to overall academic success in bilingual learners.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Translanguaging
Translanguaging in bilingual education addresses challenges by promoting fluid language practices that validate students' entire linguistic repertoire, enhancing comprehension and engagement. Teachers implement strategic scaffolding techniques, such as code-switching and integrated language activities, to bridge gaps in language proficiency and cultural understanding. Integrating translanguaging fosters equitable learning environments, reducing linguistic barriers and supporting cognitive flexibility among bilingual students.
Case Studies: Successful Translanguaging in Bilingual Classrooms
Case studies of successful translanguaging in bilingual classrooms demonstrate how students effectively use both languages to enhance comprehension and participation, facilitating deeper cognitive connections and cultural awareness. For instance, research in dual-language immersion programs shows significant improvements in literacy outcomes when educators encourage fluid language switching during instruction and peer interactions. These findings underscore translanguaging as a dynamic pedagogical strategy that supports bilingualism and academic achievement in diverse educational settings.
example of translanguaging in bilingualism Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com