Didactic methods in education focus on structured teaching where information is explicitly presented to students. An example of a didactic method is the lecture format, where an instructor delivers content directly to learners. This approach emphasizes clear, authoritative explanation to ensure comprehension of subject matter. Another example includes the use of textbooks and worksheets designed to guide students through specific lessons step-by-step. Didactic teaching relies heavily on repetition and reinforcement of facts to build foundational knowledge. It is particularly effective for introducing new topics and ensuring consistent understanding across a classroom.
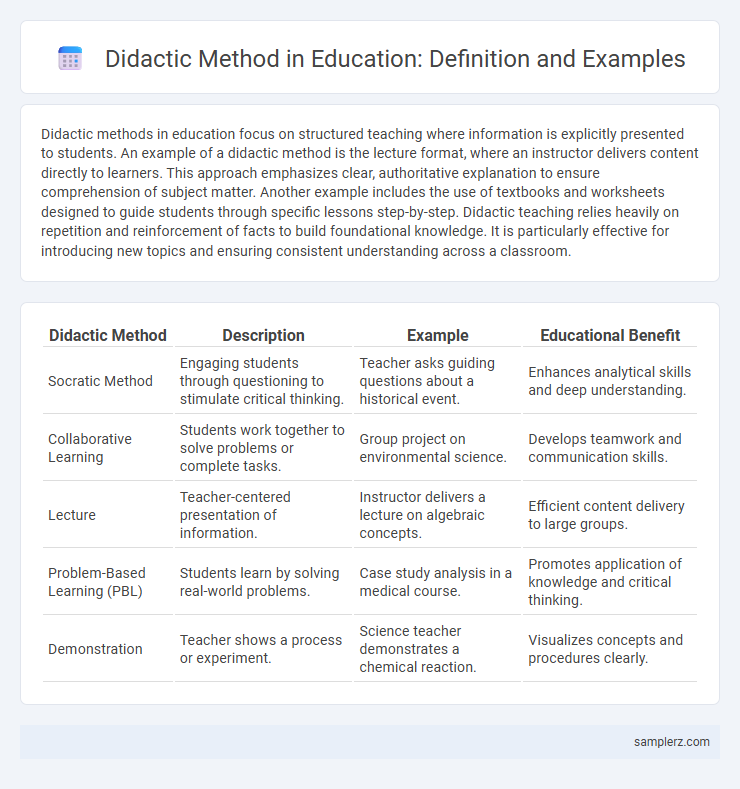
Table of Comparison
| Didactic Method | Description | Example | Educational Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Socratic Method | Engaging students through questioning to stimulate critical thinking. | Teacher asks guiding questions about a historical event. | Enhances analytical skills and deep understanding. |
| Collaborative Learning | Students work together to solve problems or complete tasks. | Group project on environmental science. | Develops teamwork and communication skills. |
| Lecture | Teacher-centered presentation of information. | Instructor delivers a lecture on algebraic concepts. | Efficient content delivery to large groups. |
| Problem-Based Learning (PBL) | Students learn by solving real-world problems. | Case study analysis in a medical course. | Promotes application of knowledge and critical thinking. |
| Demonstration | Teacher shows a process or experiment. | Science teacher demonstrates a chemical reaction. | Visualizes concepts and procedures clearly. |
Understanding Didactic Methods in Education
Didactic methods in education emphasize structured, teacher-centered approaches that facilitate direct knowledge transmission through lectures, demonstrations, and guided practice. These methods prioritize clarity, organization, and sequential presentation to enhance student comprehension and retention. Utilizing didactic strategies supports efficient curriculum delivery, particularly in foundational subjects such as mathematics and science.
Key Principles of Didactic Teaching
Didactic teaching emphasizes clear instruction, structured content delivery, and active reinforcement of key concepts to enhance student comprehension and retention. Central principles include the alignment of learning objectives with teaching activities, systematic assessment to monitor progress, and the use of feedback to adapt instruction effectively. These elements collectively support a focused and efficient learning process in educational settings.
Classic Examples of Didactic Instruction
Classic examples of didactic instruction include lecture-based teaching where the teacher systematically imparts knowledge directly to students, often using textbooks and structured lesson plans. This method emphasizes clear, concise delivery of information, fostering comprehension through repetition and explanation. Didactic strategies often incorporate questioning to reinforce understanding and guide learners toward mastering specific content.
Structured Lesson Planning with Didactic Approaches
Structured lesson planning incorporates didactic approaches by organizing content into clear, sequential steps that facilitate effective knowledge transmission and skill acquisition. Teachers design objectives, select appropriate instructional materials, and implement assessment tools to reinforce learning outcomes and ensure student comprehension. This method enhances engagement and retention by providing a well-defined framework for teaching complex concepts.
Role of Teacher-Centered Methods in Didactics
Teacher-centered methods in didactics emphasize direct instruction, where the teacher acts as the primary knowledge source and authority in the classroom. This approach facilitates structured learning environments, enabling efficient delivery of curriculum content and clear guidance on educational objectives. Studies show that teacher-centered strategies improve foundational skill acquisition, particularly in subjects requiring sequential knowledge like mathematics and sciences.
Didactic Strategies for Effective Knowledge Transfer
Didactic strategies for effective knowledge transfer include techniques such as scaffolding, which supports learners by building on prior knowledge incrementally, and the use of visual aids to enhance comprehension and retention. Employing question-and-answer sessions encourages active learner participation, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking. Structured feedback mechanisms further reinforce learning by providing timely guidance and clarifying misconceptions.
Case Studies: Didactic Method in Classroom Practice
Case studies serve as a powerful didactic method in classroom practice by fostering critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills among students. This approach encourages active learning through in-depth analysis of complex scenarios, promoting engagement and deeper comprehension of subject matter. Case studies are particularly effective in disciplines such as law, medicine, and business, where practical application of theoretical knowledge is essential.
Advantages and Limitations of Didactic Teaching
Didactic teaching emphasizes structured lessons with clear objectives, promoting efficient knowledge transfer and standardized learning outcomes. Its advantages include consistency in content delivery and ease of assessment, fostering foundational understanding in large groups. Limitations involve reduced student engagement and minimal opportunities for critical thinking or personalized learning experiences.
Integrating Didactic Methods with Modern Pedagogy
Integrating didactic methods with modern pedagogy enhances student engagement by combining structured content delivery with interactive learning techniques such as problem-based and collaborative learning. Utilizing multimedia tools and technology-driven platforms supports differentiated instruction, catering to diverse learning styles and improving knowledge retention. This fusion of traditional didactic approaches and innovative pedagogical strategies fosters critical thinking and deeper understanding in educational settings.
Assessing Student Outcomes in Didactic Learning Environments
Assessing student outcomes in didactic learning environments involves utilizing formative and summative evaluation methods such as quizzes, standardized tests, and performance tasks to measure knowledge retention and comprehension. Incorporating rubrics and feedback mechanisms ensures alignment with learning objectives and enhances students' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Data-driven assessment tools provide educators with insights to tailor instruction and improve overall academic achievement.
example of didactic in method Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com