In the field of education, a null example in the curriculum refers to an instance where a particular topic or skill is intentionally excluded or left unaddressed within the coursework. This often occurs when certain subjects are deemed irrelevant or outdated for the target educational objectives. For example, a modern computer science curriculum may present a null case by excluding obsolete programming languages like COBOL or Fortran to focus on current technologies like Python and JavaScript. Curriculum planners analyze data related to job market demands and student engagement metrics to determine which elements to omit. This process ensures the curriculum remains relevant and effective for the students' future career paths. Null examples serve as a control within curriculum design, highlighting what is excluded to clarify and strengthen the educational focus on essential knowledge and competencies.
Table of Comparison
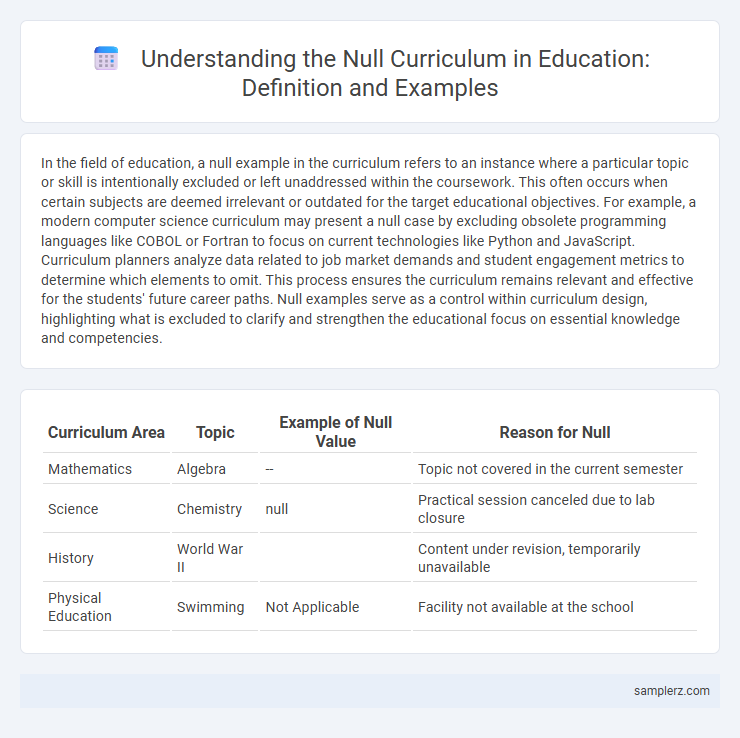
| Curriculum Area | Topic | Example of Null Value | Reason for Null |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mathematics | Algebra | -- | Topic not covered in the current semester |
| Science | Chemistry | null | Practical session canceled due to lab closure |
| History | World War II | Content under revision, temporarily unavailable | |
| Physical Education | Swimming | Not Applicable | Facility not available at the school |
Understanding Null Concepts in Curriculum Design
Understanding null concepts in curriculum design involves identifying gaps where essential knowledge or skills are missing, which can hinder comprehensive learning outcomes. For example, a science curriculum might omit climate change topics, creating a null element that leaves students unprepared for environmental challenges. Addressing these nulls requires deliberate inclusion and integration of critical content areas to ensure balanced and effective education.
The Role of Null Content in Educational Programs
Null content in educational programs refers to intentionally omitted topics or gaps within a curriculum that reflect evolving knowledge or cultural sensitivity. These omissions can influence learning outcomes by shaping what students prioritize and how critical thinking is developed through addressing what is excluded. Understanding the role of null content helps educators design balanced curricula that foster comprehensive knowledge while acknowledging societal and disciplinary shifts.
Examples of Null in School Curricula
Examples of null in school curricula include omitted topics such as comprehensive sex education, critical thinking skills, and digital literacy. These gaps often reflect societal norms or political decisions, resulting in incomplete student knowledge and preparedness. Addressing these null elements can enhance curriculum relevance and foster well-rounded education.
Identifying Null Gaps in Subject Matter
Identifying null gaps in subject matter involves analyzing curriculum content to pinpoint areas where essential topics or skills are missing, such as the absence of digital literacy modules in traditional literature courses. These null gaps can hinder comprehensive student understanding and limit interdisciplinary learning opportunities, impacting overall educational outcomes. Addressing these gaps requires targeted curriculum revisions informed by data-driven assessments and stakeholder feedback.
Implications of Null Content for Student Learning
Null content in a curriculum refers to topics or skills that are intentionally or unintentionally omitted, leading to gaps in student knowledge and understanding. These omissions can hinder students' ability to make connections between concepts, resulting in fragmented learning experiences and reduced academic performance. Addressing null content is critical to ensure comprehensive coverage of essential competencies and promote equitable educational outcomes.
Case Studies: Null in History and Literature Courses
Case studies in history and literature courses demonstrate the concept of null as the absence of data or events, such as missing historical records or undocumented perspectives in primary sources. These examples highlight how null values affect interpretation and analysis, emphasizing the importance of critical evaluation when evidence is incomplete or absent. Understanding null in this context teaches students to recognize gaps in information and develop nuanced arguments based on both presence and absence within curricular content.
The Impact of Null Topics on Educational Equity
Null topics in curriculum refer to subjects or content areas that are completely omitted from educational programs. The exclusion of certain cultural histories or perspectives disproportionately affects marginalized student groups, perpetuating educational inequities. Addressing these null topics by integrating diverse and inclusive materials enhances representation and promotes equitable learning environments.
Addressing Null Spaces in Curriculum Development
Addressing null spaces in curriculum development involves identifying and filling gaps where essential topics or skills are missing, ensuring comprehensive student learning outcomes. For example, a science curriculum may lack a unit on environmental sustainability, creating a null space that hinders students' understanding of current global challenges. Integrating interdisciplinary content and regularly reviewing curriculum maps can effectively eliminate these null spaces, promoting a balanced and relevant education.
Strategies for Revealing and Filling Null in Curriculum
Teaching strategies that identify gaps or "nulls" in the curriculum include comprehensive curriculum mapping and student feedback analysis to uncover unaddressed topics or skills. Educators implement targeted interventions such as supplemental lessons and interdisciplinary projects to fill these gaps effectively. Continuous assessment and collaboration among instructional teams ensure the curriculum remains holistic and responsive to learners' needs.
Best Practices for Mitigating Null in Educational Planning
Identifying null values in educational data, such as missing attendance records or incomplete assessment scores, is crucial for accurate curriculum analysis. Best practices for mitigating null in educational planning include implementing comprehensive data validation protocols, using imputation techniques like mean substitution or predictive modeling to estimate missing values, and fostering continuous teacher training on precise data entry. Integrating robust data management systems enhances the reliability of curriculum evaluations and supports informed decision-making in education.
example of null in curriculum Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com