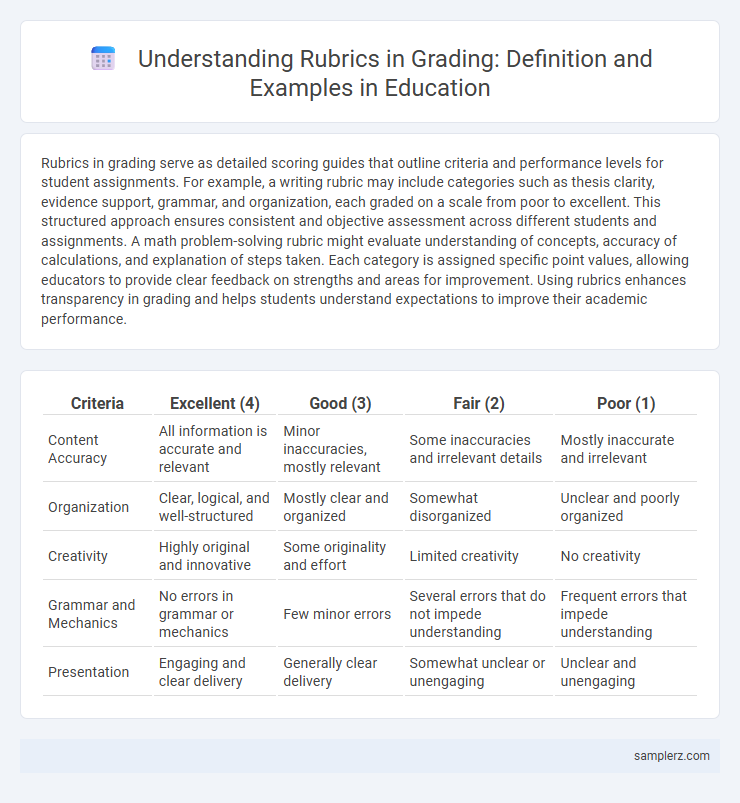
Rubrics in grading serve as detailed scoring guides that outline criteria and performance levels for student assignments. For example, a writing rubric may include categories such as thesis clarity, evidence support, grammar, and organization, each graded on a scale from poor to excellent. This structured approach ensures consistent and objective assessment across different students and assignments. A math problem-solving rubric might evaluate understanding of concepts, accuracy of calculations, and explanation of steps taken. Each category is assigned specific point values, allowing educators to provide clear feedback on strengths and areas for improvement. Using rubrics enhances transparency in grading and helps students understand expectations to improve their academic performance.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Excellent (4) | Good (3) | Fair (2) | Poor (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content Accuracy | All information is accurate and relevant | Minor inaccuracies, mostly relevant | Some inaccuracies and irrelevant details | Mostly inaccurate and irrelevant |
| Organization | Clear, logical, and well-structured | Mostly clear and organized | Somewhat disorganized | Unclear and poorly organized |
| Creativity | Highly original and innovative | Some originality and effort | Limited creativity | No creativity |
| Grammar and Mechanics | No errors in grammar or mechanics | Few minor errors | Several errors that do not impede understanding | Frequent errors that impede understanding |
| Presentation | Engaging and clear delivery | Generally clear delivery | Somewhat unclear or unengaging | Unclear and unengaging |
Understanding Rubrics: Key Components in Grading
Understanding rubrics in grading involves clearly defined criteria such as content accuracy, organization, and creativity, which guide both teachers and students in assessing performance. Each criterion is divided into performance levels with specific descriptors that detail what constitutes excellent, satisfactory, or needs improvement work. This structured approach enhances objectivity and transparency in evaluating student assignments and projects.
Types of Rubrics Used in Education
Analytic rubrics break down grading criteria into specific components such as clarity, accuracy, and creativity, allowing educators to assess each aspect of student performance separately. Holistic rubrics provide a single overall score based on an integrated judgment of multiple criteria, streamlining evaluation for assignments like essays or presentations. Additionally, developmental rubrics focus on the progression of skills over time, supporting formative assessment and targeted feedback in educational settings.
Sample Analytic Rubrics for Classroom Assessment
Sample analytic rubrics for classroom assessment break down grading criteria into distinct categories such as content accuracy, organization, and presentation quality, providing clear performance levels for each. These rubrics enable educators to assess specific skills and competencies methodically, ensuring transparent and consistent evaluation. Utilizing detailed analytic rubrics enhances feedback precision and guides student improvement effectively.
Example Holistic Rubrics for Project-Based Learning
Holistic rubrics for project-based learning assess overall student performance by evaluating criteria such as creativity, critical thinking, collaboration, and presentation quality in a single score. For example, a rubric might rate projects on a scale from 1 to 5, with descriptors emphasizing originality, problem-solving effectiveness, teamwork, and clarity of communication. This approach streamlines grading while capturing the comprehensive skills demonstrated in complex, real-world assignments.
Rubric Templates for Essay Evaluation
Rubric templates for essay evaluation typically include specific criteria such as thesis clarity, argument development, evidence use, organization, grammar, and mechanics, each assigned distinct point values to ensure consistent and objective grading. These templates help educators provide detailed feedback while streamlining the assessment process, promoting transparency and fairness in scoring. Customizable rubric templates are widely used in educational institutions to align grading with learning outcomes and academic standards.
Using Rubrics for Group Work Assessment
Rubrics for group work assessment clearly define criteria such as collaboration, communication, task completion, and problem-solving, providing transparent expectations and consistent grading across all members. Each criterion is rated on a scale, often from 1 to 5, with specific descriptors that differentiate levels of performance. This structured approach fosters accountability, enhances peer evaluation, and promotes equitable assessment within collaborative educational environments.
Performance Task Rubrics: Practical Examples
Performance task rubrics in education often include criteria such as accuracy, creativity, and time management to assess student work in practical assignments. For instance, a science project rubric may evaluate hypothesis formulation, experimental procedure, data analysis, and presentation skills. These rubrics provide clear, objective standards that guide both teachers and students in understanding expectations and measuring learning outcomes effectively.
Creating Effective Self-Assessment Rubrics
Creating effective self-assessment rubrics involves clearly defining criteria that align with learning objectives, such as critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Each criterion should include performance levels with descriptive indicators that help students accurately evaluate their own progress and identify areas for improvement. Incorporating student-friendly language and visual aids enhances understanding and encourages reflective learning, fostering greater student engagement and responsibility.
Peer Assessment Rubrics: Examples and Best Practices
Peer assessment rubrics in education typically include criteria such as clarity of communication, depth of analysis, and constructive feedback quality to ensure objective evaluation. Examples often feature a five-point scale for each criterion, with detailed descriptors to guide students in providing consistent and meaningful peer feedback. Best practices emphasize clear expectations, student training on rubric use, and iterative calibration to improve reliability and foster critical thinking skills during peer evaluations.
Digital Tools for Generating Grading Rubrics
Digital tools like Google Classroom, RubiStar, and Turnitin provide customizable grading rubrics that enhance consistency and transparency in education assessment. These platforms allow educators to design criteria-based evaluation frameworks tailored to specific assignments, improving objectivity and student feedback quality. Integrating such tools streamlines grading processes while promoting clear communication of expectations.
example of rubrics in grading Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com