Register in dialogue refers to the level of formality or style of language used depending on the context and participants. For instance, a business meeting often employs a formal register, featuring technical terms and polite expressions, whereas casual conversations among friends use an informal register with slang and colloquialisms. Recognizing the appropriate register helps ensure effective communication and mutual understanding. In professional environments, the register may include specific jargon related to the industry, such as legal or medical terminology. When speaking with a superior, speakers typically adopt a more respectful and formal tone, contrasting with a relaxed and familiar tone used among peers. Adapting register according to social context and relationship influences the clarity and reception of the message conveyed.
Table of Comparison
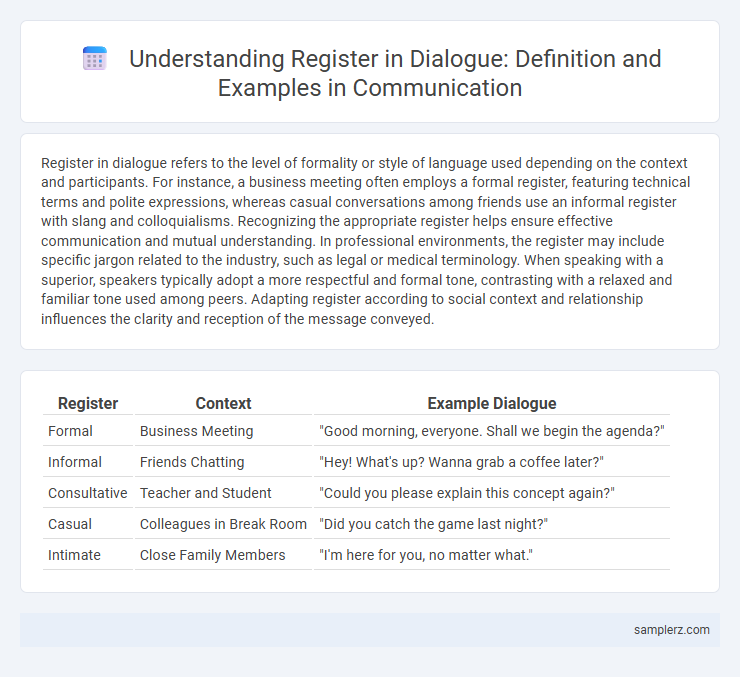
| Register | Context | Example Dialogue |
|---|---|---|
| Formal | Business Meeting | "Good morning, everyone. Shall we begin the agenda?" |
| Informal | Friends Chatting | "Hey! What's up? Wanna grab a coffee later?" |
| Consultative | Teacher and Student | "Could you please explain this concept again?" |
| Casual | Colleagues in Break Room | "Did you catch the game last night?" |
| Intimate | Close Family Members | "I'm here for you, no matter what." |
Introduction to Register in Communication
Register in communication varies based on context, purpose, and audience, reflecting formal, informal, or consultative language styles. For example, an informal register might include slang or colloquial expressions used among friends, while a formal register employs complete sentences, technical vocabulary, and polite tone in professional settings. Understanding these variations ensures effective and appropriate communication across different social and cultural interactions.
Defining Register in Dialogue
Register in dialogue refers to the level of formality and style of language used depending on the social context, audience, and purpose of the interaction. For example, a conversation between close friends typically employs an informal register with colloquial expressions, while a business meeting requires a formal register with precise and professional vocabulary. Understanding and adapting register is crucial for effective communication, ensuring messages are appropriate and well-received.
Formal Register: Professional Conversations
In professional conversations, formal register features precise vocabulary and structured sentences to convey respect and clarity, often seen in business meetings or official correspondence. Speakers use titles, full names, and avoid slang or contractions to maintain professionalism. Examples include phrases like "Could you please provide the report by Friday?" or "I appreciate your prompt attention to this matter.
Informal Register: Everyday Interactions
In everyday interactions, informal register frequently features casual vocabulary, contractions, and colloquial expressions such as "gonna," "wanna," or slang terms like "cool" and "chill." This register is commonly used among friends, family, and peers to create a relaxed and friendly tone that fosters rapport and ease of communication. Speech in informal register avoids technical jargon and excessive politeness, prioritizing clarity and immediacy over formality.
Casual Register: Friendly Exchanges
Casual register in dialogue is evident in friendly exchanges where informal language, slang, and contractions dominate, creating a relaxed and approachable tone. Phrases like "Hey, what's up?" or "Can't wait to catch up!" reflect this register, emphasizing personal connection and ease. This style prioritizes spontaneity and warmth over formal structure, enhancing interpersonal rapport.
Frozen Register: Ceremonial Speech Examples
Frozen register in communication is characterized by formal, ritualistic language often found in ceremonial speeches such as weddings, graduations, or official proclamations. Phrases like "I now pronounce you husband and wife" or "We hereby declare this ceremony open" exemplify the unchanging, traditional nature of frozen register. This style reinforces solemnity and respect, ensuring the message's significance remains intact across contexts and generations.
Consultative Register: Expert and Client Dialogue
In consultative register, the expert uses precise terminology and structured sentences to convey information clearly, while the client asks questions for clarification. This interaction often involves specialized vocabulary relevant to the field, such as medical terms in a doctor's consultation or legal jargon in attorney-client discussions. The dialogue remains formal yet interactive, emphasizing clarity, professionalism, and mutual understanding.
Intimate Register: Private Conversations
Intimate register in dialogue includes private conversations characterized by informal language, personalized vocabulary, and shared understanding between close individuals such as family members or romantic partners. This register often features nicknames, inside jokes, and non-standard grammar, reflecting emotional closeness and trust. Examples include whispered exchanges, affectionate terms, and spontaneous, unstructured speech patterns unique to the relationship.
Shifting Registers in Real-life Dialogue
Shifting registers in real-life dialogue occur when speakers adjust their language style to suit different social contexts or interlocutors, such as using formal language with a supervisor and informal slang with friends. This dynamic shift enhances clarity and social rapport by matching vocabulary, tone, and level of politeness to the situation. Understanding register shifts is crucial for effective communication, as it reflects social awareness and adaptability in diverse conversational settings.
The Impact of Register Choices on Communication
In dialogue, register choices significantly affect clarity and tone, shaping how messages are received and interpreted. Formal register often establishes professionalism and respect in workplace conversations, while informal register fosters intimacy and ease among friends. Selecting an appropriate register enhances effective communication by aligning language with social context and audience expectations.
example of register in dialogue Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com