A speech act in communication is a verbal action that conveys intention. In a request, the speaker asks the listener to perform a specific action, demonstrating an interaction between the parties. For example, when someone says, "Could you please pass the salt?" they are performing a request speech act. This request involves direct language that seeks compliance or assistance from the listener, highlighting the social dynamics of communication. The data shows that requests can vary in politeness, urgency, and formality depending on context and relationship. Understanding speech acts enhances effective communication by enabling clearer interpretation of intentions and responses.
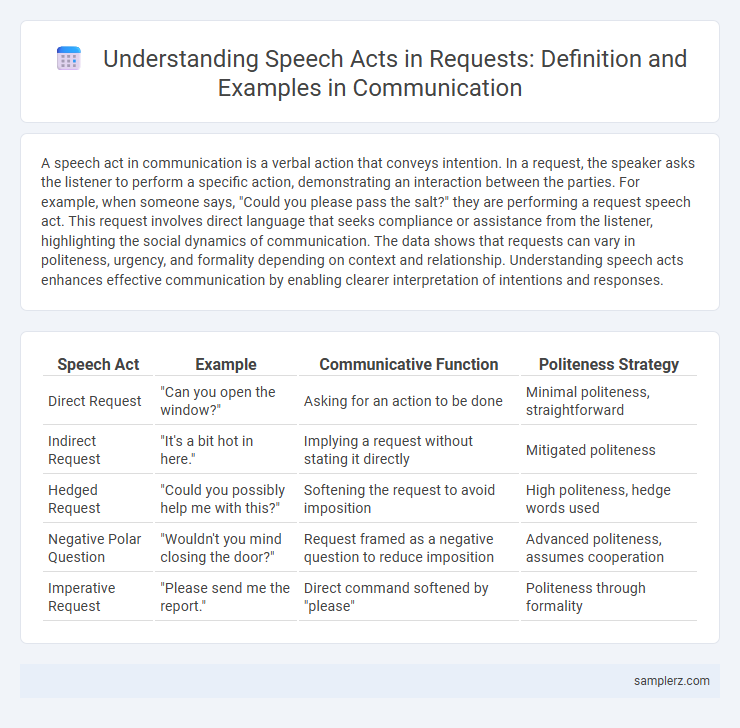
Table of Comparison
| Speech Act | Example | Communicative Function | Politeness Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Request | "Can you open the window?" | Asking for an action to be done | Minimal politeness, straightforward |
| Indirect Request | "It's a bit hot in here." | Implying a request without stating it directly | Mitigated politeness |
| Hedged Request | "Could you possibly help me with this?" | Softening the request to avoid imposition | High politeness, hedge words used |
| Negative Polar Question | "Wouldn't you mind closing the door?" | Request framed as a negative question to reduce imposition | Advanced politeness, assumes cooperation |
| Imperative Request | "Please send me the report." | Direct command softened by "please" | Politeness through formality |
Understanding Speech Acts in Request Communication
Speech acts in request communication involve utterances designed to achieve specific actions, such as asking for information, assistance, or permission. Effective understanding requires recognizing the speaker's intent behind direct or indirect requests, like "Could you send the report?" or "It's cold in here." Analyzing pragmatics and context helps interpret the politeness strategies and social factors influencing how requests are conveyed and received.
Key Elements of Request Speech Acts
Request speech acts involve the essential key elements of the speaker's intention to ask for something, the form of the utterance, and the expected response from the listener. These elements include the illocutionary force indicating a request, the level of politeness tailored to the social context, and the specific wording that clarifies the desired action. For example, indirect requests like "Could you please send me the report?" incorporate politeness and clarity, facilitating effective communication and increasing the likelihood of compliance.
Direct vs. Indirect Requests: Semantic Distinctions
Direct requests explicitly use imperative forms or modal verbs, such as "Please close the door" or "Can you send the report?" Indirect requests employ more polite or softened expressions like "Would you mind closing the door?" or "I was wondering if you could send the report." The semantic distinctions between direct and indirect requests often reflect degrees of politeness, social hierarchy, and context sensitivity in communication.
Politeness Strategies in Request Speech Acts
Politeness strategies in request speech acts commonly involve indirect language, such as using modal verbs ("could you," "would you") and hedging expressions ("perhaps," "if possible") to soften the imposition. Employing honorifics and mitigating phrases helps maintain social harmony and shows respect to the interlocutor. These strategies optimize the request's effectiveness while minimizing potential face-threatening acts according to Brown and Levinson's politeness theory.
Pragmatic Functions of Requests in Dialogue
Requests in dialogue function pragmatically to initiate action, seek assistance, or obtain information through indirect or direct speech acts. For example, a speaker saying, "Can you pass the salt?" performs a request that indirectly prompts the listener to act, highlighting the cooperative nature of communication. This pragmatic use of requests manages social interactions by balancing politeness, urgency, and context sensitivity.
Speech Act Verbs Commonly Used in Requests
Speech act verbs commonly used in requests include "ask," "request," "inquire," "demand," and "plead," each indicating varying degrees of politeness and urgency. For example, "ask" typically conveys a polite request, while "demand" expresses a more forceful or authoritative tone. Understanding these verbs enhances effective communication by aligning the speaker's intention with the listener's perception in social interactions.
Contextual Factors Influencing Request Speech Acts
Request speech acts are heavily influenced by contextual factors such as social distance, power relations, and the urgency of the situation. For instance, a subordinate making a request to a superior typically employs more politeness strategies to mitigate imposition, while peers may use direct language. The situational context, including cultural norms and setting formality, also determines the choice of indirect or direct request forms, impacting the effectiveness of the communication.
Cultural Variations in Requesting Behavior
Requesting behavior varies significantly across cultures, influencing the choice of politeness strategies and directness levels in speech acts. In Japanese culture, indirect requests such as "Could you possibly..." are preferred to maintain harmony and avoid imposing on others, contrasting with the more direct requests common in American English like "Can you...?". Understanding these cultural variations is essential for effective intercultural communication and preventing misunderstandings in request exchanges.
Analyzing Real-life Examples of Request Speech Acts
Request speech acts manifest in everyday interactions, such as a customer politely asking a waiter, "Could you bring me the menu?" This utterance demonstrates indirectness by using modal verbs to soften the directive, aligning with Brown and Levinson's politeness theory. Analyzing such real-life examples reveals how speakers strategically manage social distance and power dynamics to achieve communicative goals effectively.
Enhancing Communication Skills through Effective Requests
Effective requests in communication involve clear, polite, and specific speech acts that facilitate mutual understanding and cooperation. Utilizing direct but courteous language, such as "Could you please send the report by Monday?" ensures the message is conveyed without ambiguity. Mastering this technique enhances interpersonal skills by promoting active listening, reducing misunderstandings, and fostering positive responses.
example of speech act in request Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com